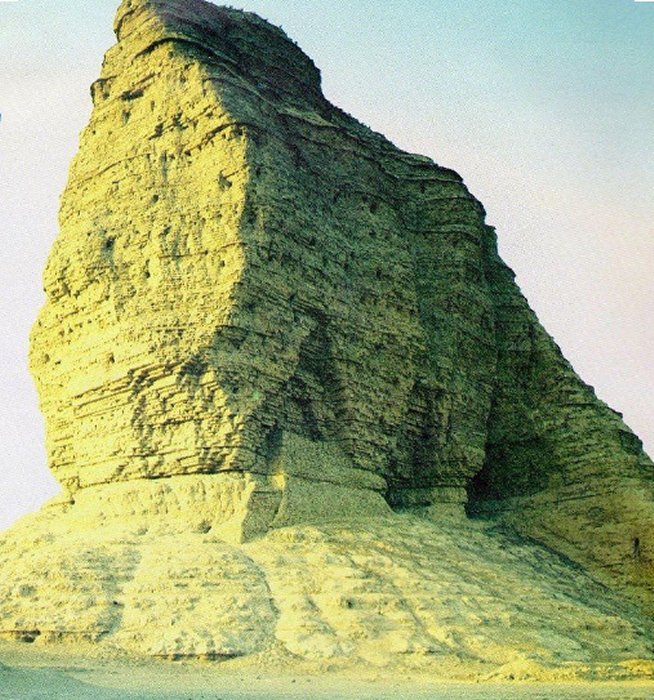
Ancient Ziggurat Of Aqar Quf Dedicated To God Enlil
A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com - Aqar Quf, currently an archaeological site of the ancient city of Dur Kurigalzu (or the “Fortress of Kurigalzu”) is located in central Iraq, 30 km northwest of Baghdad, on the left bank of the Euphrates.
It was founded in the 14/15th century BC by the Kassite King Kurigalzu I, (c. 1400–c. 1375) and later the city was several times controlled by the Assyrians and Elamites and in the middle of the 11th-century, BC destroyed by the Syrians.
The ziggurat at Aqar Quf rises 180 feet above the desert west of Baghdad. Image credit: Spc. David Robbins - Working to Restore Iraq's Past for the Future - CC0
The ancient site, which was made up of several tells, was the capital of Babylonia during the reign of the Kassite dynasty (ca. 1600 BC – 1155 BC). After the fall of the Kassite Dynasty, the city was abandoned by the late 14th century AD.
Around the 1940s, an Iraqi and British team led by Taha Baqir and Seton Lloyd found approximately a hundred clay tablets and fragments of a statue decorated with texts in Sumerian. It is a representation of the Kassite King Kurigalzi, who reigned over all of Mesopotamia from his city of Kurigalzu.
Additionally, excavations revealed the ruins of Aqar Quf ziggurat, approximately 3,500 years old. The lowest terrace of the ziggurat ruins was restored and the structure’s foundations are 69 by 67.6 meters.
The ziggurat - dedicated to the god Enlil - is an unusually well-preserved building, with a mud-brick core that still stands to a height of about 170 feet on the flat plain in the vicinity of Baghdad. Other structures included three temples and a palace, where the walls of the corridors, were found decorated with numerous male figures (perhaps court dignitaries), and several sanctuaries.
 Cylinder seal of Kassite king Kurigalzu II (c. 1332–1308 BC). Louvre Museum AOD 105. source
Cylinder seal of Kassite king Kurigalzu II (c. 1332–1308 BC). Louvre Museum AOD 105. source
Interestingly, archaeologists also stumbled upon the remains of another place, which existed there at least a century earlier and was probably called Daksa or Parsa.
At its peak, the city with several ramparts, extended over an area of 225 ha.
The original homeland of the Kassites is not well-known, but appears to have been located in the Zagros Mountains, (now the Lorestan Province of Iran).
The ziggurat of Dur-Kurigalzu was built in the 14th BC by the Kassites’ king Kurigalzu. The central structure is composed of sun-dried bricks. Source
They were a warlike people that invaded Babylon during the 16th century BC and ruled the area for almost six centuries. It is claimed that their rule was the longest in the history of ancient Babylon.
The Kassites were powerful rulers and their royal cities were powerful as well. In addition to Babylon and Dur-Kurigalzu (Aqar Quf), the almost equal city of Nippur was the most important provincial center. Nippur once virtually abandoned c. 1730 BC, but later rebuilt in the Kassite period, as well as Larsa, Susa, and Sippar.
Among the achievements of the art associated with the rule of the Kassites, is the production of modeled bricks. From it, temples decorated with a frieze from burnt brick were erected. This technique was later taken over by the builders from the New-Babylonian period and by the Persians.
Their capital city, Dur-Kurigalzu, was destroyed around the 12th century by the Elamites and the city was burned.
Written by – A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com Senior Staff Writer
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
Expand for referencesMore From Ancient Pages
-
 Maya Site With At Least 300 Buildings Some Of Which Are Over 8 Meters High – Discovered
Archaeology | Sep 16, 2022
Maya Site With At Least 300 Buildings Some Of Which Are Over 8 Meters High – Discovered
Archaeology | Sep 16, 2022 -
 This Ancient Roman Painting Survived Eruption Of Mount Vesuvius In 79 A.D.
