Teotihuacán: Enigmatic Birthplace Of The Gods And Its Obscure History
A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com - Teotihuacán is an ancient site where the circumstances of its destruction are not entirely clear. The people who created it are completely unknown, and no satisfactory explanation has ever been found for what appears to have been the sudden decline of the city.
There is no good reason to suggest a foreign invasion. The city was destroyed through burning and deliberate destruction, and it must have been sacked. It happened in the middle of the 6th century CE.
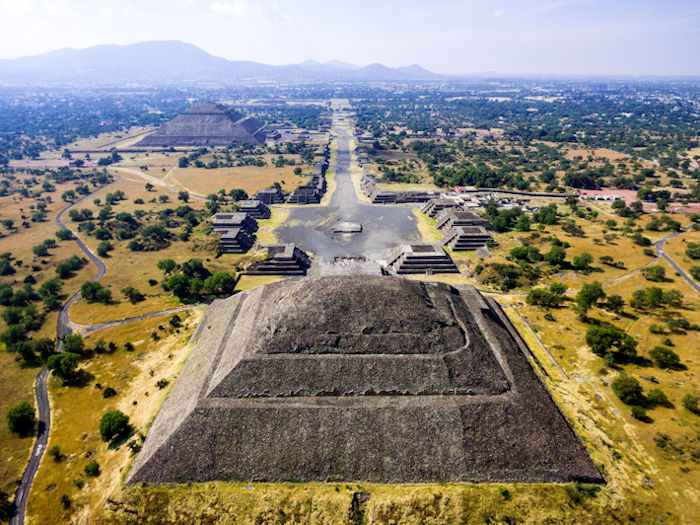
Teotihuacan. Credit: Adobe Stock - Luis
Mysterious, massive Teotihuacán - which is one of the intriguing archaeological sites in the Americas - remains a historical mystery.
Situated in the Valley of Mexico, 40 km (25 miles) north of Mexico City, on the central highland plateau of Mexico, Teotihuacán was first inhabited in about 150 BC, but the first ceremonial buildings were constructed in the 1st and 2nd centuries AD. It is believed that Teotihuacán, most probably the largest city in the New World, had about 150,000 – 200,000 inhabitants at its height.
Many archaeologists are divided regarding the dating of the site, some believing the city flourished from 1500 to 1000 BC; others suggest a later period of 100 BC to 700 AD but there are also scholars who believe that Teotihuacan is much older.
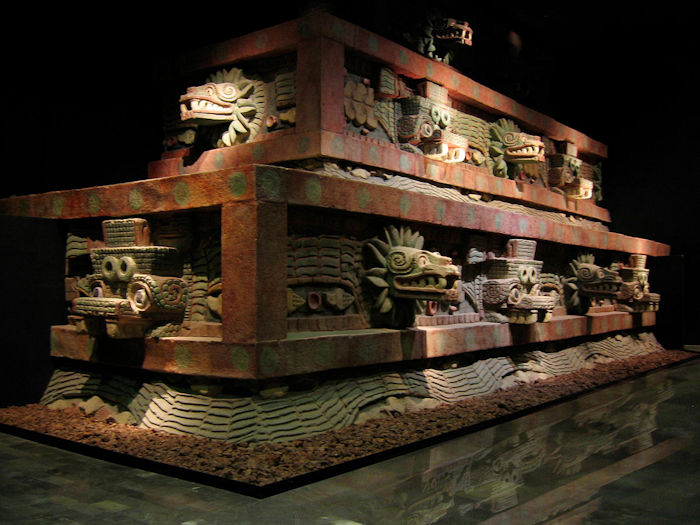
Reconstruction of the facade of the Temple of the Feathered Serpent (Teotihuacán) Now located in the National Museum of Anthropology. Credit: Rose Mania - CC BY 2.0
It had many pyramids and other large public areas and the city was laid out at this time on a regular grid, never before seen in the New World.
Archaeological findings do not give clear answers regarding the enigmatic people of Teotihuacán, who built and ruled it.
No written records have ever been found that could shed light on Teotihuacán’s past.
It is unknown what the original name of the city was; the name Teotihuacan ‘the place of the gods’ or "place where gods were born", was given by the Nahuatl-speaking Aztecs several centuries after the fall of the city around 550 AD.
