Lost Ancient Greco-Bactrian Kingdom Of 1,000 Cities
A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com - The Graeco-Bactrian Kingdom was located in the easternmost region of the Hellenistic world. This ancient kingdom covered Bactria (northern Afghanistan) and lands to the north (known in ancient times as Sogdiana, in present-day Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and Tajikistan).
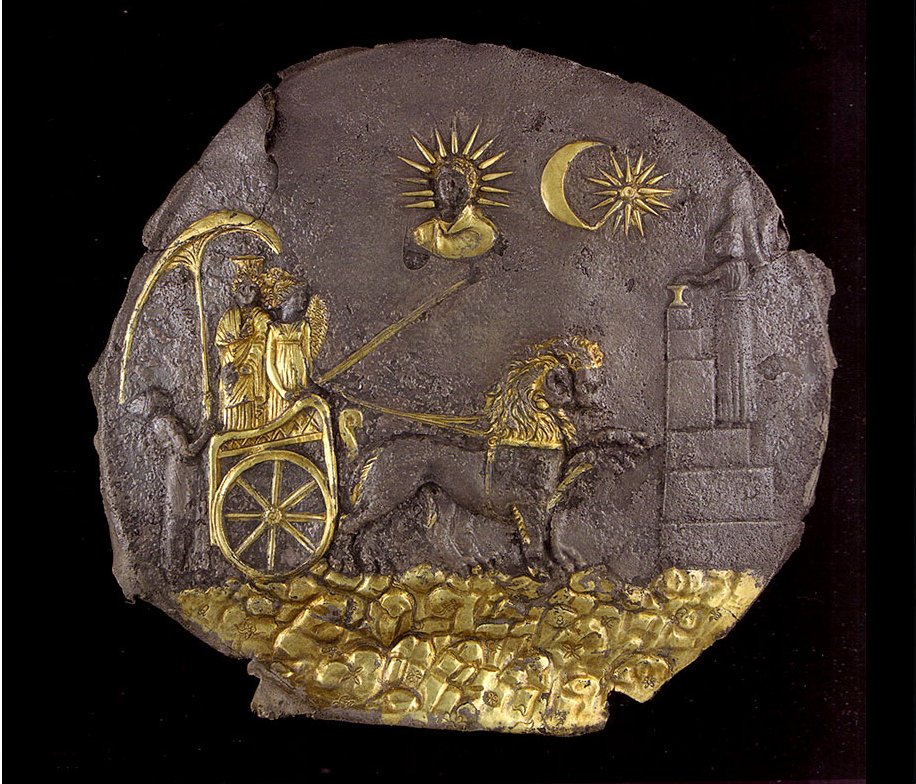 Silver plaque depicting the Greek goddess Cybele on a chariot is from a temple in Ai Khanum Afghanistan, 200 BC - Temporarily in Paris Musée Guimet. Image source - https://www.flickr.com/photos/28433765@N07/7102760363
Silver plaque depicting the Greek goddess Cybele on a chariot is from a temple in Ai Khanum Afghanistan, 200 BC - Temporarily in Paris Musée Guimet. Image source - https://www.flickr.com/photos/28433765@N07/7102760363
For at least two centuries before Alexander arrived in 330 BC, Bactria had been a prized part of the Achaemenid Empire (559-330 BC) and, before that, the Median Empire (728-559 BC).
Greek prisoners captured in wars between the Achaemenids and Greeks during the 5th and 4th centuries BC were often exiled to Bactria and taken to Bactria.
When Alexander the Great and his army arrived in Bactria, many Greeks were already there. As a result, the Greek population grew more extensive in the region.
Bactrian Greeks were often employed by the Achaemenids in significant battles and conscripted by Alexander for his campaigns in the East.
Left: Philosophical papyrus Ai Khanoum - Claude Rapin, 1992 (Non-creative 2D photograph of a 2nd century BCE papyrus.); Right: Sculpture of an old man, possibly a philosopher. Ai Khanoum, 2nd century BCE. Musee Guimet. Personal photograph 2006 - Public Domain
After the unexpected death of Alexander the Great, the situation in the region changed. Many of his Macedonian generals were left without a home. The kingdoms of the East were divided among Alexander, the Great's successors.
The government of Parthia was committed to Stasanor, a foreign ally because none of the Macedonians would deign to accept it. Subsequently, when the Macedonians were divided into parties by civil discord, the Parthians, with the other people of Upper Asia, followed Eumenes and went over to Antigonus when he was defeated.
After his death, they were under the rule of Seleucus Nicator and then under Antiochus and his successors, from whose great-grandson Seleucus they first revolted, in the first Punic war, when Lucius Manlius Vulso and Marcus Attilius Regulus were consuls.
 Gold coin of Diodotus I, Seleucid satrap of Bactria who rebelled against Seleucid emperor Antiochus and became the self-crowned ruler of the Greco- Bactrian kingdom. Image credit: National Library in Paris
Gold coin of Diodotus I, Seleucid satrap of Bactria who rebelled against Seleucid emperor Antiochus and became the self-crowned ruler of the Greco- Bactrian kingdom. Image credit: National Library in Paris
For their revolt, the dispute between the two brothers, Seleucus and Antiochus, procured them impunity; for a while, they sought to wrest the throne from one another, but they neglected to pursue the revolters.
