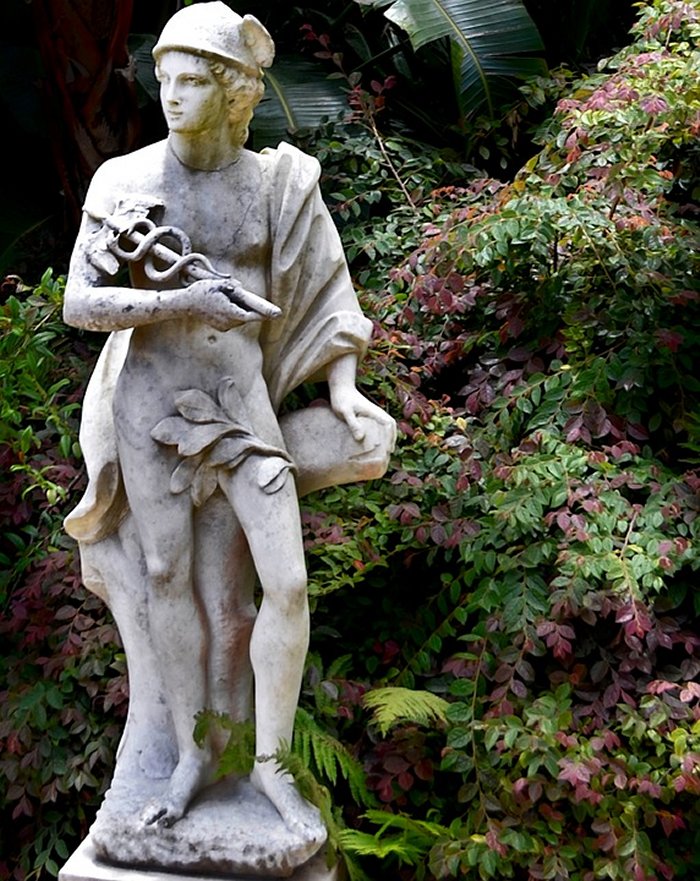
Hermes – Divine Trickster, Psychopomp, Patron Of Merchants And Thieves In Greek Mythology
A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com - In Greek mythology, Hermes (Roman name: Mercury) was the emissary and messenger of the gods, the patron of shepherds and their flocks and wanderers. Hermes guarded the roads as the patron of merchants and thieves, making them safe from dangers for all passing travelers.
Greek god Hermes. Image credit: aszak - Pixabay
Like the Egyptian god Anubis, he is a psychopomp responsible for escorting newly deceased souls to the afterlife.
As the patron of commerce and merchants, Hermes was supposed to be the promoter of intercourse among nations and a skilled mediator between merchant and customer. With these skills, he was a bringer of wealth in business.
Besides many divine characteristics, Hermes has a weakness that makes him a more human-like figure. For instance, he likes to steal, and this impulse has followed him since infancy. He was the one who could quickly settle disputes thanks to his gift of eloquent speech and moved freely between the worlds of the mortal and divine.
In some myths, he is a trickster god who outsmarts other gods for his satisfaction; it is one of his characteristics that he reminds of Norse God Loki.
Birth And Family Of Hermes
He was born in a cave on Mount Cyllene in Arcadia, southern Greece. His parents were Zeus, the King of the Gods, and Maia, a daughter of the Titan Atlas and one of the Pleiades.
God council in Olympus: Hermes with his mother Maia. Detail of the side B of an Attic red-figure belly-amphora, ca. 500 BC. (Nikoxenos Painter). Image credit: Bibi Saint-Pol/Wikipedia
Hermes did not have a wife, but he had children. According to one account, he was considered the father of Odysseus's grandfather Autolycus, who was conceived when Hermes had intercourse with the virgin Chione. With the goddess Aphrodite, he had a son Hermaphroditos (Hermaphroditus), known as the deity of unions, marriage, sexuality, and fertility.
According to some versions, Hermes and Penelope became closer, and the fruity of this relationship was the god, Pan.
Appearance Of Hermes And His Attributes
Hermes was a young man, wearing traveling clothes, a flat hat known as "petasus," and winged sandals on his feet. Often, he was depicted having wings attached to his shoulders and cap.
