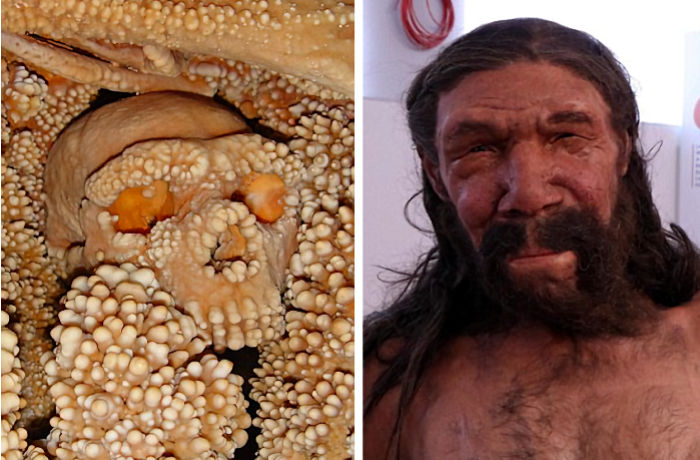
10 Surprising Facts About The Neanderthals Who Were Not As Primitive As Previously Thought
AncientPages.com - Archaeological excavations and examinations of bones, caves, and various ancient artifacts reveal that the Neanderthals were not as primitive as previously thought.
Neanderthals are our closest extinct relatives and modern humans share 99.7% of their DNA. These intriguing beings were widespread across Europe and Western Asia for a long time, about 400,000 years ago, and they died out in Europe about 40,000 years ago.
Many recent discoveries show us the Neanderthals tried to create a complex society based on various traditions, beliefs and we have underestimated their intelligence.
1. Neanderthal DNA Still Influence Modern Human Genes
Everyone living outside of Africa today has a small amount of Neanderthal in them and much of their genome lives and contribute to certain traits in modern humans.
The impact of Neanderthals’ genetic contribution has been uncertain, but scientists have discovered evidence that Neanderthal DNA sequences still influence how genes are turned on or off in modern humans. Neanderthal genes’ effects on gene expression likely contribute to traits such as height and susceptibility to schizophrenia or lupus, the researchers found. Scientists have previously also found correlations between Neanderthal genes and traits such as fat metabolism and depression. Read more
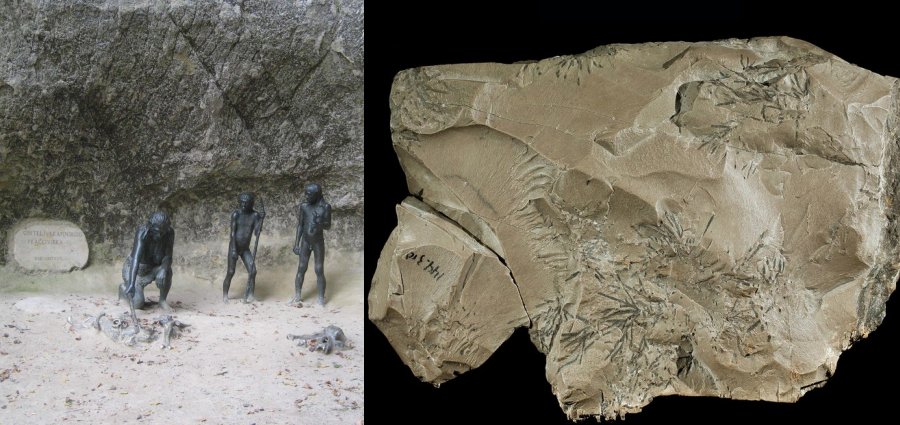
2. Neanderthals Decorated Their Caves With Rocks
The Neanderthals shared humans’ curiosity for nature and appreciated beauty. Archaeologists have discovered that the Neanderthals collected artifacts they considered valuable. At the Croatian site of Krapina, there is evidence the Neanderthals who lived there 130,000 years ago collected striped limestone rocks and used them to decorate their caves.
