Charlemagne – Most Famous Emperor Of Education And Enemy Of Pagan Worshippers – What Did He Really Mean For Europe?
A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com - Charlemagne, also known as Charles the Great (742 - 814), is considered the most remarkable of all medieval rulers in the history of the European continent.
His kingdom stretched to the territories today, including France, Germany, Benelux, part of Italy, and Switzerland; his contemporaries called him the 'Father of Europe.'
For some, he was a national hero. For others, he was the almost semi-legendary figure, and after his death - in a way - he was still alive. His life was remembered, and his achievements inspired the Crusades and later European leaders such as Louis XIV, Napoleon I, and Hitler. Even today, some people claim Charlemagne as the founder of European unity.
Charlemagne proved to be a talented diplomat and able administrator of the vast European kingdom he controlled. He was a true enemy of pagan worshippers.
Charlemagne was an enthusiastic promoter of literacy, respected education, and loved books. An excellent scholar in many other subjects, including language and mathematics, unfortunately, he never learned to write.
Charlemagne was born around 742, but his birthplace is unknown, although Aachen in modern-day Germany and Liege in present-day Belgium were proposed as possible locations.
Very little is known about his childhood. He was illiterate for much of his life. He studied grammar, rhetoric, and mathematics and learned to speak Latin and understand some Greek in addition to his native Frankish, but he had difficulties to learn to write.
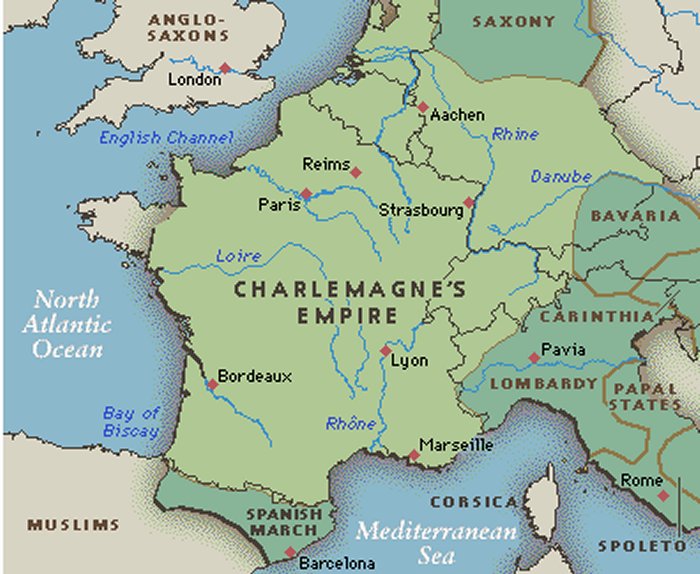
Charlemagne was a successful conqueror. He defeated the Lombards in northern Italy and made himself their king. He campaigned in Spain and Hungary.
He hired learned men to read out loud to him at dinner. We know from ancient historical records that he practiced writing on his wax tablets while in bed and then hid them under his pillows.
When his father, Pepin the Short (714 – 768), died, the kingdom was divided between Charlemagne and his brother Carloman. When his brother died in 771, Charlemagne became the leader of the reunified Frankish empire, which ruled from several cities and was engaged in many military battles during his reign.
He conquered Saxony in the 8th century, but winning the battle over the Saxons was not easy. He spread Christianity into Northern Europe by forcing Catholicism on the conquered people and slaughtering those who refused to convert. Charlemagne financially supported churches and protected the popes. He also made churches function as refugee shelters.
