Hephaestus (Hephaistos) – God Of Fire And Master Craftsman Constructed Talos, First Greek Robot And Divine Weapons Of The Gods
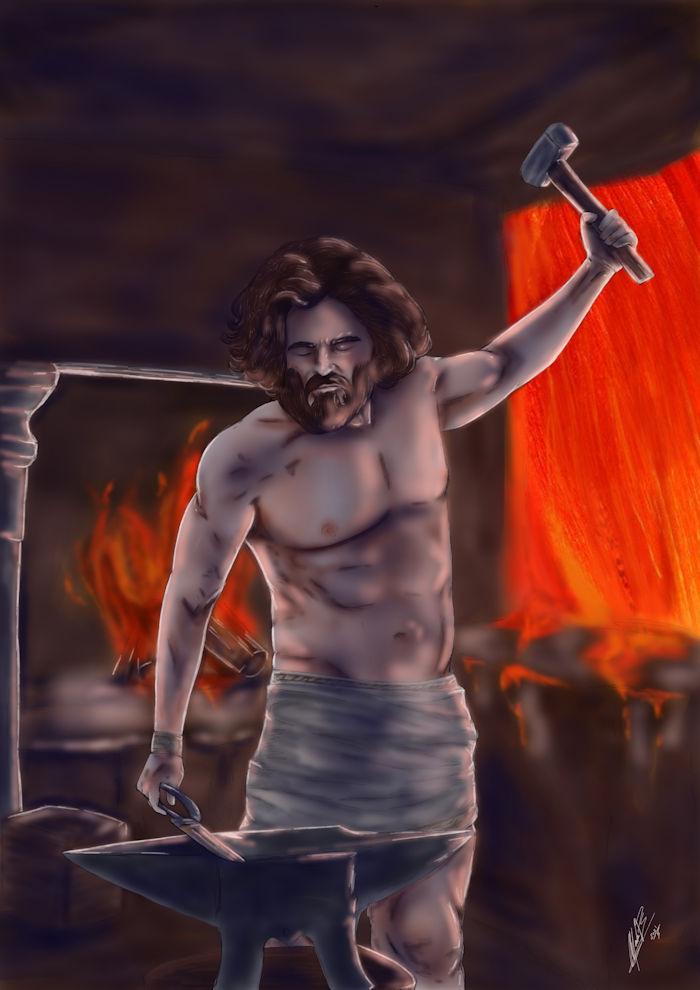
A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com - In Greek mythology, Hephaestus was the god of fire, divine blacksmith, inventor, and patron of crafts. He was often depicted with blacksmiths' attributes such as a sword, a hammer, or pincers. The cult of Hephaestus was based in Lemnos, a Greek island in the northern part of the Aegean Sea.
Hephaestus was the god of fire, divine blacksmith, inventor, and patron of crafts. Credit: Adobe Stock - Alejandro
In Roman mythology, he is Vulcan, and he also has his counterparts in Svarog, the Slavic god of celestial fire and patron of blacksmiths. He can also be compared to Wayland the Smith, widely known in Scandinavian, German, and Anglo-Saxon legends. As Hephaestus also Wayland was hurt badly, so he could not walk.
His supernatural skills and deep devotion to blacksmithing helped him make weapons, which "no blow could break," many ornaments of gold and silver, and other magical items.
Hephaestos Was Lame And Had A Sad Childhood
Hephaestos' life from the beginning was hard. No one was interested in celebrating the birth of Hephaestus, even his mother, Hera, who was a pre-Greek deity, the earth goddess of Argos, the sister-wife of Zeus. It is unclear whether Hephaestus was born lame or whether he was lamed.
Hera had awaited Hephaestus - child impatiently, hoping to see a beautiful and gifted child that would make her husband Zeus forget all his consorts and children he had with them. It should be mentioned that various ancient authors were uncertain whether Zeus was the father of Hephaestus. Many ancient literary sources say that Hera gave birth to Hephaestus on her own.
Though the identity of Hephaestus' parents is still a topic of discussion, most myths reveal this mighty blacksmith was credited with several incredible inventions.
According to one version of the story, when the baby was born, Hera was shocked because the child was ugly. She knew that such an ugly child would be more trouble for her than happiness, so she threw him from the residence of the gods, Mount Olympus, to Earth. The boy survived this fall because he was immortal and was found by Eurynome, one of the three thousand daughters of Okeanos and the Nereid Thetis.