These rocks had a symbolic meaning to the Neanderthals and the items were also considered beautiful. Read more
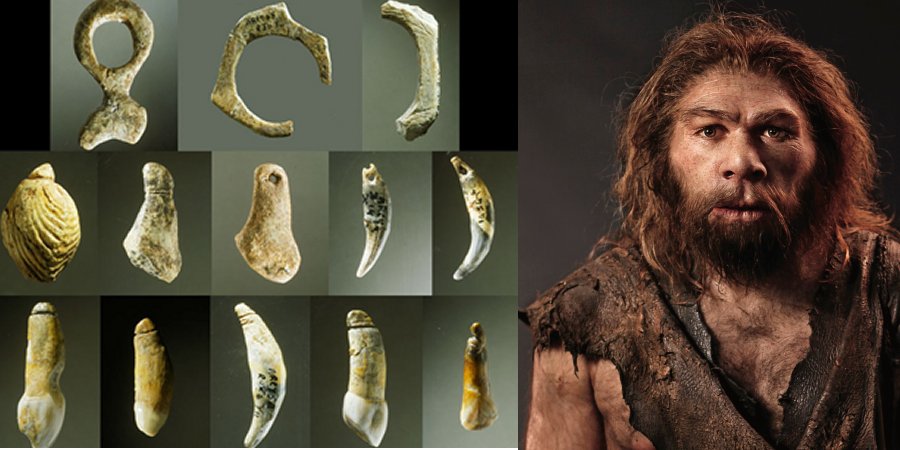
3. Neanderthals Created Jewelry 40,000 Years Ago
Ancient jewelry has been found in several prehistoric tombs all across the world, but who would have thought Neanderthals enjoyed and created jewelry as far back as 40,000 years ago!
Artifacts discovered at Grotte Du Renne, France reveal a number of bone fragments and ancient artifacts that have now been properly investigated and the results of the analysis are intriguing. Scientists have determined that bone fragments were used to produce Neanderthal jewelry. Read more
4. Neanderthals Used Plant-Based Medicine To Treat Pain And Illness
Scientists have examined ancient DNA found in the dental plaque from four Neanderthals found at the cave sites of Spy in Belgium and El Sidrón in Spain. The study reveals Neanderthals used plant-based medicine to treat pain and illness. Researchers discovered that the Neanderthals who lived in the El Sidrón Cave were vegetarians. They ate pine nuts, moss, mushrooms, and tree bark. The Neanderthals who inhabited the Spy Cave consumed woolly rhinoceros and European wild sheep, supplemented with wild mushrooms.
So, the two groups had different quite different lifestyles, but both were familiar with the benefits of plant medicine. Read more
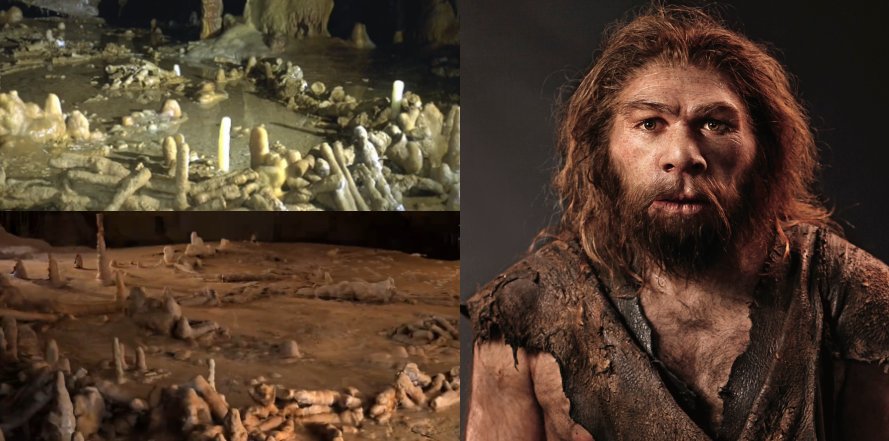
5. Neanderthals Built Ancient Underground Stone Rings For Unknown Reasons
Located deep in a cave in France there are two mysterious ancient stone rings that were made by a group of people that mastered the underground environment.
The builders of these stone rings that are now considered to be one of the world’s oldest constructions have puzzled archaeologists and historians for years, but recent research suggests the structure was constructed by Neanderthals 176,500 years ago, but it remains unknown why the underground stone rings were built. Read more
See also:
10 Fascinating Facts About Pharaohs
12 Ancient Myths, Legends And Biblical Stories Confirmed By Modern Science
10 Most Bizarre Forms Of Ancient Taxes: Surprising And Funny
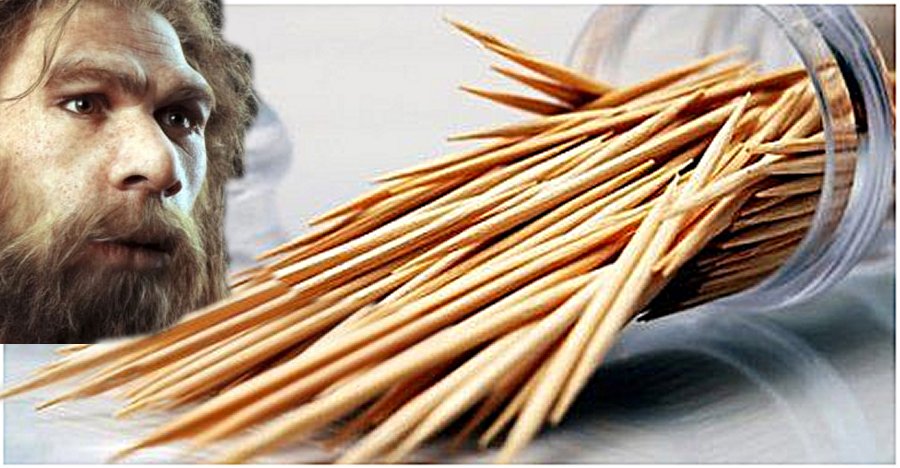
6. Neanderthals Used Toothpicks Long Before Us
Researchers excavating in northern Spain have confirmed that toothpicks were used long before our times.
