Hephaestus (Hephaistos) – God Of Fire And Master Craftsman Constructed Talos, First Greek Robot And Divine Weapons Of The Gods
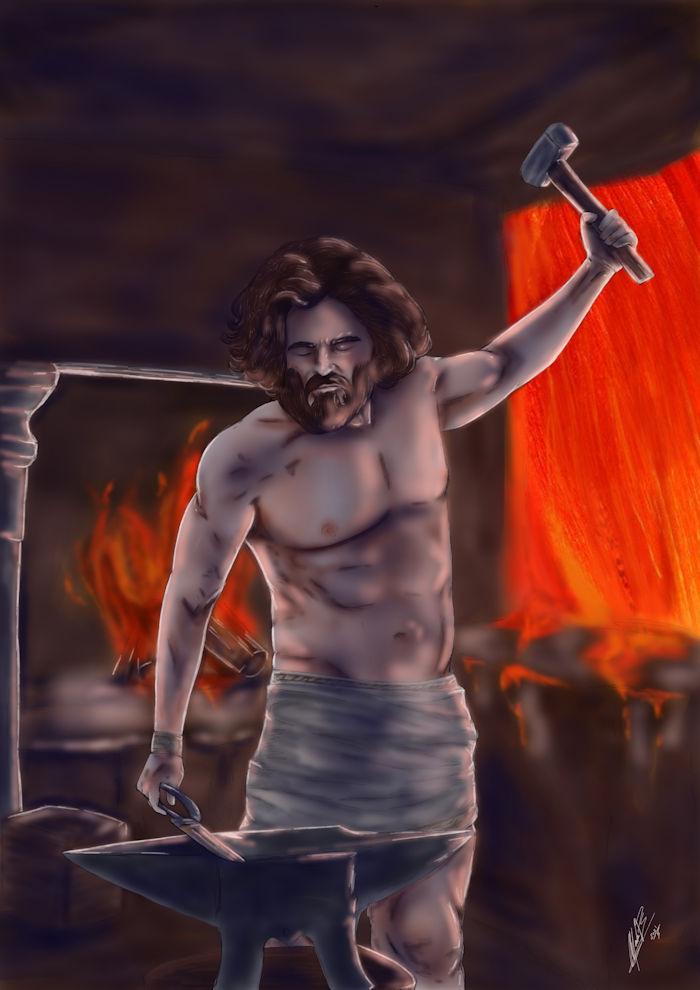
A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com - In Greek mythology, Hephaestus was the god of fire, divine blacksmith, inventor, and patron of crafts. He was often depicted with blacksmiths' attributes such as a sword, a hammer, or pincers. The cult of Hephaestus was based in Lemnos, a Greek island in the northern part of the Aegean Sea.
Hephaestus was the god of fire, divine blacksmith, inventor, and patron of crafts. Credit: Adobe Stock - Alejandro
In Roman mythology, he is Vulcan, and he also has his counterparts in Svarog, the Slavic god of celestial fire and patron of blacksmiths. He can also be compared to Wayland the Smith, widely known in Scandinavian, German, and Anglo-Saxon legends. As Hephaestus also Wayland was hurt badly, so he could not walk.
His supernatural skills and deep devotion to blacksmithing helped him make weapons, which "no blow could break," many ornaments of gold and silver, and other magical items.
Hephaestos Was Lame And Had A Sad Childhood
Hephaestos' life from the beginning was hard. No one was interested in celebrating the birth of Hephaestus, even his mother, Hera, who was a pre-Greek deity, the earth goddess of Argos, the sister-wife of Zeus. It is unclear whether Hephaestus was born lame or whether he was lamed.
Hera had awaited Hephaestus - child impatiently, hoping to see a beautiful and gifted child that would make her husband Zeus forget all his consorts and children he had with them. It should be mentioned that various ancient authors were uncertain whether Zeus was the father of Hephaestus. Many ancient literary sources say that Hera gave birth to Hephaestus on her own.
Though the identity of Hephaestus' parents is still a topic of discussion, most myths reveal this mighty blacksmith was credited with several incredible inventions.
According to one version of the story, when the baby was born, Hera was shocked because the child was ugly. She knew that such an ugly child would be more trouble for her than happiness, so she threw him from the residence of the gods, Mount Olympus, to Earth. The boy survived this fall because he was immortal and was found by Eurynome, one of the three thousand daughters of Okeanos and the Nereid Thetis.