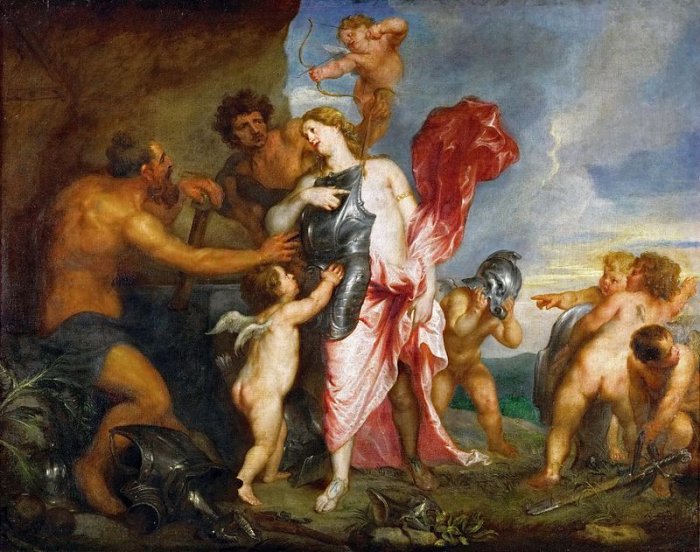
Thetis Receiving the Weapons of Achilles from Hephaestus by Anthony van Dyck (1630-1632). Credit: Public Domain
The goddesses nursed the young god, but unfortunately, the terrible fall had injured his legs and left him lame for the rest of his life. Raised by Eurynome and Thetis in secret, Hephaestus lived for nine years hidden away beneath the waters and spent his time perfecting his tools and creating formidable objects for the sea-nymphs, the only friends he had. He loved his work and blacksmithing, which were his great passion from a very young age, but he was also a vulnerable, angry young man with personal feelings. He knew Olympus rejected him.
Indeed, no one was waiting for him there, but he decided to return to rejoin his mother and take his rightful place among the Olympian gods.
Palace And Workshop Of Hephaestus
One day, his mother Hera saw the goddess Thetis wearing a beautiful necklace, and she learned Hephaestus had made it. She brought her earlier rejected son to Mount Olympus and arranged a palace and a workshop for him.
"His palace was said to have shone as brilliantly as the stars. Inside the palace was his workshop, where he made exquisite items for both humans and his fellow gods…" (Walsh Nicos, Greek Mythology).
Talos was an advanced ancient Greek robot - Credit: Adobe Stock: kuco
Hephaestus was still not treated equally, and his brothers and sisters looked down on him because he was a disabled god. It took a long time before Hephaestus was finally recognized for his incredible talent and honored in the family.
In later versions of Hephaestus' myth, his workspace was located within Mount Aetna in Sicily. Many believed that when the volcanoes of Sicily and Lemnos showed signs of activity, Hephaestus was busy with forging. It is also why Hephaestus was also considered the god of volcanoes.
Some myths say that the Cyclopes, great forgers themselves, worked as Hephaestus' assistants in his volcanic workshops.
Our earlier article wrote that "Talos" was the first ancient Greek robot. This fully operational machine was constructed by Hephaestus, who invented various automated devices, delicate jewelry, household machines, and developed techniques comparable to our modern technological achievements.
Among his many achievements were, for example, Zeus' thunderbolts, Eros's arrows, Achilles' shield described in Homer's "Iliad" and a "magical" helmet, so-called Hades' cap of invisibility, and he even fashioned the first woman from clay.
Updated on January 13, 2022
Written by – A. Sutherland AncientPages.com Senior Staff Writer
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
Expand for referencesCotterell, Arthur. A Dictionary of World Mythology
Sears K. From Gods and Goddesses to Monsters And Mortals
Hamilton, E. Mythology: Timeless Tales of Gods and Heroes
More From Ancient Pages
-
 On This Day In History: Mount Tambora Volcano Begins A Three-Month-Long Eruption – On Apr 10, 1815
News | Apr 10, 2017
On This Day In History: Mount Tambora Volcano Begins A Three-Month-Long Eruption – On Apr 10, 1815
News | Apr 10, 2017 -
 4,000 Years Ago Women Of El Argar Used Their Teeth As Tools
Archaeology | Nov 10, 2020
4,000 Years Ago Women Of El Argar Used Their Teeth As Tools
Archaeology | Nov 10, 2020 -
 Mysterious Osirion Of Abydos Egypt – Was It An Ancient Energy Plant?
Featured Stories | Feb 26, 2020
Mysterious Osirion Of Abydos Egypt – Was It An Ancient Energy Plant?