Wood fibers were found on a tooth in a 1.2-million-year-old hominin jawbone discovered at the excavation site. The fibers were found in a groove at the bottom of the tooth, suggesting they came from regular tooth picking. Scientists found the oldest known example of this type of dental cleaning while investigating teeth of the 49,000-year-old remains of a Neanderthal at the El Sidron cave in Spain. Read more
7. Neanderthals Visited A Special Cave In Jersey For Over 100,000 Years
Image credit: Jersey Heritage
Archaeologists excavating in Jersey have discovered that despite globally significant changes in climate and landscape Neanderthals kept visiting La Cotte de St Brelade, a coastal cave for over 100,000 years. Why was this particular cave so important to our ancestors?
The first time these ancient people visited the cave was about 180,000 years ago and they kept coming back until 40,000 years ago.
Obviously, the cave was of great importance to the Neanderthals and it was considered a special place. Read more
8. Varggrottan: Mysterious ‘Wolf Cave’ Was Home To Neanderthals 130,000 Years Ago – Oldest Human Dwelling In Scandinavia
In Finland, there are still many unexplored ancient caves that hold many secrets. One of them is called Varggrottan, which means the Wolf Cave in English.
When archaeologists explored the mysterious cave, they found a number of artifacts that suggest this was home to Neanderthals 130,000 years ago.
There is still a debate about these controversial artifacts unearthed in the cave, but if they did belong to the Neanderthals, then there is no doubt that Varggrottan holds a special place in history, making it one of the oldest discovered homes of ancient people in Scandinavia. Read more
9. Neanderthals Buried Their Dead And Developed Spirituals Beliefs
There are still many things we don't know about the Neanderthals. Reconstruction of the child's burial by Neandertals at La Ferrassie. © Emmanuel Roudier
There is evidence that Neanderthals made symbolic or ornamental objects, and deliberately buried their dead. Sometimes they also marked their graves with offerings, such as flowers. No other primates, and no earlier human species, had ever practiced this sophisticated and symbolic behavior.
But were the Neanderthals religious too?
There is evidence from the late Middle Paleolithic period (around 50,000 years ago) which does show an early form of religious or spiritual belief amongst Neanderthals. The evidence is based on their deliberate burials with grave goods. To ritualistically bury dead is a very ancient tradition that goes back for at least tens of thousands of years. There are signs of offerings in graves going back 120,000 years and deliberate burials were ascribed to the Neanderthals. Read more
10. ‘Altamura Man’ – The Oldest Neanderthal DNA Ever Collected
Left image: The Altamura Man. Credit: Redazione Research Italy - Right image: The reconstruction of the Altamura man. Credit: EPA
The fossil skeleton of ‘Altamura Man’ imprisoned in calcite formations and found in a cave in 1993 in Puglia, Italy, belongs to the species Homo neanderthalensis. Analysis of calcium formations on ‘Altamura Man’ – embedded in an Italian cave and coated in a thick layer of calcite – shows that it formed 172,000 to 130,000 years ago during a period when ice sheets were expanding from out of Antarctica and Greenland.
Thus, the skeleton from Altamura represents the most ancient Neanderthal from which endogenous DNA has been extracted. Read more
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
More From Ancient Pages
-
 Humans’ Evolutionary Relatives Butchered One Another 1.45 Million Years Ago
Ancient Symbols | Jun 26, 2023
Humans’ Evolutionary Relatives Butchered One Another 1.45 Million Years Ago
Ancient Symbols | Jun 26, 2023 -
 On This Day In History: Vädersol Painting Depicting ‘Sun Dog’ Phenomenon Observed Over Stockholm – On Apr 20, 1535
News | Apr 20, 2017
On This Day In History: Vädersol Painting Depicting ‘Sun Dog’ Phenomenon Observed Over Stockholm – On Apr 20, 1535
News | Apr 20, 2017 -
 Intriguing And Suprising Ancient History Of Swimming That Started Over 100,000 Years Ago
Featured Stories | Dec 28, 2022
Intriguing And Suprising Ancient History Of Swimming That Started Over 100,000 Years Ago
Featured Stories | Dec 28, 2022 -
 Unravelling The Mystery Of Apollonius Of Tyana – Was He A Superhuman?