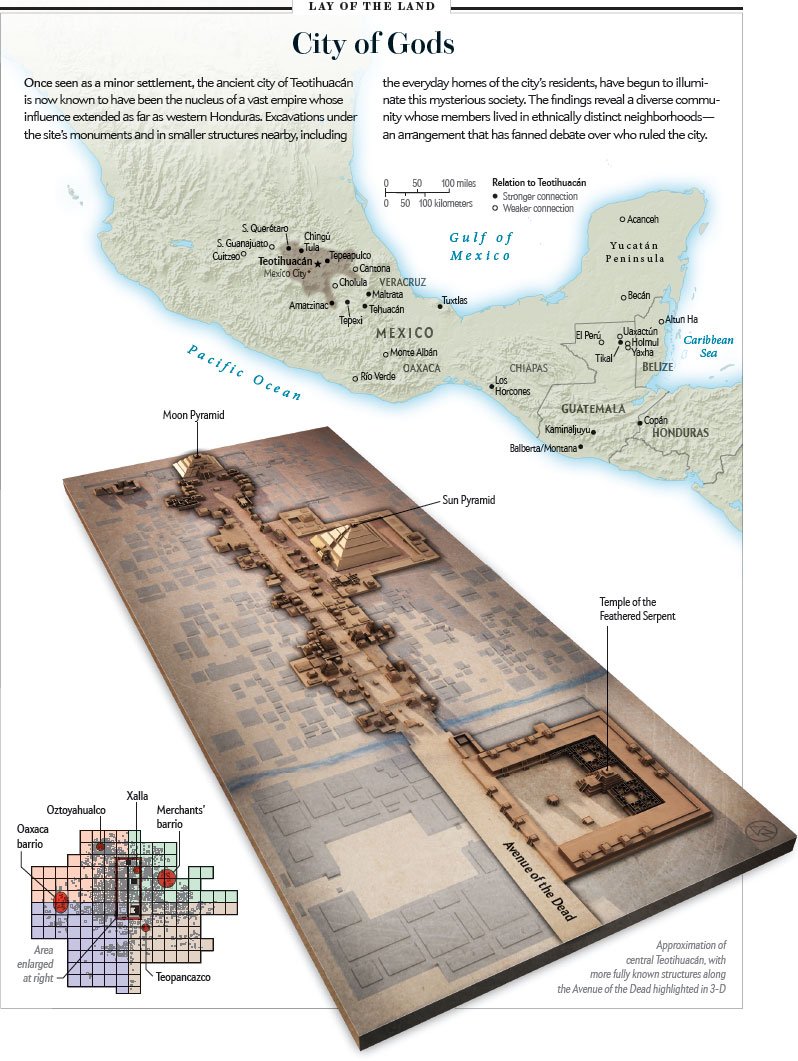
Credit: Maps by XNR Productions, Illustrations by José Miguel Mayo; sources: based on work by Rene Millon (all maps). Image via Nature.com/Scientific American
This name could be associated with Nahua creation myths linked to Teotihuacán. The Aztecs believed that the gods created the universe, with the sun and the moon at Teotihuacán and the city’s motifs and symbols were adopted by the Aztecs as their own. Most recognized of the Mesoamerican deities was Quetzalcoatl, the Feathered Serpent and in the Aztec pantheon, Quetzalcoatl was the primary sky god, associated with wind and air but first of all a god of creation and wisdom.
Myths of Central America tell that the world had undergone four cycles or "suns"; they lived in the fifth sun, which was already old, so the end of the world by earthquakes, was expected at any moment.
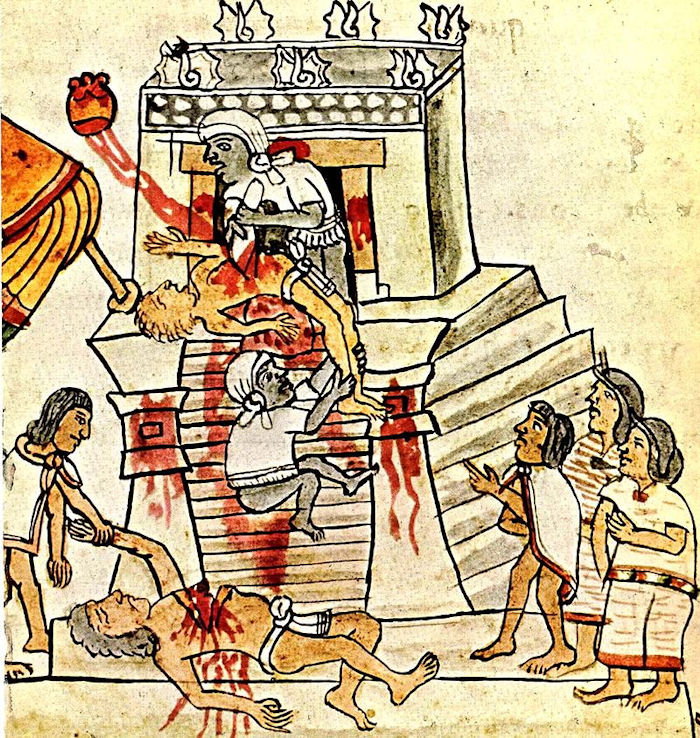
In an attempt to delay the cataclysmic event, thousands of people were sacrificed; in the Pyramid of the Sun, the corner of each step was found full of skeletons of children and three burial pits with skeletons were discovered by archaeologists beneath the Temple of Quetzalcoatl.