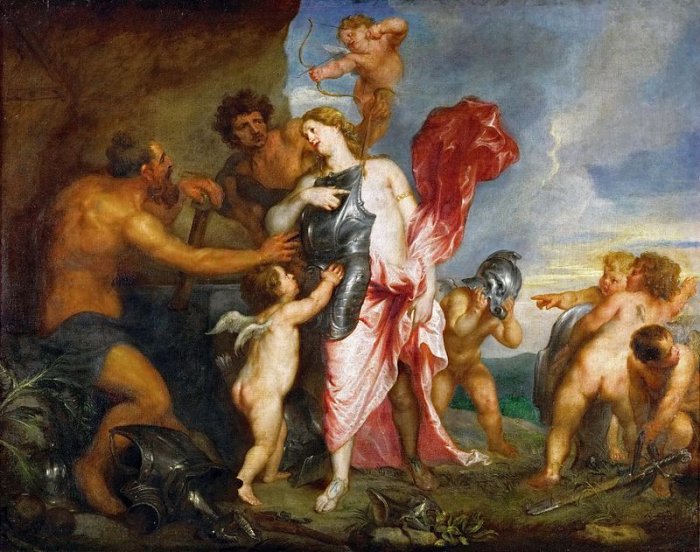
Thetis Receiving the Weapons of Achilles from Hephaestus by Anthony van Dyck (1630-1632). Credit: Public Domain
The goddesses nursed the young god, but unfortunately, the terrible fall had injured his legs and left him lame for the rest of his life. Raised by Eurynome and Thetis in secret, Hephaestus lived for nine years hidden away beneath the waters and spent his time perfecting his tools and creating formidable objects for the sea-nymphs, the only friends he had. He loved his work and blacksmithing, which were his great passion from a very young age, but he was also a vulnerable, angry young man with personal feelings. He knew Olympus rejected him.
Indeed, no one was waiting for him there, but he decided to return to rejoin his mother and take his rightful place among the Olympian gods.
Palace And Workshop Of Hephaestus
One day, his mother Hera saw the goddess Thetis wearing a beautiful necklace, and she learned Hephaestus had made it. She brought her earlier rejected son to Mount Olympus and arranged a palace and a workshop for him.
"His palace was said to have shone as brilliantly as the stars. Inside the palace was his workshop, where he made exquisite items for both humans and his fellow gods…" (Walsh Nicos, Greek Mythology).
Talos was an advanced ancient Greek robot - Credit: Adobe Stock: kuco
Hephaestus was still not treated equally, and his brothers and sisters looked down on him because he was a disabled god. It took a long time before Hephaestus was finally recognized for his incredible talent and honored in the family.
In later versions of Hephaestus' myth, his workspace was located within Mount Aetna in Sicily. Many believed that when the volcanoes of Sicily and Lemnos showed signs of activity, Hephaestus was busy with forging. It is also why Hephaestus was also considered the god of volcanoes.
Some myths say that the Cyclopes, great forgers themselves, worked as Hephaestus' assistants in his volcanic workshops.
Our earlier article wrote that "Talos" was the first ancient Greek robot. This fully operational machine was constructed by Hephaestus, who invented various automated devices, delicate jewelry, household machines, and developed techniques comparable to our modern technological achievements.
Among his many achievements were, for example, Zeus' thunderbolts, Eros's arrows, Achilles' shield described in Homer's "Iliad" and a "magical" helmet, so-called Hades' cap of invisibility, and he even fashioned the first woman from clay.
Updated on January 13, 2022
Written by – A. Sutherland AncientPages.com Senior Staff Writer
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
Expand for referencesCotterell, Arthur. A Dictionary of World Mythology
Sears K. From Gods and Goddesses to Monsters And Mortals
Hamilton, E. Mythology: Timeless Tales of Gods and Heroes
More From Ancient Pages
-
 Evidence Of Unusual Solar Activity Discovered On Ancient Cuneiform Tablets
Archaeology | Oct 16, 2019
Evidence Of Unusual Solar Activity Discovered On Ancient Cuneiform Tablets
Archaeology | Oct 16, 2019 -
 Silver Jewelry Buried In Leather Purse Discovered In Bulgaria
Archaeology | Apr 5, 2016
Silver Jewelry Buried In Leather Purse Discovered In Bulgaria
Archaeology | Apr 5, 2016 -
 Hypnos: God Of Sleep Who Owns Much Of Our Lives In Greek Mythology
Featured Stories | Mar 22, 2021
Hypnos: God Of Sleep Who Owns Much Of Our Lives In Greek Mythology
Featured Stories | Mar 22, 2021 -
 Sumerian ‘Mask Of Warka’ From Uruk: Sculptured Face May Depict Goddess Inanna
Featured Stories | Sep 15, 2016
Sumerian ‘Mask Of Warka’ From Uruk: Sculptured Face May Depict Goddess Inanna
Featured Stories | Sep 15, 2016 -