Ancient Mysteries | Sep 17, 2015
Unravelling The Mystery Of Apollonius Of Tyana – Was He A Superhuman?
Ancient Mysteries | Sep 17, 2015 -
 Enigmatic Newport Tower – Built By The Vikings, Knights Templar, Freemasons Or Someone Else?
Featured Stories | Aug 1, 2024
Enigmatic Newport Tower – Built By The Vikings, Knights Templar, Freemasons Or Someone Else?
Featured Stories | Aug 1, 2024 -
 Kingdoms Of Judah And Babylon Remained In Long-Lasting Conflict
Featured Stories | Sep 5, 2019
Kingdoms Of Judah And Babylon Remained In Long-Lasting Conflict
Featured Stories | Sep 5, 2019 -
 Skeleton Of Irish Giant Charles Byrne Will Not Be Displayed In The Hunterian Museum In London
Historical Figures | Jan 13, 2023
Skeleton Of Irish Giant Charles Byrne Will Not Be Displayed In The Hunterian Museum In London
Historical Figures | Jan 13, 2023 -
 Native American Legend Of Apotamkin Teaches Children Obedience
Featured Stories | May 14, 2019
Native American Legend Of Apotamkin Teaches Children Obedience
Featured Stories | May 14, 2019 -
 9,500-Year-Old Baskets And 6,200-Year-Old Sandals Found In Spanish Cave
Archaeology | Sep 28, 2023
9,500-Year-Old Baskets And 6,200-Year-Old Sandals Found In Spanish Cave
Archaeology | Sep 28, 2023 -
 Mirpur Jain Temple: Stunning Artwork Of Ancient Craftsmen Of India
Featured Stories | May 17, 2021
Mirpur Jain Temple: Stunning Artwork Of Ancient Craftsmen Of India
Featured Stories | May 17, 2021 -
 Astronomers Confirm Solar Eclipses Mentioned In Indigenous Folklore And Historical Documents In Japan
Folklore | Nov 9, 2022
Astronomers Confirm Solar Eclipses Mentioned In Indigenous Folklore And Historical Documents In Japan
Folklore | Nov 9, 2022 -
 The Egyptian Dream Book Reveals Ancient Predictions Of The Future
Egyptian Mythology | Jun 6, 2020
The Egyptian Dream Book Reveals Ancient Predictions Of The Future
Egyptian Mythology | Jun 6, 2020 -
 Amazing ‘Guennol Lioness’ – One Of The Greatest Ancient Works Of Art Of All Time
Artifacts | Sep 6, 2018
Amazing ‘Guennol Lioness’ – One Of The Greatest Ancient Works Of Art Of All Time
Artifacts | Sep 6, 2018 -
 88 Ice Age Human Footprints In Utah Desert Shed New Light On Ancient Americans
Archaeology | Aug 11, 2022
88 Ice Age Human Footprints In Utah Desert Shed New Light On Ancient Americans
Archaeology | Aug 11, 2022 -
 Gigantic Viking Age Burial Ground With Artifacts And 50-Meter-Long Shipwreck Unearthed In Tvååker, Halland, Sweden
Archaeology | Oct 18, 2024
Gigantic Viking Age Burial Ground With Artifacts And 50-Meter-Long Shipwreck Unearthed In Tvååker, Halland, Sweden
Archaeology | Oct 18, 2024 -
 Face-To-Face Encounter With Young Scottish Soldier Who Lived And Died Over 300 Years Ago
Archaeology | Dec 23, 2017
Face-To-Face Encounter With Young Scottish Soldier Who Lived And Died Over 300 Years Ago
Archaeology | Dec 23, 2017 -
 Mysterious Prehistoric Statues In Bada Valley, Indonesia Surrounded With Countless Legends
Civilizations | Jan 9, 2019
Mysterious Prehistoric Statues In Bada Valley, Indonesia Surrounded With Countless Legends
Civilizations | Jan 9, 2019 -
 Mystery Of The Forgotten Explorers And Ancient Artifacts That Re-Write History Of North And South America
Ancient Mysteries | Apr 13, 2020
Mystery Of The Forgotten Explorers And Ancient Artifacts That Re-Write History Of North And South America
Ancient Mysteries | Apr 13, 2020 -
 2,000-Year-Old Sundial Discovered In Ancient City Of Laodicea, Turkey
Archaeology | Mar 25, 2020
2,000-Year-Old Sundial Discovered In Ancient City Of Laodicea, Turkey
Archaeology | Mar 25, 2020 -
 Ancient Egyptian Papyrus Tells A Different Story About Biblical Isaac’s Fate
Archaeology | May 1, 2018
Ancient Egyptian Papyrus Tells A Different Story About Biblical Isaac’s Fate
Archaeology | May 1, 2018