Human sacrifice is shown in the Codex Magliabechiano. Credit: Public Domain
Most impressive depictions of the plumed serpent existed at Teotihuacan four-hundreds years before Palenque, and almost 1000 years before they were seen at Tula or Chichen Itza.
Did the mysterious visitor make his first appearance at Teotihuacan? Was the worship of this powerful god taken into the Maya region early in the Christian era by Teotihuacan missionaries anxious to spread their beliefs, or was it brought back from Mayan traditions?, asks T. J. O'Brien, in his book ‘Fair Gods and Feathered Serpents: A Search for Ancient America's Bearded White God’.
Teotihuacán has been mapped by Rene Millon with the help of photogrammetry, in a project lasting many years.
René Millon, a professor emeritus of anthropology at Rochester, dedicated to mapping and excavating a historic pre-Columbian site in Mexico, led an international team of researchers who produced the first complete building-by-building map of Teotihuacán, a 2,000-year-old city that lies 30 miles northeast of Mexico City.
The city’s pyramids are gigantic; the Pyramid of the Sun is the largest building at Teotihuacan. Its base measures 738 feet long and stands 246 feet tall. A temple once stood upon the pyramid’s top but was removed. The powerful city directly controlled a large area of central Mexico and had influence over an even greater area nit the lack of written records makes the hierarchical structure of Teotihuacán unknown.
The rulers probably lived in palaces within the Citadel (Ciudadela): The Citadel was a large complex that constituted the religious, political, administrative, and military center of the city. Within the rest of the city, archaeologists identified hundreds of workshops of which many produced pottery and objects of obsidian. Not all lived comfortably in the city; there have been found many slum dwellings and hundreds of painted murals but only very few stone carvings.
At about 750 AD Teotihuacán was destroyed, burned, and sacked. It was never rebuilt; however, some of the ruins were still inhabited by some illegal settlers.
The Aztecs gradually strengthen their power in the region and the mysterious city of Teotihuacán remained an important place of pilgrimage until the downfall of the Aztecs in 1521.
Updated on March 30, 2022
Written by – A. Sutherland AncientPages.com Staff Writer
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
Expand for referencesReferences:
T. J. O'Brien, ‘Fair Gods and Feathered Serpents A Search for Ancient America's Bearded White God’
C. Arnold, R. R Hewett, City of the Gods: Mexico's Ancient City of Teotihuacan
S. Vogel, Teotihuacan
More From Ancient Pages
-
 Legend Of Kauravas – Ancient Cloning And Test Tube Babies In India?
Featured Stories | Apr 21, 2017
Legend Of Kauravas – Ancient Cloning And Test Tube Babies In India?
Featured Stories | Apr 21, 2017 -
 Rare Bulla (Seal) And 2,600-Year-Old Stamp With Biblical Name Unearthed In City Of David
Archaeology | Apr 3, 2019
Rare Bulla (Seal) And 2,600-Year-Old Stamp With Biblical Name Unearthed In City Of David
Archaeology | Apr 3, 2019 -
 America’s Ancient “Mystery Stone” Remains An Unexplained Puzzle
Artifacts | Apr 17, 2014
America’s Ancient “Mystery Stone” Remains An Unexplained Puzzle
Artifacts | Apr 17, 2014 -
 Why Was The Urnes Brooch So Popular At The End Of The Viking Age?
Archaeology | May 27, 2023
Why Was The Urnes Brooch So Popular At The End Of The Viking Age?