Featured Stories | Feb 26, 2020 -
 Family Looking For Lost Gold Ring Finds Viking Age Artifacts In Their Garden On The Island Of Jomfruland
Archaeology | Sep 30, 2023
Family Looking For Lost Gold Ring Finds Viking Age Artifacts In Their Garden On The Island Of Jomfruland
Archaeology | Sep 30, 2023 -
 Oldest Known Spearthrowers Found At 31,000-Year-Old Archaeological Site Of Maisières-Canal
Archaeology | Nov 6, 2023
Oldest Known Spearthrowers Found At 31,000-Year-Old Archaeological Site Of Maisières-Canal
Archaeology | Nov 6, 2023 -
 Fascinating 3,000-Year-Old Artifacts Found At Herne Bay, Kent, UK
Archaeology | Jun 24, 2022
Fascinating 3,000-Year-Old Artifacts Found At Herne Bay, Kent, UK
Archaeology | Jun 24, 2022 -
 Mysterious Bones May Re-Write History Of North America – Humans Were Present On The Continent 10 Times Earlier
Archaeology | May 8, 2017
Mysterious Bones May Re-Write History Of North America – Humans Were Present On The Continent 10 Times Earlier
Archaeology | May 8, 2017 -
 Being A Roman Emperor Was Dangerous – Only One Of Four Died Of Natural Causes
Archaeology | Nov 12, 2021
Being A Roman Emperor Was Dangerous – Only One Of Four Died Of Natural Causes
Archaeology | Nov 12, 2021 -
 Oldest Case Of A Rare Genetic Condition Discovered
Archaeology | Aug 27, 2022
Oldest Case Of A Rare Genetic Condition Discovered
Archaeology | Aug 27, 2022 -
 William The Conqueror: Ruthless And Powerful Ruler Who Changed Britain Forever
Featured Stories | Feb 25, 2023
William The Conqueror: Ruthless And Powerful Ruler Who Changed Britain Forever
Featured Stories | Feb 25, 2023 -
 Is The Puzzling Miami Circle Much Older Than Previously Thought?
Featured Stories | Mar 14, 2021
Is The Puzzling Miami Circle Much Older Than Previously Thought?
Featured Stories | Mar 14, 2021 -
 Mysterious Ancient ‘Triangle Code’ And Curious Markings Discovered On Vessels In Israel Reveal Something Interesting
Archaeology | Feb 11, 2019
Mysterious Ancient ‘Triangle Code’ And Curious Markings Discovered On Vessels In Israel Reveal Something Interesting
Archaeology | Feb 11, 2019 -
 Chilling Graffiti Found In 1,600-Year-Old Roman Prison In Corinth, Greece
Archaeology | Aug 19, 2024
Chilling Graffiti Found In 1,600-Year-Old Roman Prison In Corinth, Greece
Archaeology | Aug 19, 2024 -
 Mysterious Ancient Figure Depicted On A Jade Cong May Re-Write History Of China
Artifacts | Oct 11, 2019
Mysterious Ancient Figure Depicted On A Jade Cong May Re-Write History Of China
Artifacts | Oct 11, 2019 -
 Rare 1,400-Year-Old Temple Possibly Used By East Anglian Kings Discovered In Suffolk, UK
Archaeology | Nov 22, 2023
Rare 1,400-Year-Old Temple Possibly Used By East Anglian Kings Discovered In Suffolk, UK
Archaeology | Nov 22, 2023 -
 Half-A-Million Year Old Signs Of Extinct Human Species Discovered In Polish Cave
Archaeology | Nov 30, 2022
Half-A-Million Year Old Signs Of Extinct Human Species Discovered In Polish Cave
Archaeology | Nov 30, 2022 -
 The 426-Km-Long Roman Aqueduct Provided Water For Constantinople – New Study
Archaeology | May 11, 2021
The 426-Km-Long Roman Aqueduct Provided Water For Constantinople – New Study
Archaeology | May 11, 2021 -
 Ancient Children Played Marbles Thousands Of Years Ago
Ancient History Facts | May 22, 2019
Ancient Children Played Marbles Thousands Of Years Ago
Ancient History Facts | May 22, 2019 -
 Olmec Civilization Remains An Intriguing Ancient Puzzle
Civilizations | Feb 2, 2017
Olmec Civilization Remains An Intriguing Ancient Puzzle
Civilizations | Feb 2, 2017 -
 Lost Since 1362: Researchers Discover The Church Of Rungholt – A Sunken Medieval Trading Place
Archaeology | May 25, 2023
Lost Since 1362: Researchers Discover The Church Of Rungholt – A Sunken Medieval Trading Place
Archaeology | May 25, 2023