He usually held a caduceus, a winged staff with snakes wrapped around it, in his hands so he could gain access everywhere. This staff helped Hermes to charm the gods or to wake up those who the god of sleep tamed.
Later, he was depicted as a very young boy or sometimes an elder, bearded man with the lamb thrown over his back. His other attributes were a broad hat of a wanderer covering the face, a cape, winged sandals on his feet, a palm tree, turtle, rooster, goat, the number four, several kinds of fish, and incense. Sacrifices included honey, pigs, goats, lambs, and cakes.
Hermes, The God's Messenger And Conductor Of Souls
Wearing wings on his sandals, Hermes was the speediest of all Greek gods. He enjoyed his popularity among all the Greek gods and spirits. Because of his speed, Hermes received the role of the messenger and conductor of souls to the Underworld. He was the only Olympian god authorized to visit Heaven, Earth, and the Underworld.
Statue of God Hermes. Credit: Stock photo
As the messenger of the gods, Hermes – "the divine trickster" - was sent to many places; he was, among others, at Troy, at the court of Paris, accompanying three goddesses on Mount Ida in Phrygia.
According to Carl Jung, a Swiss psychiatrist and psychoanalyst who founded analytical psychology, Hermes's role as messenger between realms and as a guide to the Underworld made him the master of the unconscious, the mediator between the conscious and unconscious parts of the mind.
Worship Of Hermes Across The Whole Greece
Originally, Hermes was worshiped in the form of piles of stones, placed along the roads and their intersections to protect travelers from dangers. Hermes was venerated as a god of nature, farmers, and herdmen in remote areas of Greece.
One of Hermes's oldest places of worship was Mount Cyllene in Arcadia, where he was born. The first temple dedicated to him was where the myth says he was born. Tradition says that by the end of the fifth century BC, Hermes had acquired many cult names and activities.
In the Hellenistic era, worship of the Greek god Hermes was combined with the cult of the Egyptian god Thoth, which gave rise to the cult of Hermes Trismegistus ("thrice-greatest Hermes").
As such, Hermes played his role in later esoteric cults.
Updated on August 24, 2022
Written by – A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com Senior Staff Writer
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
Expand for referencesMore From Ancient Pages
-
 Unexplained Cases Of Holographic Projections In Ancient And Modern Times
Featured Stories | Sep 14, 2018
Unexplained Cases Of Holographic Projections In Ancient And Modern Times
Featured Stories | Sep 14, 2018 -
 Civita di Bagnoregio – Magnificent 2,500-Year-Old Etruscan City In The Sky Is Struggling To Survive
Featured Stories | Jun 23, 2021
Civita di Bagnoregio – Magnificent 2,500-Year-Old Etruscan City In The Sky Is Struggling To Survive
Featured Stories | Jun 23, 2021 -
 What Was Lex Salica?
Ancient History Facts | Dec 13, 2017
What Was Lex Salica?