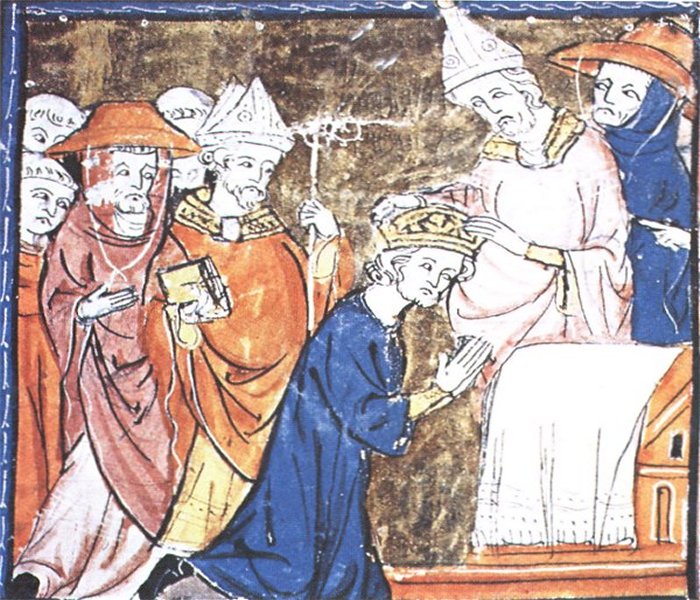
The coronation of Charlemagne by Pope Leo III. source
Pope Leo III acknowledged Charlemagne as a ruler, and in 800, at Mass on Christmas day at St. Peter's Basilica in Rome, he was named Roman Emperor.
Interestingly, Charlemagne began to use this title much later, probably because he feared it would create dependence on the Pope.
Charlemagne made many contributions to the future of European education. He sponsored the creation of a new uniform script for copying texts, developing textbooks for teaching Latin to non-Latin speakers, and collecting Latin manuscripts. Charlemagne also promoted learning that was given a time and a place to flourish. He set up monastic schools, supported authors and artists, and devised the pounds, shillings, and pence system used during the middle ages and in Britain until the 1970s.
Among his other achievements was the creation of the "Carolingian Miniscule," an alternative to the capital letters used in the Latin text.
Charlemagne died in 814 and was buried at the cathedral in Aachen. His empire encompassed much of Western Europe at the time of his death. He left control of his kingdom to his son, Louis the Pious.
His enormous cultural legacy has survived until today.
Written by A.Sutherland - AncientPages.com Senior Staff Writer
Updated on March 14, 2023
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
Expand for referencesReferences:
Fried J. Charlemagne
Becher M. Charlemagne
More From Ancient Pages
-
 African Stonehenge – Extraordinary Stone Circles Of Senegambia – Who Were The Unknown Builders?
Civilizations | Mar 29, 2014
African Stonehenge – Extraordinary Stone Circles Of Senegambia – Who Were The Unknown Builders?
Civilizations | Mar 29, 2014 -
 Ancient Mystery In The Alpes Remains Unsolved Because Of Contradicting Information
Ancient Mysteries | May 15, 2018
Ancient Mystery In The Alpes Remains Unsolved Because Of Contradicting Information
Ancient Mysteries | May 15, 2018 -
 The Caesar Cipher: Ancient And Simple Yet Effective Cipher Used By Julius Caesar
Ancient History Facts | May 30, 2018
The Caesar Cipher: Ancient And Simple Yet Effective Cipher Used By Julius Caesar
Ancient History Facts | May 30, 2018 -
 Mysterious Gobi Sea And A Huge Land Inhabited By The Real Sons Of God
Featured Stories | Aug 20, 2018
Mysterious Gobi Sea And A Huge Land Inhabited By The Real Sons Of God
Featured Stories | Aug 20, 2018 -
 Lost World Of Doggerland: Parts Of Britain’s Sunken Stone Age Atlantis Discovered
Archaeology | Jul 4, 2012
Lost World Of Doggerland: Parts Of Britain’s Sunken Stone Age Atlantis Discovered
Archaeology | Jul 4, 2012 -
 Insects Played An Important Role In The Biblical Exodus
Biblical Mysteries | Jan 13, 2018
Insects Played An Important Role In The Biblical Exodus
Biblical Mysteries | Jan 13, 2018 -
 Rare Roman Mosaic Of Amazon Warriors Unearthed In Syria Hailed As Major Archaeological Discovery
Archaeology | Oct 12, 2022
Rare Roman Mosaic Of Amazon Warriors Unearthed In Syria Hailed As Major Archaeological Discovery
Archaeology | Oct 12, 2022 -
 Bacho Kiro Cave: Genomes Of The Earliest Europeans – Sequenced
Archaeology | Apr 8, 2021
Bacho Kiro Cave: Genomes Of The Earliest Europeans – Sequenced
Archaeology | Apr 8, 2021 -
 On This Day In History: Battle Of Langside Was Fought – On May 13, 1568
News | May 13, 2016
On This Day In History: Battle Of Langside Was Fought – On May 13, 1568
News | May 13, 2016 -
 Mysterious Ancient Human Skeletons Found In Florida Lake Puzzle Archaeologists – Unknown Lost Settlement?
