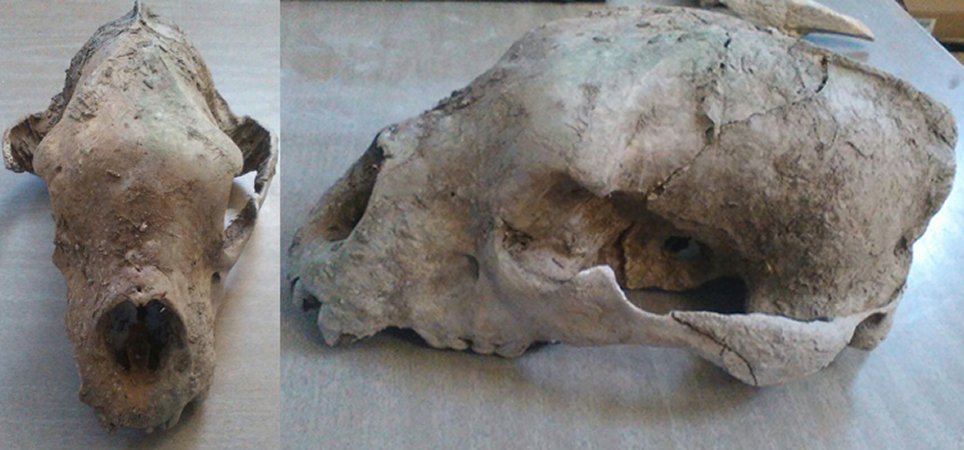
AncientPages.com - Researchers in Argentina report they have discovered remains of a giant bear of the late Pleistocene, near Buenos Aires. It’s an extraordinary find and the skull and jaw of this giant bear are still almost complete.
The discovery was made on the banks of the Salado River, northwest of the province of Buenos Aires, a paleontological site has revealed a lot of fossils in recent weeks.
Credit: Agencia CTyS-UNLaM
In an interview with CTYS-UNLaM Agency, paleontologist of the Museo La Plata and CONICET Leopoldo Soibelzon explained that find a bear in the Pampean region is an extraordinary find.
"Finding a carnivore already is an extraordinary finding because they are always fewer in ecosystems," said Dr. Soibelzon. He added: "And within carnivores, the bears are not frequently found, and even less a complete skull with a jaw, as was found now in Junin."
According to experts, “it is an excellent material, because the most frequent thing is to find a tooth, a canine, a phalanx, a piece of a long bone, but finding a complete skull with jaw is very interesting.”
Credit: Agencia CTyS-UNLaM
The giant bear belongs to the genus of the Arctotherium, among which is the largest specimen of the record. "This material from Junín surely corresponds to the late Pleistocene, with an age that does not exceed 120 thousand years, while giant bears of greater size existed in South America during the early Pleistocene, almost a million years ago."
The largest specimen known, belonging to the species Arctotherium angustidens, was a carnivore-omnivore that lived 780 thousand years ago and was discovered in the city of La Plata. "Since the middle of the Pleistocene, the bears were decreasing in size and, within their omnivorous diet, they were becoming a little more herbivores, but in comparison to the size of the current bears, this copy of Junín was also gigantic," said Dr. Soibelzon.
Credit: Agencia CTyS-UNLaM
“This practically complete skull is missing what would be the right cheekbone, the zygomatic arch and part of the maxilla; then, it has even the two mandibular branches, although it also lacks the piece that joins both mandibles,” Professor José María Marchetto, director of the Museo del Legado del Salado de Junín said.
For his part, Dr. Luciano Brambilla, a biologist at the National University of Rosario, agreed that "it is extraordinary to find a fossil bear, but strikingly, in Junín, another specimen had been found decades ago; it's as if two needles had been found in a haystack. "
Credit: Agencia CTyS-UNLaM
According to CTYS-UNLaM Agency, “last Friday, fragments of a phalanx and a metapodium were found - bones that are part of what would be the hand or leg of a saber-toothed tiger. The bear and saber-toothed tiger are presented as the most striking findings in the midst of a large number of fossils of herbivorous animals that continue to emerge in this site located northwest of Buenos Aires. There are remains of species that inhabited the Pampean region towards the end of the Pleistocene, until its extinction about 10 thousand years ago.”
Scientists are now working to ensure this site is declared a reserve. It is vital not only to protect the paleontological site, but also the flora and fauna of the place.
Original story here
AncientPages.com