Incredible Technology In Mysterious Huashan Caves, China
A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com - Is it just a coincidence or do certain laws of nature lie behind the phenomenon observed in the ancient Huashan Caves in China's Anhui Province?
A most mysterious discovery is the slope of the caves. The inclined plane of the walls has exactly the same slope as the outside hill.
Yet according to the technology of that time, how could the ancient people have managed that?
Located in the eastern suburbs of Tunxi district in the Anhui province city of Huangshan, a visitor will find Huashan Caves steeped in ancient, mysterious legends.
The history and purposes of Huashan Caves - accidentally discovered by a local farmer - are now untraceable due to the lack of any words in books or on cave walls describing their use.
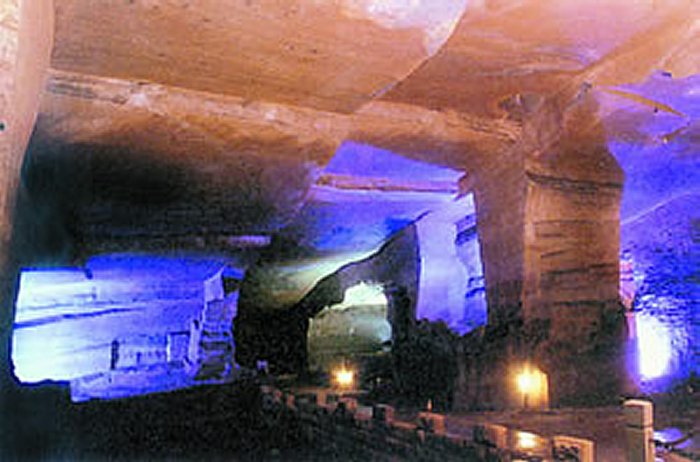
All the Huashan Caves, each ranging from 10 meters to 20 meters in height and according to tests made on manually chiseled stones, the caves have existed for more than 1,700 years. Stone chambers - in various shapes – such as an elephant or a boot – support the ceiling. These chambers - filled with water, and some are two-story chambers are connected by way of corridors.
Altogether 36 caves have been found among the rolling Huashan hills, near the crystal-clear Xin'an River. Deep inside, there is a crystal-clear pool but no living fish live there due to the high mineral content. The neatly chiseled walls and roofs, the big pillars, and the stone stairs indicate that the caves were dug by men.
Mysterious caves tested on chiseled stones showed that the caves have existed for at least 1,500 years. Image credit: china.org.cn/
Yet nobody knows for what purpose the ancient people created them. A most mysterious discovery is the slope of the caves. The inclined plane of the walls has exactly the same slope as the outside hill.
Not a single word about the caves has ever been found among China's numerous ancient records although their size has already ranked them as the biggest ever discovered so far in China.
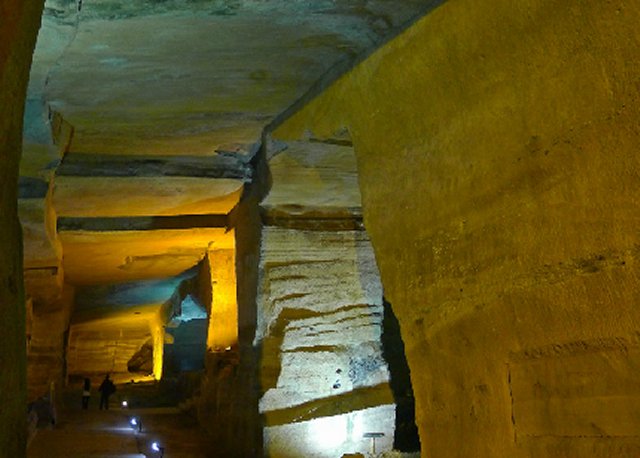
Huanxi cave, with a length of 140 meters and a size of 4,800 square meters, is one of the two now open to the public. After a walk of 100 meters, you find a grand hall inside the cave, with pools, pillars, and small rooms on each side.
Among all the 36 caves, the biggest and no doubt most impressive is the Qingliang Cave, which is known as the 'Underground Palace' due to its scale and magnificent layout.
With a total length of 170 meters, the cave covers a space of 12,600 square meters. The original digging-out of the cave could have produced at least 50,000 cubic meters of stone.
Image credit: China.org.cn.