The ancient Greco-Bactrian kingdom first appeared in 250 BC. E when the satrap Diodotos (or Theodotus in Latin), governor of the thousand cities of Bactria, rebelled against his Seleucid ruler, Antiochos II assumed the title of king.
In the third century BC, the Greco-Bactrian kingdom became so powerful that it declared independence.
People from various nationalities, such as Persians, Indians, Scythians, and many nomadic groups, contributed to developing a unique kingdom. Greco-Bactrian art was known to be one of the finest at this time.
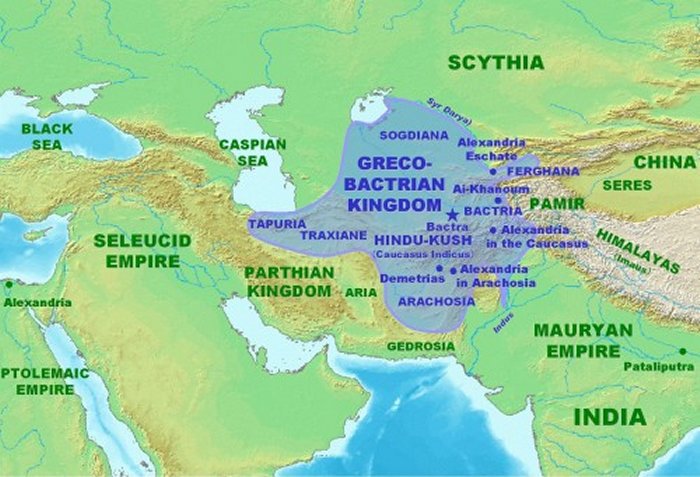 Greco Bactria Kingdom map -Approximate maximum extent of the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom circa 170 BC, under the reign of Eucratides the Great, including the regions of Tapuria and Traxiane to the West, Sogdiana and Ferghana to the north, Bactria and Arachosia to the south. Martinez-Sève, Laurianne (2020) "Afghan Bactria" in Mairs, Rachel , ed. The Graeco-Bactrian and Indo-Greek World (1st ed.), London: Routledge, pp. 218–219
Greco Bactria Kingdom map -Approximate maximum extent of the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom circa 170 BC, under the reign of Eucratides the Great, including the regions of Tapuria and Traxiane to the West, Sogdiana and Ferghana to the north, Bactria and Arachosia to the south. Martinez-Sève, Laurianne (2020) "Afghan Bactria" in Mairs, Rachel , ed. The Graeco-Bactrian and Indo-Greek World (1st ed.), London: Routledge, pp. 218–219
The culture and vast wealth these nomadic warriors accumulated during their advance were documented by the jewelry, ceremonial weapons, and other treasure found at the Scythian-era site, Tillia Tepe, in northwestern Afghanistan, where five princely graves yielded some 20,000 pieces of gold.
The Greco-Bactrian kingdom became known as the empire of 1,000 cities, but sooner or later, everything ended.
In 126 BC, the Chinese chronicler Zhang Qian visited Bactria (known as Daxia in Chinese) and described a kingdom that had collapsed while its large population and urban infrastructure remained:
 Ancient ruins of the Greco-Bactrian kingdom. Image credit: Center For Environmental Management
Ancient ruins of the Greco-Bactrian kingdom. Image credit: Center For Environmental Management
"Daxia (Bactria) is located ... south of the Gui (Oxus) river. Its people cultivate the land and have cities and houses. It has no great ruler but only several petty chiefs ruling the various cities. The people are poor in using arms and afraid of battle, but they are clever at commerce. After the Great Yuezhi moved west and attacked Daxia, the entire country came under their sway.
The country's population is large, numbering some 1,000,000 or more persons. The capital is called the city of Lanshi (Bactra) and has a market where all sorts of goods are bought and sold."
The last Graeco-Bactrian king was Heliocles, who ruled 150-125 BC and moved his capital to the Kabul Valley.
Written by – A. Sutherland AncientPages.com Staff Writer
Updated on January 21, 2023
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
More From Ancient Pages
-
 Legendary Uchchaihshravas: Divine Seven-Headed Flying Horse Of God Indra
Featured Stories | May 1, 2017
Legendary Uchchaihshravas: Divine Seven-Headed Flying Horse Of God Indra
Featured Stories | May 1, 2017 -
 Naupa Huaca: The Enigmatic Stone Temple In A Cave In Peru
Featured Stories | Sep 10, 2020
Naupa Huaca: The Enigmatic Stone Temple In A Cave In Peru
Featured Stories | Sep 10, 2020 -
 Kap Dwa – Mysterious Two-Headed Mummified Patagonian Giant – Real Or Fake?