Featured Stories | May 21, 2024
Mysterious Ancient Human Skeletons Found In Florida Lake Puzzle Archaeologists – Unknown Lost Settlement?
Featured Stories | May 21, 2024 -
 Ancient Civilizations Invented Alcohol 10,000 Years Ago
Ancient History Facts | Sep 13, 2016
Ancient Civilizations Invented Alcohol 10,000 Years Ago
Ancient History Facts | Sep 13, 2016 -
 On This Day In History: Terracotta Army Buried With Emperor Qin Shi Huang Discovered – On Mar 29, 1974
News | Mar 29, 2017
On This Day In History: Terracotta Army Buried With Emperor Qin Shi Huang Discovered – On Mar 29, 1974
News | Mar 29, 2017 -
 Secret Ancient Lunar Calendar May Be Hidden At A Hittite Sanctuary
Archaeology | Jul 3, 2019
Secret Ancient Lunar Calendar May Be Hidden At A Hittite Sanctuary
Archaeology | Jul 3, 2019 -
 Unknown Lost Civilization Of Ancient Megalithic Super-Builders In The Middle East – Can Prehistoric Rock Art Solve The Mystery?
Featured Stories | Jul 13, 2020
Unknown Lost Civilization Of Ancient Megalithic Super-Builders In The Middle East – Can Prehistoric Rock Art Solve The Mystery?
Featured Stories | Jul 13, 2020 -
 Why Are Christmas Ghost Stories So Fascinating?
Christmas Traditions | Dec 24, 2019
Why Are Christmas Ghost Stories So Fascinating?
Christmas Traditions | Dec 24, 2019 -
 Man-Made Square Burial Cave Dated To Rameses II-Era Accidentally Found In Israel
Archaeology | Sep 19, 2022
Man-Made Square Burial Cave Dated To Rameses II-Era Accidentally Found In Israel
Archaeology | Sep 19, 2022 -
 Mystery Of Giant Ancient Statues And A Vanished Civilization With Unusual Physical Characteristics – Strange American Connection – Part 2
Ancient Mysteries | Aug 20, 2020
Mystery Of Giant Ancient Statues And A Vanished Civilization With Unusual Physical Characteristics – Strange American Connection – Part 2
Ancient Mysteries | Aug 20, 2020 -
 Frigg: Chief Norse Goddess Who Knew Secrets Of Humans’ Fates
Featured Stories | Dec 13, 2022
Frigg: Chief Norse Goddess Who Knew Secrets Of Humans’ Fates
Featured Stories | Dec 13, 2022 -
 On This Day In History: Emperor Constantine I Passes His Famous National Sunday Law – On March 7, 321 AD
News | Mar 7, 2017
On This Day In History: Emperor Constantine I Passes His Famous National Sunday Law – On March 7, 321 AD
News | Mar 7, 2017 -
 A 19th-Century Sailing Ship Loaded With Champagne, Wine, Porcelain And Mineral Water Found At The Bottom Of The Baltic Sea
Underwater Discoveries | Jul 25, 2024
A 19th-Century Sailing Ship Loaded With Champagne, Wine, Porcelain And Mineral Water Found At The Bottom Of The Baltic Sea
Underwater Discoveries | Jul 25, 2024