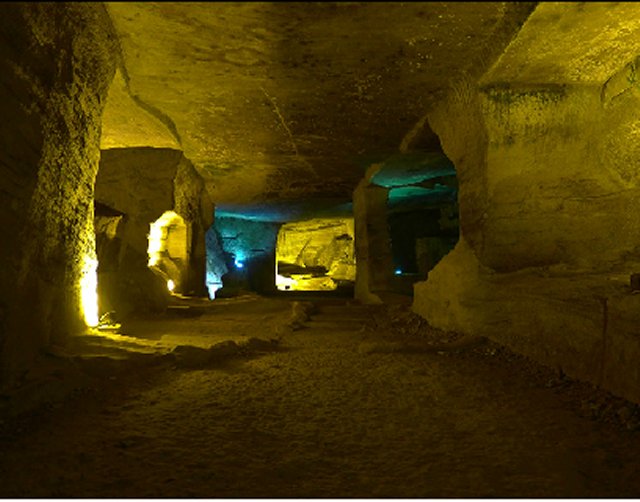
Inside the cave, there is a stone bridge above an underground river and stone paths leading to different halls. A two-story stone structure is nearby where visitors have a bird's eye view of the huge cave from a balcony. No food remains were found in the cave, nor were any smoking or signs of fire.
But without fire how could the ancient diggers have produced light in the cave?
As there are no historical records telling why the ancient people dug the caves, a variety of guesses are made by tourists as well as by experts.
Image credit: http://www.china.org.cn/
Some people hold that the ancient people dug the caves just to produce stone as, at that time, a large quantity of stone was needed to build the town. But if it was only for stone, why did they leave exquisite smoothed chisel marks on the walls and roofs?
Another hypothesis is that the caves were used to station troops. According to history texts, a large-scale peasant uprising occurred near the caves in 1120. The caves could have been the place to station soldiers.
Yet as mentioned before, the stone tests showed that the caves have a history as long as 1,700 years, so the caves were already there before the peasant uprising. So this theory is also questionable.
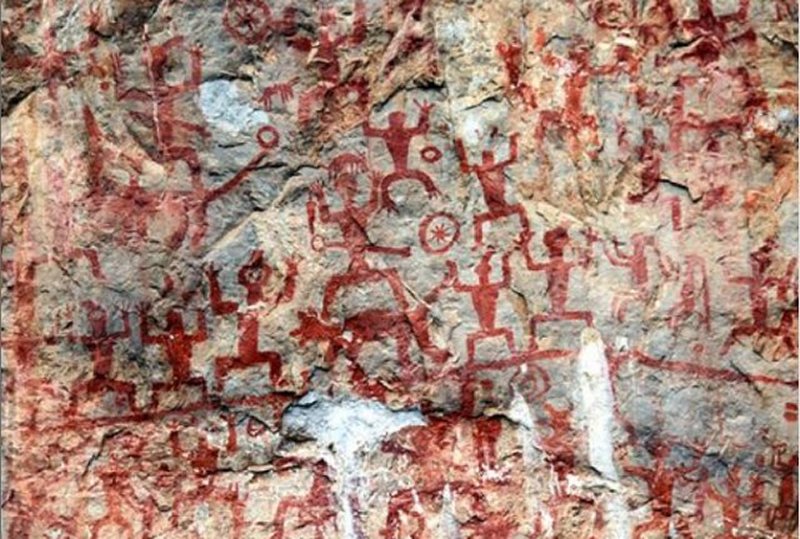
Rock Paintings of Hua Mountain, located on a cliff face along the west bank of the Mingjiang River in Yaoda Town, Ningming County, Guangxi, China. Image credit: Rolfmueller - CC BY-SA 3.0
Perhaps the caves were used as imperial tombs and later, for whatever reason, they were abandoned.
Another interesting place to admire includes the rock paintings of Huashan Mountain, the biggest, most content-rich, and best-preserved ancient rock carvings in China among all the discovered cultural relics to date.
The paintings are believed to be between 1800 and 2500 or between 1600 and 2400 years old. The period of their creations hence spans the times from the Warring States period (475-221BC) and Eastern Han Dynasty (25-220AD).
The paintings are attributed to the ancient Luo Yue people, who are believed to be ancestors of the present-day Zhuang nationality and inhabited the valley of Zuo River during this period.
Carbon dating suggests that the oldest paintings were executed around 16,000 years ago whereas the youngest is around 690 years old.
The whole painting stretches more than 200 meters in length and around 40 meters in height, with more than 1800 images in it, including people, horses, dogs, knives, swords, and drums.
The exact reason for its creation still remains unknown.
