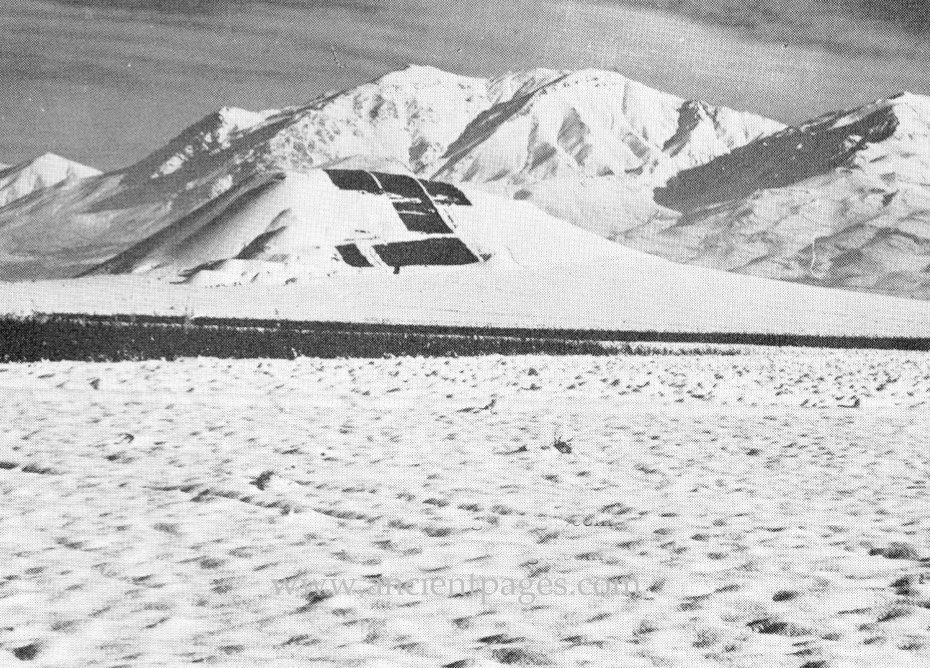
Norsuntepe – Little-Known Mysterious Prehistoric Site In Anatolia, Turkey: Why Was It Abandoned And Destroyed By Fire?
A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com - Norsuntepe is located in the Keban area (modern eastern Turkey) on the Upper Euphrates, about 25 km from Elazig.
The crown of the hill had an area of approximately 500 m to 300 m, within which settlement traces were detectable by archaeologists.
Excavations at Norsuntepe were conducted between 1968 and 1974 by the German Archaeological Institute archaeologists led by Harald Hauptmann, the Heidelberg professor of Prehistory and Early History.
The field works had to be finished by 1974 because of the construction of the Keban Dam works and the rising water level.
In the excavations of Norsuntepe, archaeologists conducted investigations on the extractive metallurgy of copper, arsenic, and a lustrous gray metalloid found in nature and known as antimony.
They also analyzed excavated smelting products from Norsuntepe (Keban) area on the Upper Euphrates.
In Anatolia, most artifacts of a late Chalcolithic date were made of unalloyed copper. Some others were arsenical coppers with low arsenic content.
At Norsuntepe (a site now under the waters of Keban dam), smelting furnaces, copper ore, slag, fragments of clay crucibles or molds, and finished metal artifacts were found in the courtyards and buildings probably belonging to metal workers.
Norsuntepe was probably a fortified site, with mudbrick houses finished with plaster, and in some instances, they had wall paintings.
Archaeologists identified 40 settlement layers from different periods, namely the late Chalcolithic (4,000- 3,000 BC), through all phases of the Bronze Age until an Urartian settlement in the Iron Age.
Norsuntepe was one of the most important sites of this period.
The Chalcolithic (sometimes referred to as the 'Copper Age') was an important period with achievements, of which the most striking development was the extensive use of copper.
Until this period, natural stones were the only material humankind used to make their weapons.
Later, they learned to process and shape this metal copper to make solid weapons and ornamentation. We also see a considerable increase in the number of towns scattered across the area.
The new towns of this period were usually built on the water or in rich valleys.
The great mother goddess of Asia Minor was the main deity, and they made many figurines of this goddess, which they used in their religious rituals. The burials within the houses of the preceding Neolithic period now occur outside the towns.
After the Iron Age, which supplied several richly furnished graves, the settlement was abandoned and destroyed by fire.
Written by – A. Sutherland AncientPages.com Staff Writer
Updated on October 10, 2022
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
Expand for referencesReferences:
Rothman Mitchell S. Tepe Gawra: The Evolution of a Small, Prehistoric Center in Northern
More From Ancient Pages
-
 Emperor Kublai Khan: One Of The Most Powerful People In Human History
Featured Stories | May 23, 2017
Emperor Kublai Khan: One Of The Most Powerful People In Human History
Featured Stories | May 23, 2017 -
 Inscribed Fragments Of Stone Slabs Unearthed In Matariya, Ancient Heliopolis
Archaeology | Nov 9, 2018
Inscribed Fragments Of Stone Slabs Unearthed In Matariya, Ancient Heliopolis
Archaeology | Nov 9, 2018 -
 Rare Phoenician Necropolis Discovered In Andalucia, Spain Is Extraordinary, Scientists Say
Archaeology | May 2, 2022
Rare Phoenician Necropolis Discovered In Andalucia, Spain Is Extraordinary, Scientists Say
Archaeology | May 2, 2022 -
 Unexplained Encounters: Beings With Inhuman Eyes – A Darker Side Of Humanity Or Groundless Worries?