Featured Stories | May 20, 2021
Kap Dwa – Mysterious Two-Headed Mummified Patagonian Giant – Real Or Fake?
Featured Stories | May 20, 2021 -
 Mysterious Bronze Age Viksö Helmets With Horns Related To Myths, Holy Animals And Divine Power
Artifacts | Feb 27, 2018
Mysterious Bronze Age Viksö Helmets With Horns Related To Myths, Holy Animals And Divine Power
Artifacts | Feb 27, 2018 -
 Huge Ancient Animal Sculptures Made By Unknown Carvers At Camel Site In Saudi Arabia Puzzle Archaeologists
Archaeology | Feb 14, 2018
Huge Ancient Animal Sculptures Made By Unknown Carvers At Camel Site In Saudi Arabia Puzzle Archaeologists
Archaeology | Feb 14, 2018 -
 The Invisible Plant Technology Of The Prehistoric Philippines
Archaeology | Jul 1, 2023
The Invisible Plant Technology Of The Prehistoric Philippines
Archaeology | Jul 1, 2023 -
 Frightening Edinburgh Vaults: The Spooky Underground City Of The Dead
Featured Stories | Jun 4, 2016
Frightening Edinburgh Vaults: The Spooky Underground City Of The Dead
Featured Stories | Jun 4, 2016 -
 A Large ‘Tableman’ Sheds Some Light On People’s Fun And Games In Medieval Bedfordshire
Archaeology | Jun 19, 2023
A Large ‘Tableman’ Sheds Some Light On People’s Fun And Games In Medieval Bedfordshire
Archaeology | Jun 19, 2023 -
 Tracking Prehistoric Relations With AI From The Middle Stone Age To Antiquity
Archaeology | Jul 14, 2023
Tracking Prehistoric Relations With AI From The Middle Stone Age To Antiquity
Archaeology | Jul 14, 2023 -
 Are Bones Of Apostle Peter Hidden Inside A 1000-Year-Old Roman Church?
Archaeology | Sep 16, 2017
Are Bones Of Apostle Peter Hidden Inside A 1000-Year-Old Roman Church?
Archaeology | Sep 16, 2017 -
 Large Collection Of 2,200-Year-Old Tombs With Boat Coffins Made Of Nanmu Wood, Unearthed In SW China
Archaeology | Feb 10, 2017
Large Collection Of 2,200-Year-Old Tombs With Boat Coffins Made Of Nanmu Wood, Unearthed In SW China
Archaeology | Feb 10, 2017 -
 Jiroft’s Konar Sandal – Home To A Huge Ziggurat And Many Ancient Treasures
Featured Stories | Jun 8, 2021
Jiroft’s Konar Sandal – Home To A Huge Ziggurat And Many Ancient Treasures
Featured Stories | Jun 8, 2021 -
 Sacred Cherokee Star Mound And The Legend Of The Star People – Beneath The Ground May Lie A Secret That Should Remain Hidden Forever
Featured Stories | Mar 23, 2025
Sacred Cherokee Star Mound And The Legend Of The Star People – Beneath The Ground May Lie A Secret That Should Remain Hidden Forever
Featured Stories | Mar 23, 2025 -
 Who Were The Goths And Where Did They Come From?
Civilizations | Apr 16, 2019
Who Were The Goths And Where Did They Come From?
Civilizations | Apr 16, 2019 -
 Freemasons Secrets – American Democracy Is Part Of An Ancient Universal Plan – Secret Societies’ Role – Part 3
Ancient Mysteries | Jul 14, 2018
Freemasons Secrets – American Democracy Is Part Of An Ancient Universal Plan – Secret Societies’ Role – Part 3
Ancient Mysteries | Jul 14, 2018 -
 Mediterranean Migration Was Low Over 8,000 Years – New Study
Archaeology | Mar 3, 2021
Mediterranean Migration Was Low Over 8,000 Years – New Study
Archaeology | Mar 3, 2021 -
 Beautiful Zeugma-Like Mosaics Unearthed In Sinop Province, Northern Turkey
Archaeology | Oct 17, 2020
Beautiful Zeugma-Like Mosaics Unearthed In Sinop Province, Northern Turkey
Archaeology | Oct 17, 2020 -
 Evidence Of Unusual Solar Activity Discovered On Ancient Cuneiform Tablets
Archaeology | Oct 16, 2019
Evidence Of Unusual Solar Activity Discovered On Ancient Cuneiform Tablets
Archaeology | Oct 16, 2019 -
 Inscribed Fragments Of Stone Slabs Unearthed In Matariya, Ancient Heliopolis
Archaeology | Nov 9, 2018
Inscribed Fragments Of Stone Slabs Unearthed In Matariya, Ancient Heliopolis
Archaeology | Nov 9, 2018 -
 Survivors Of The Latest Ice Age Thrived Near The Sea Of Galilee 23,000 Years Ago
Archaeology | Jan 27, 2022
Survivors Of The Latest Ice Age Thrived Near The Sea Of Galilee 23,000 Years Ago
Archaeology | Jan 27, 2022