Ancient History Facts | Dec 13, 2017 -
 On This Day In History: Magellan’s Expedition Circumnavigates Globe – On Sep 6, 1522
News | Sep 6, 2016
On This Day In History: Magellan’s Expedition Circumnavigates Globe – On Sep 6, 1522
News | Sep 6, 2016 -
 Chocolate Was A ‘Hot Property’ In 17th Century England And There Were Rules For Safe Consumption
Featured Stories | Jun 27, 2018
Chocolate Was A ‘Hot Property’ In 17th Century England And There Were Rules For Safe Consumption
Featured Stories | Jun 27, 2018 -
 Peterborough Petroglyphs Could Offer Evidence Ancient Celts Visited Canada 2,000 Years Ago
Archaeology | May 27, 2015
Peterborough Petroglyphs Could Offer Evidence Ancient Celts Visited Canada 2,000 Years Ago
Archaeology | May 27, 2015 -
 Ancient Secrets Of Karelia: Mysterious Vottovaara Mountain Was Sacred To The Sami People
Featured Stories | Apr 5, 2017
Ancient Secrets Of Karelia: Mysterious Vottovaara Mountain Was Sacred To The Sami People
Featured Stories | Apr 5, 2017 -
 A 500-Year-Old Stolen Copy Of da Vinci’s “Salvator Mundi” Painting – Found By Italian Police
News | Jan 20, 2021
A 500-Year-Old Stolen Copy Of da Vinci’s “Salvator Mundi” Painting – Found By Italian Police
News | Jan 20, 2021 -
 What Was On The Menu For Stonehenge’s Builders, 2500 BC? Milk, Yoghurt And Cheese Only Eaten In Exclusive Ceremonies
Archaeology | Oct 14, 2015
What Was On The Menu For Stonehenge’s Builders, 2500 BC? Milk, Yoghurt And Cheese Only Eaten In Exclusive Ceremonies
Archaeology | Oct 14, 2015 -
 Analysis Of Ancient Tools Challenges Long-Held Ideas About What Drove Major Changes In Ancient Greek Society
Archaeology | Aug 23, 2022
Analysis Of Ancient Tools Challenges Long-Held Ideas About What Drove Major Changes In Ancient Greek Society
Archaeology | Aug 23, 2022 -
 ‘Arcade’ Of Ancient Mancala Game Boards Carved On Rocks Found In Lewa Wildlife Conservancy, Kenya
Archaeology | Feb 2, 2024
‘Arcade’ Of Ancient Mancala Game Boards Carved On Rocks Found In Lewa Wildlife Conservancy, Kenya
Archaeology | Feb 2, 2024 -
 Were Neanderthals Really As Well Adapted To A Life In The Cold As Previously Assumed? New Study
Archaeology | Apr 26, 2022
Were Neanderthals Really As Well Adapted To A Life In The Cold As Previously Assumed? New Study
Archaeology | Apr 26, 2022 -
 More Greek Gods’ Heads And A Life-Sized Statue Of A Man Unearthed In The Ancient City Of Aizanoi
Archaeology | Dec 28, 2022
More Greek Gods’ Heads And A Life-Sized Statue Of A Man Unearthed In The Ancient City Of Aizanoi
Archaeology | Dec 28, 2022 -
 Prehistoric Sime Skeleton And Now 15,000-Year-Old Bone Pendant Depicting ‘Venus’ Found In Vlakno Cave, Croatia
Archaeology | Dec 4, 2017
Prehistoric Sime Skeleton And Now 15,000-Year-Old Bone Pendant Depicting ‘Venus’ Found In Vlakno Cave, Croatia
Archaeology | Dec 4, 2017 -
 3,000-Year-Old Female Statue Unearthed In Turkey
Archaeology | Aug 11, 2017
3,000-Year-Old Female Statue Unearthed In Turkey
Archaeology | Aug 11, 2017 -
 Hundreds Of Undiscovered Roman Forts Revealed By Spy Satellites
Archaeology | Oct 27, 2023
Hundreds Of Undiscovered Roman Forts Revealed By Spy Satellites
Archaeology | Oct 27, 2023 -
 Huge Defensive Wall Excavated At Tel Erani, Israel Is More Than 5,300 Years Old
Archaeology | Sep 12, 2019
Huge Defensive Wall Excavated At Tel Erani, Israel Is More Than 5,300 Years Old
Archaeology | Sep 12, 2019 -
 Precious Lost Ancient Book Of Wisdom Could Solve Biblical Mysteries
Artifacts | Nov 26, 2018
Precious Lost Ancient Book Of Wisdom Could Solve Biblical Mysteries
Artifacts | Nov 26, 2018 -
 Egyptian Necropolis Of Asyut And Funerary Culture That Dates Back To Old Kingdom
Archaeology | Feb 24, 2020
Egyptian Necropolis Of Asyut And Funerary Culture That Dates Back To Old Kingdom
Archaeology | Feb 24, 2020 -
 Ancient DNA Reveals The Earliest Evidence Of The Last Massive Human Migration To Western Europe
DNA | Jul 24, 2023
Ancient DNA Reveals The Earliest Evidence Of The Last Massive Human Migration To Western Europe
DNA | Jul 24, 2023