 Abduction Of Idun, Goddess-Keeper Of Golden Juvenile Apples In Norse Mythology
Featured Stories | Nov 16, 2019
Abduction Of Idun, Goddess-Keeper Of Golden Juvenile Apples In Norse Mythology
Featured Stories | Nov 16, 2019 -
 Shamash: Mesopotamian God Of Sun, Truth, Justice And Healing
Featured Stories | Jan 11, 2016
Shamash: Mesopotamian God Of Sun, Truth, Justice And Healing
Featured Stories | Jan 11, 2016 -
 Scientific Disagreement Over The Bronze Age Tin Ingots From The Uluburun Shipwreck
Archaeology | Sep 25, 2023
Scientific Disagreement Over The Bronze Age Tin Ingots From The Uluburun Shipwreck
Archaeology | Sep 25, 2023 -
 26,000-Year-Old Footprints In Chauvet Cave: Oldest Evidence Of Human-Canine Relationship
Featured Stories | Dec 29, 2016
26,000-Year-Old Footprints In Chauvet Cave: Oldest Evidence Of Human-Canine Relationship
Featured Stories | Dec 29, 2016 -
 Ancient Coffin Of Priest Psamtik, Son Of Osiris And Five Replicas Of Goddess Maat Sent On Upcoming Expo
Archaeology | Oct 5, 2021
Ancient Coffin Of Priest Psamtik, Son Of Osiris And Five Replicas Of Goddess Maat Sent On Upcoming Expo
Archaeology | Oct 5, 2021 -
 Never-Before-Seen Object Found In The Skull Of Powerful Ancient Ruler Raises Many Questions
Featured Stories | Nov 12, 2024
Never-Before-Seen Object Found In The Skull Of Powerful Ancient Ruler Raises Many Questions
Featured Stories | Nov 12, 2024 -
 Mystery Why Vikings Left Greenland Has Been Solved By Scientists
Archaeology | Mar 23, 2022
Mystery Why Vikings Left Greenland Has Been Solved By Scientists
Archaeology | Mar 23, 2022 -
 Did The Plague Of Athens Come From Egypt Or Is It A Myth?
Archaeology | Dec 13, 2023
Did The Plague Of Athens Come From Egypt Or Is It A Myth?
Archaeology | Dec 13, 2023 -
 Small House With Beautiful Mythical Frescoes Discovered In Pompeii
Archaeology | Nov 4, 2024
Small House With Beautiful Mythical Frescoes Discovered In Pompeii
Archaeology | Nov 4, 2024 -
 Ashur – First Capital And Powerful Religious Center Of The Assyrian Empire
Featured Stories | Jun 28, 2019
Ashur – First Capital And Powerful Religious Center Of The Assyrian Empire
Featured Stories | Jun 28, 2019 -
 The Tuli Mummy: Botswana’s Only Ancient Mummified Human Body Discovered So Far
Ancient History Facts | Oct 14, 2016
The Tuli Mummy: Botswana’s Only Ancient Mummified Human Body Discovered So Far
Ancient History Facts | Oct 14, 2016 -
 Unknown Purpose Of The Mysterious Huge Iron Age Ceramic Sharjah Jar Puzzles Scientists
Archaeology | Oct 7, 2022
Unknown Purpose Of The Mysterious Huge Iron Age Ceramic Sharjah Jar Puzzles Scientists
Archaeology | Oct 7, 2022 -
 Mysterious Relics Can Retrieve Leonardo da Vinci’s DNA And Provide New Information About The Great Renaissance Man
Archaeology | Apr 22, 2017
Mysterious Relics Can Retrieve Leonardo da Vinci’s DNA And Provide New Information About The Great Renaissance Man
Archaeology | Apr 22, 2017 -
 Yokai Hone-Onna (‘Skeleton Woman’): Deceptive Succubus That Feeds On Man’s Soul And Vitality In Japanese Folklore
Featured Stories | Jan 20, 2020
Yokai Hone-Onna (‘Skeleton Woman’): Deceptive Succubus That Feeds On Man’s Soul And Vitality In Japanese Folklore
Featured Stories | Jan 20, 2020 -
 Scotland’s Mysterious Ballachulish Figure Could Be Cailleach Bheithir – Ancient Hag Goddess Of Winds And Storms
Artifacts | Nov 23, 2018
Scotland’s Mysterious Ballachulish Figure Could Be Cailleach Bheithir – Ancient Hag Goddess Of Winds And Storms
Artifacts | Nov 23, 2018 -
 2,000-Year-Old Statue Of Priest’s Head Excavated In Laodicea On The Lycus
Archaeology | Dec 5, 2020
2,000-Year-Old Statue Of Priest’s Head Excavated In Laodicea On The Lycus
Archaeology | Dec 5, 2020