Written by – A. Sutherland AncientPages.com Staff Writer
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
More From Ancient Pages
-
 Archaeologists Unearthed Shrine To Apostle Peter In Israel’s Galilee
Archaeology | Aug 2, 2019
Archaeologists Unearthed Shrine To Apostle Peter In Israel’s Galilee
Archaeology | Aug 2, 2019 -
 Waru Waru – Ancient Andean Irrigation System Brought Back To Life
Ancient History Facts | Apr 28, 2018
Waru Waru – Ancient Andean Irrigation System Brought Back To Life
Ancient History Facts | Apr 28, 2018 -
 Mount’s Bay, Lyonesse, Langarroc: Legendary Submerged Lands And Buried Towns Of Cornwall
Featured Stories | Apr 21, 2022
Mount’s Bay, Lyonesse, Langarroc: Legendary Submerged Lands And Buried Towns Of Cornwall
Featured Stories | Apr 21, 2022 -
 Undeciphered Singapore Stone’s Carvings – New Attempt To Crack The Puzzle
Artifacts | Jun 11, 2024
Undeciphered Singapore Stone’s Carvings – New Attempt To Crack The Puzzle
Artifacts | Jun 11, 2024 -
 Mysterious Rock Inscription Found In Brittany Baffles Experts – Reward If You Can Decipher It
Archaeology | May 15, 2019
Mysterious Rock Inscription Found In Brittany Baffles Experts – Reward If You Can Decipher It
Archaeology | May 15, 2019 -
 Secrets Of 160,000 Ancient Texts Kept In The Abbey Library Of St. Gall May Soon Be Unlocked By AI
Linguistic Discoveries | Aug 23, 2021
Secrets Of 160,000 Ancient Texts Kept In The Abbey Library Of St. Gall May Soon Be Unlocked By AI
Linguistic Discoveries | Aug 23, 2021 -
 New Study Reveals Who Destroyed New York’s First Dinosaur Museum
News | May 29, 2023
New Study Reveals Who Destroyed New York’s First Dinosaur Museum
News | May 29, 2023 -
 Ancient Egyptian Women Had Equal Rights As Men – Egyptian Cosmology And Goddess Maat Reveal Why
Ancient History Facts | Dec 18, 2017
Ancient Egyptian Women Had Equal Rights As Men – Egyptian Cosmology And Goddess Maat Reveal Why
Ancient History Facts | Dec 18, 2017 -
 Reconstructed – Incredibly Well-Preserved 1,700-Year-Old Lendbreen Tunic – Norway’s Oldest Piece Of Clothing
Archaeology | Feb 21, 2018
Reconstructed – Incredibly Well-Preserved 1,700-Year-Old Lendbreen Tunic – Norway’s Oldest Piece Of Clothing
Archaeology | Feb 21, 2018 -
 Louvre Museum’s Entire Collection Is Now Available Online To Anyone
News | Mar 31, 2021
Louvre Museum’s Entire Collection Is Now Available Online To Anyone
News | Mar 31, 2021 -
 Rare Three-Bladed Arrowhead Hidden Under The Ice Was Last Touched By A Viking – Scientists Say
Archaeology | Jan 4, 2023
Rare Three-Bladed Arrowhead Hidden Under The Ice Was Last Touched By A Viking – Scientists Say
Archaeology | Jan 4, 2023 -
 Hidden Story Of The Sacred Wiradjuri Carved Trees Revealed
Archaeology | Nov 28, 2023
Hidden Story Of The Sacred Wiradjuri Carved Trees Revealed
Archaeology | Nov 28, 2023 -
 New Trove Of Treasures, Funerary Temple, 50 Sarcophagi Unearthed In Saqqara, Cairo
Archaeology | Jan 18, 2021
New Trove Of Treasures, Funerary Temple, 50 Sarcophagi Unearthed In Saqqara, Cairo
Archaeology | Jan 18, 2021 -
 Mawangdui Medical Manuscripts: Oldest Surviving Anatomical Atlas In The World
News | Sep 2, 2020
Mawangdui Medical Manuscripts: Oldest Surviving Anatomical Atlas In The World
News | Sep 2, 2020 -
 Clapping To Show Appreciation Is An Ancient And Widespread Behavior
Ancient History Facts | May 16, 2016
Clapping To Show Appreciation Is An Ancient And Widespread Behavior
Ancient History Facts | May 16, 2016 -
 Glastonbury Tor – One Of The Most Mysterious Sacred Places In England
Civilizations | Aug 30, 2018
Glastonbury Tor – One Of The Most Mysterious Sacred Places In England
Civilizations | Aug 30, 2018 -
 Study Reveals Average Age That Women And Men Had Children Over Past 250,000 Years
DNA | Jan 10, 2023
Study Reveals Average Age That Women And Men Had Children Over Past 250,000 Years
DNA | Jan 10, 2023 -
 Neanderthals Had Capacity To Speak And Understand Language Like Humans
Archaeology | Mar 2, 2021
Neanderthals Had Capacity To Speak And Understand Language Like Humans
Archaeology | Mar 2, 2021 -
 Kudurru Of Melishihu – Stone Records From The Kassite Dynasty In Babylonia
Artifacts | Jan 17, 2016
Kudurru Of Melishihu – Stone Records From The Kassite Dynasty In Babylonia
Artifacts | Jan 17, 2016 -
 The Ebers Papyrus – Most Famous Plant Medicine ‘Encyclopedia’ Of Ancient Egypt
Civilizations | Feb 3, 2016
The Ebers Papyrus – Most Famous Plant Medicine ‘Encyclopedia’ Of Ancient Egypt
Civilizations | Feb 3, 2016





