DNA Study Of Controversial Ancient North American Mummies, Including The Spirit Cave Mummy Opens An Extraordinary Chapter In Human History
AncientPages.com - Scientists can learn a lot by examining DNA of ancient skeletons, but sometimes it’s easier said than done. It’s not always possible to get permission to study all ancient skeletons.
A legal battle over the 'Spirit Cave Mummy', a 10,600-year-old ancient skeleton called has ended after advanced DNA sequencing found it was related to a Native American tribe.
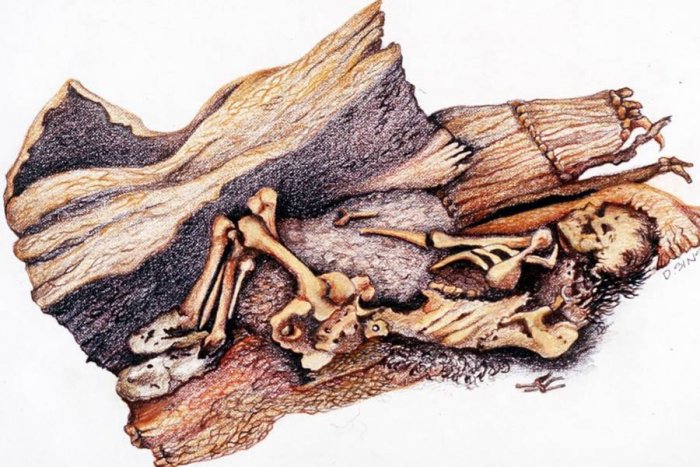
Discovered in 1940, in Spirit Cave, some miles northeast of Fallon, Nevada, the Spirit Cave Mummy is today recognized as the oldest human mummy found in North America.
A drawing of the remains of the 10,600-year-old "Spirit Cave Mummy" found in a rock shelter near Fallon, Nevada, in 1940. Credit: AP
It has now been announced an international team of researchers have genetically analyzed the DNA of a series of famous and controversial ancient remains across North and South America including Spirit Cave, the Lovelock skeletons, the Lagoa Santa remains, an Inca mummy, and the oldest remains in Chilean Patagonia. The study also looked at the second oldest human remains from Trail Creek Cave in Alaska—a 9,000-year-old milk tooth from a young girl.
Did Paleoamericans Exist In North America Before Native Americans?
Scientists sequenced 15 ancient genomes spanning from Alaska to Patagonia and were able to track the movements of the first humans as they spread across the Americas at "astonishing" speed during the Ice Age, and also how they interacted with each other in the following millennia.
The team of academics not only discovered that the Spirit Cave remains—the world's oldest natural mummy—was a Native American but they were able to dismiss a longstanding theory that a group called Paleoamericans existed in North America before Native Americans.
The ground-breaking research also discovered clues of a puzzling Australasian genetic signal in the 10,400-year-old Lagoa Santa remains from Brazil revealing a previously unknown group of early South Americans—but the Australasian link left no genetic trace in North America. It was described by one of the scientists as 'extraordinary evidence of an extraordinary chapter in human history'.
Professor Eske Willerslev, who holds positions both at St John's College, University of Cambridge, and the University of Copenhagen, and led the study, said: "Spirit Cave and Lagoa Santa were very controversial because they were identified as so-called 'Paleoamericans' based on craniometry—it was determined that the shape of their skulls was different to current day Native Americans. Our study proves that Spirit Cave and Lagoa Santa were actually genetically closer to contemporary Native Americans than to any other ancient or contemporary group sequenced to date."
The Lagoa Santa remains were retrieved by Danish explorer Peter W. Lund in the 19th century and his work led to this 'Paleoamerican hypothesis' based on cranial morphology that theorized the famous group of skeletons could not be Native Americans. But this new study disproves that theory
He added: "Looking at the bumps and shapes of a head does not help you understand the true genetic ancestry of a population—we have proved that you can have people who look very different but are closely related."
The scientific and cultural significance of the Spirit Cave remains, which were found in 1940 in a small rocky alcove in the Great Basin Desert, was not properly understood for 50 years. The preserved remains of the man in his forties were initially believed to be between 1,500 and 2000 years old, but during the 1990s new textile and hair testing dated the skeleton at 10,600 years old.
The Fallon Paiute-Shoshone Tribe, a group of Native Americans based in Nevada near Spirit Cave, claimed cultural affiliation with the skeleton and requested immediate repatriation of the remains under the Native American Graves Protection and Repatriation Act.
The request was refused because the ancestry was disputed, the tribe sued the federal government and the lawsuit pitted tribal leaders against anthropologists, who argued the remains provided invaluable insights into North America's earliest inhabitants and should continue to be displayed in a museum.
The deadlock continued for 20 years until the tribe agreed that Professor Willerslev could carry out genome sequencing on DNA extracted from the Spirit Cave for the first time.
Professor Willerslev said: "I assured the tribe that my group would not do the DNA testing unless they gave permission and it was agreed that if Spirit Cave was genetically a Native American the mummy would be repatriated to the tribe."