Archaeology | May 27, 2023 -
 On This Day In History: Alexander The Great Died In Babylon – On June 11, 323 BC
News | Jun 11, 2016
On This Day In History: Alexander The Great Died In Babylon – On June 11, 323 BC
News | Jun 11, 2016 -
 Codes Of Ur Nammu: World’s Oldest Known Law Code
Ancient History Facts | Mar 11, 2016
Codes Of Ur Nammu: World’s Oldest Known Law Code
Ancient History Facts | Mar 11, 2016 -
 2,000-Year-Old Stela And ‘Laboratory’ Of Early Maya Writing Found In Guatemala
Archaeology | Mar 15, 2020
2,000-Year-Old Stela And ‘Laboratory’ Of Early Maya Writing Found In Guatemala
Archaeology | Mar 15, 2020 -
 On This Day In History: Copernicus’ s Book Banned By Catholic Church – On Mar 5, 1616
News | Mar 5, 2017
On This Day In History: Copernicus’ s Book Banned By Catholic Church – On Mar 5, 1616
News | Mar 5, 2017 -
 Mysterious 2,000-Year-Old Lost City Of Natounia May Have Been Found!
Archaeology | Jul 20, 2022
Mysterious 2,000-Year-Old Lost City Of Natounia May Have Been Found!
Archaeology | Jul 20, 2022 -
 Levänluhta People Could Survive Fimbulwinter Thanks To Their Diverse Livelihoods
Archaeology | Apr 24, 2020
Levänluhta People Could Survive Fimbulwinter Thanks To Their Diverse Livelihoods
Archaeology | Apr 24, 2020 -
 Deception And Hidden Truth – Ancient Struggle Of The Eagle And Serpent – Part 3
Ancient Mysteries | Sep 9, 2019
Deception And Hidden Truth – Ancient Struggle Of The Eagle And Serpent – Part 3
Ancient Mysteries | Sep 9, 2019 -
 On This Day In History: Coverdale Bible Printed In English For The First Time – On Oct 4, 1535
News | Oct 4, 2016
On This Day In History: Coverdale Bible Printed In English For The First Time – On Oct 4, 1535
News | Oct 4, 2016 -
 Secret Underground Chambers Of Caynton Caves And The Knights Templar Connection
Featured Stories | Aug 13, 2019
Secret Underground Chambers Of Caynton Caves And The Knights Templar Connection
Featured Stories | Aug 13, 2019 -
 Cretaceous Fossil From Antarctica Reveals Earliest Modern Bird
Fossils | Mar 6, 2025
Cretaceous Fossil From Antarctica Reveals Earliest Modern Bird
Fossils | Mar 6, 2025 -
 Ajanta Caves: Incredible Accomplishment Of India’s Ancient Stonecutters
Featured Stories | Oct 1, 2015
Ajanta Caves: Incredible Accomplishment Of India’s Ancient Stonecutters
Featured Stories | Oct 1, 2015 -
 Curious 6,000-Year-Old Skull May Confirm Mythical Ancient Tribe Of Small Dark-Skinned People Did Exist!
Archaeology | Oct 11, 2022
Curious 6,000-Year-Old Skull May Confirm Mythical Ancient Tribe Of Small Dark-Skinned People Did Exist!
Archaeology | Oct 11, 2022 -
 Unique Lost Runestone Of The Hunnestad Monument Finally Found After 300 Years In Sweden
Archaeology | Dec 16, 2020
Unique Lost Runestone Of The Hunnestad Monument Finally Found After 300 Years In Sweden
Archaeology | Dec 16, 2020 -
 Unique Viking Age Shipyard Discovered At Birka Challenges Maritime Activities Of The Viking Age
Archaeology | Jun 16, 2022
Unique Viking Age Shipyard Discovered At Birka Challenges Maritime Activities Of The Viking Age
Archaeology | Jun 16, 2022 -
 Överhogdal Tapestry: Amazingly Well-Preserved Ancient Textiles With Norse And Christian Motifs
Artifacts | Apr 26, 2019
Överhogdal Tapestry: Amazingly Well-Preserved Ancient Textiles With Norse And Christian Motifs
Artifacts | Apr 26, 2019 -
 Ptolemaic-Era Warship Discovered Near The Sunken City Of Heracleion In Alexandria By Underwater Archaeologists
Archaeology | Jul 20, 2022
Ptolemaic-Era Warship Discovered Near The Sunken City Of Heracleion In Alexandria By Underwater Archaeologists
Archaeology | Jul 20, 2022