Featured Stories | Mar 2, 2025
Unexplained Encounters: Beings With Inhuman Eyes – A Darker Side Of Humanity Or Groundless Worries?
Featured Stories | Mar 2, 2025 -
 Sweden’s Tanum And Skredsvik Petroglyphs: Thousands Of Spectacular And Intriguing Rock Art
Featured Stories | Aug 28, 2018
Sweden’s Tanum And Skredsvik Petroglyphs: Thousands Of Spectacular And Intriguing Rock Art
Featured Stories | Aug 28, 2018 -
 Ancient Enigma Of Mercator’s Amazing Map
Ancient Technology | May 4, 2015
Ancient Enigma Of Mercator’s Amazing Map
Ancient Technology | May 4, 2015 -
 Upside Down Chambers For The Dead Found At Maeshowe, Orkney
Archaeology | Sep 8, 2020
Upside Down Chambers For The Dead Found At Maeshowe, Orkney
Archaeology | Sep 8, 2020 -
 Secrets Of 2,000-Year-Old Tomb Of Cerberus Revealed To The Public
Archaeology | Jul 29, 2024
Secrets Of 2,000-Year-Old Tomb Of Cerberus Revealed To The Public
Archaeology | Jul 29, 2024 -
 Untouched 1,300-Year-Old Grave Of Merovingian Warrior With Complete Armor Found In Ingelheim, Germany
Archaeology | Sep 19, 2023
Untouched 1,300-Year-Old Grave Of Merovingian Warrior With Complete Armor Found In Ingelheim, Germany
Archaeology | Sep 19, 2023 -
 Dead City Of Serjilla – Byzantine Village In Syria Struggling To Survive The Middle Of A War Zone
Featured Stories | Jan 27, 2020
Dead City Of Serjilla – Byzantine Village In Syria Struggling To Survive The Middle Of A War Zone
Featured Stories | Jan 27, 2020 -
 On This Day In History: Ferdinand Magellan Reached Pacific And South American Strait – On Nov 28, 1520
News | Nov 28, 2016
On This Day In History: Ferdinand Magellan Reached Pacific And South American Strait – On Nov 28, 1520
News | Nov 28, 2016 -
 Palace Located Inside Ancient Temple Of Ramses II Discovered In Abydos, Egypt
Archaeology | Apr 1, 2019
Palace Located Inside Ancient Temple Of Ramses II Discovered In Abydos, Egypt
Archaeology | Apr 1, 2019 -
 A 3,500-Year-Old Grape Seed Sheds Light On Great Tradition Of Vineyards Of Anatolia’s Çal And Region
Archaeology | Sep 13, 2023
A 3,500-Year-Old Grape Seed Sheds Light On Great Tradition Of Vineyards Of Anatolia’s Çal And Region
Archaeology | Sep 13, 2023 -
 Enigmatic Cernunnos – Most Ancient, Stag-Antlered, Peaceful God Of Celtic People
Celtic Mythology | Aug 26, 2019
Enigmatic Cernunnos – Most Ancient, Stag-Antlered, Peaceful God Of Celtic People
Celtic Mythology | Aug 26, 2019 -
 Qanats: Ancient 3,000-Year-Old Underground Irrigation Canals Invented By People Of Persia
Ancient Technology | Jul 13, 2020
Qanats: Ancient 3,000-Year-Old Underground Irrigation Canals Invented By People Of Persia
Ancient Technology | Jul 13, 2020 -
 Viking Grave And Sword Discovered In Norwegian Garden
Archaeology | Jul 3, 2023
Viking Grave And Sword Discovered In Norwegian Garden
Archaeology | Jul 3, 2023 -
 Is A Gigantic Ancient City Hidden Underwater In The Bermuda Triangle?
Featured Stories | Jul 8, 2014
Is A Gigantic Ancient City Hidden Underwater In The Bermuda Triangle?
Featured Stories | Jul 8, 2014 -
 Hidden Records Of A Civilization Frozen In Time – Mysterious Time Capsules
Featured Stories | Aug 31, 2020
Hidden Records Of A Civilization Frozen In Time – Mysterious Time Capsules
Featured Stories | Aug 31, 2020 -
 Discovered Roman Malting Oven Could Be Evidence Of 2,000-Year-Old Beer Production In The UK
Archaeology | Apr 4, 2022
Discovered Roman Malting Oven Could Be Evidence Of 2,000-Year-Old Beer Production In The UK
Archaeology | Apr 4, 2022 -
 Food In Ancient Roman Funerary Meals Was Similar To That Consumed During Life
Archaeology | Aug 30, 2022
Food In Ancient Roman Funerary Meals Was Similar To That Consumed During Life
Archaeology | Aug 30, 2022