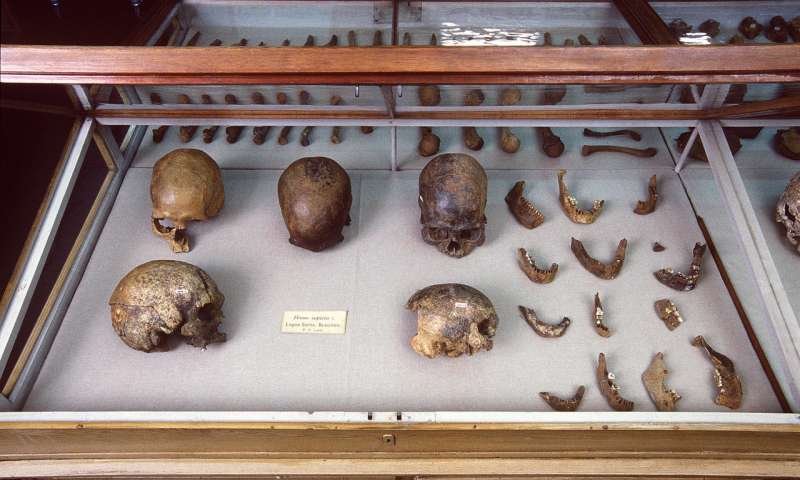
Skulls and other human remains from P.W. Lund's Collection from Lagoa Santa, Brazil kept in the Natural History Museum of Denmark. Credit: Natural History Museum of Denmark
The team painstakingly extracted DNA from the petrus bone from the inside of the skull proving that the skeleton was an ancestor of present day Native Americans. Spirit Cave was returned to the tribe in 2016 and there was a private reburial ceremony earlier this year that Professor Willerslev attended and details have just been released.
The geneticist explained: "What became very clear to me was that this was a deeply emotional and deeply cultural event. The tribe have real feelings for Spirit Cave, which as a European it can be hard to understand but for us it would very much be like burying our mother, father, sister or brother.
"We can all imagine what it would be like if our father or mother was put in an exhibition and they had that same feeling for Spirit Cave. It has been a privilege to work with them."
Surprising Traces Of Australasian Ancestry In Ancient South American Native Americans
The tribe were kept informed throughout the two year project and two members visited the lab in Copenhagen to meet the scientists and they were present when all of the DNA sampling was taken.
A statement from the Fallon Paiute-Shoshone Tribe, said: "The Tribe has had a lot of experience with members of the scientific community, mostly negative. However, there are a handful of scientists that seemed to understand the Tribe's perspective and Eske Willerslev was one of them.
"He took the time to acquaint himself with the Tribe, kept us well-informed of the process, and was available to answer our questions. His new study confirms what we have always known from our oral tradition and other evidence—that the man taken from his final resting place in Spirit Cave is our Native American ancestor."
The genome of the Spirit Cave skeleton has wider significance because it not only settled the legal and cultural dispute between the tribe and the Government, it also helped reveal how ancient humans moved and settled across the Americas. The scientists were able to track the movement of populations from Alaska to as far south as Patagonia. They often separated from each other and took their chances travelling in small pockets of isolated groups.
Dr. David Meltzer, from the Department of Anthropology, Southern Methodist University, Dallas, said: "A striking thing about the analysis of Spirit Cave and Lagoa Santa is their close genetic similarity which implies their ancestral population travelled through the continent at astonishing speed.
That's something we've suspected due to the archaeological findings, but it's fascinating to have it confirmed by the genetics. These findings imply that the first peoples were highly skilled at moving rapidly across an utterly unfamiliar and empty landscape. They had a whole continent to themselves and they were travelling great distances at breath-taking speed."
The study also revealed but no Australasian genetic link was found in North American Native Americans.
"We discovered the Australasian signal was absent in Native Americans prior to the Spirit Cave and Lagoa Santa population split which means groups carrying this genetic signal were either already present in South America when Native Americans reached the region, or Australasian groups arrived later.
That this signal has not been previously documented in North America implies that an earlier group possessing it had disappeared or a later arriving group passed through North America without leaving any genetic trace," Dr. Victor Moreno-Mayar, from the Centre for GeoGenetics, University of Copenhagen and first author of the study said in a press statement.
Dr. Peter de Barros Damgaard, from the Centre for GeoGenetics, University of Copenhagen, explained why scientists remain puzzled but optimistic about the Australasian ancestry signal in South America.
See also:
Ancient DNA Reveals Unknown Genetic Exchanges Between North And South America
DNA Study Reveals 250 Siberians Became The First Native American Population
North America Was Settled By Previously Unknown People – DNA From A 11,500-Year-Old Skeleton Reveals
He explained: "If we assume that the migratory route that brought this Australasian ancestry to South America went through North America, either the carriers of the genetic signal came in as a structured population and went straight to South America where they later mixed with new incoming groups, or they entered later. At the moment we cannot resolve which of these might be correct, leaving us facing extraordinary evidence of an extraordinary chapter in human history! But we will solve this puzzle."
The population history during the millennia that followed initial settlement was far more complex than previously thought. The peopling of the Americas had been simplified as a series of north to south population splits with little to no interaction between groups after their establishment.
The new genomic analysis presented in the study has shown that around 8,000 years ago, Native Americans were on the move again, but this time from Mesoamerica into both North and South America.
Researchers found traces of this movement in the genomes of all present-day indigenous populations in South America for which genomic data is available to date.
Dr. Moreno-Mayar added: "The older genomes in our study not only taught us about the first inhabitants in South America, but also served as a baseline for identifying a second stream of genetic ancestry, which arrived from Mesoamerica in recent millennia and that is not evident from the archaeological record.
These Mesoamerican peoples mixed with the descendants of the earliest South Americans and gave rise to most contemporary groups in the region."
AncientPages.com