Archaeology | Aug 21, 2017
This Ancient Roman Painting Survived Eruption Of Mount Vesuvius In 79 A.D.
Archaeology | Aug 21, 2017 -
 Ördög – Shapeshifting Demon Who Controls The Evil And Dark Forces In The World
Featured Stories | Oct 23, 2019
Ördög – Shapeshifting Demon Who Controls The Evil And Dark Forces In The World
Featured Stories | Oct 23, 2019 -
 South American Cultures Quickly Adopted Horses – New Study
Archaeology | Dec 26, 2023
South American Cultures Quickly Adopted Horses – New Study
Archaeology | Dec 26, 2023 -
 Has The Mystery Of The 11,000-Year-Old Amazonian Rock Art Been Solved?
Places | Nov 15, 2024
Has The Mystery Of The 11,000-Year-Old Amazonian Rock Art Been Solved?
Places | Nov 15, 2024 -
 Secret Tunnels Used By Knights Templar Leading To The Treasure Tower – Discovered
Archaeology | Oct 29, 2019
Secret Tunnels Used By Knights Templar Leading To The Treasure Tower – Discovered
Archaeology | Oct 29, 2019 -
 Ancient Roman Settlement Discovered In Deal, UK
Archaeology | Dec 16, 2022
Ancient Roman Settlement Discovered In Deal, UK
Archaeology | Dec 16, 2022 -
 New Study Sheds Light On The Phenomenon Of Female Jewish Slavery And Uncovers Gang Rape In Livorno’s Slave Prison
Archaeology | May 18, 2022
New Study Sheds Light On The Phenomenon Of Female Jewish Slavery And Uncovers Gang Rape In Livorno’s Slave Prison
Archaeology | May 18, 2022 -
 Old Unexplained Mystery Of The Frightening Woman On The Isle Of Iona
Featured Stories | Mar 8, 2024
Old Unexplained Mystery Of The Frightening Woman On The Isle Of Iona
Featured Stories | Mar 8, 2024 -
 Cursed Dwarf Fafnir Turned Into A Fearsome Norse Dragon And Guarded The Stolen Magical Ring Andvaranaut
Featured Stories | Aug 16, 2017
Cursed Dwarf Fafnir Turned Into A Fearsome Norse Dragon And Guarded The Stolen Magical Ring Andvaranaut
Featured Stories | Aug 16, 2017 -
 On This Day In History: Malcolm III, King of Scots Died – On Nov 13, 1093
News | Nov 13, 2016
On This Day In History: Malcolm III, King of Scots Died – On Nov 13, 1093
News | Nov 13, 2016 -
 Rare Discovery: 530 Knuckle Bones ‘Astragali’ For Gaming And Divination Unearthed In Ancient City Of Maresha
Archaeology | Aug 16, 2022
Rare Discovery: 530 Knuckle Bones ‘Astragali’ For Gaming And Divination Unearthed In Ancient City Of Maresha
Archaeology | Aug 16, 2022 -
 Giant Azaes-Itzamna: Ninth King Of Atlantis, Founder Of Chichen Itza And Teacher Of Maya People
Civilizations | Jun 29, 2017
Giant Azaes-Itzamna: Ninth King Of Atlantis, Founder Of Chichen Itza And Teacher Of Maya People
Civilizations | Jun 29, 2017 -
 The Govan Stones – Treasures From The Viking Era In Britain
Featured Stories | Dec 27, 2015
The Govan Stones – Treasures From The Viking Era In Britain
Featured Stories | Dec 27, 2015 -
 The Lycurgus Cup: Fascinating Artifact That Reveals Prehistoric Knowledge Of Nanotechnology
Ancient Technology | Aug 2, 2018
The Lycurgus Cup: Fascinating Artifact That Reveals Prehistoric Knowledge Of Nanotechnology
Ancient Technology | Aug 2, 2018 -
 Emperor Caligula’s Ancient Garden Found Under Piazza Pia In Rome, Italy
Archaeology | Jul 26, 2024
Emperor Caligula’s Ancient Garden Found Under Piazza Pia In Rome, Italy
Archaeology | Jul 26, 2024 -
 Ancient Tell-Tayinat Inhabitants And Climate Change Resilience – New Study
Archaeology | Oct 30, 2020
Ancient Tell-Tayinat Inhabitants And Climate Change Resilience – New Study
Archaeology | Oct 30, 2020 -
 Who Made The Mysterious Ancient Cave Paintings And Inscriptions In Oklahoma 2,500 Years Ago?
Featured Stories | Jul 23, 2024
Who Made The Mysterious Ancient Cave Paintings And Inscriptions In Oklahoma 2,500 Years Ago?
Featured Stories | Jul 23, 2024 -
 A Half-A Million-Year-Old Well-Preserved Elephant Tusk Unearthed In Israel
Archaeology | Sep 2, 2022
A Half-A Million-Year-Old Well-Preserved Elephant Tusk Unearthed In Israel
Archaeology | Sep 2, 2022 -
 Ancient Maya Ruins Of Tulum: Sea Port And Sacred Site For Worshiping Of Descending God
Featured Stories | Aug 10, 2016
Ancient Maya Ruins Of Tulum: Sea Port And Sacred Site For Worshiping Of Descending God
Featured Stories | Aug 10, 2016


