Amage: Sarmatian Warrior Queen/Regent Who Impressed With Remarkable Military Skills
A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com - Multiple burials of possible women warriors have been unearthed in sites associated with the Scythians, Sauromatians (a tribe nation ruled by women), and Sarmatians.
These ancient cultures from the late seventh through the second centuries BC had many female warriors.
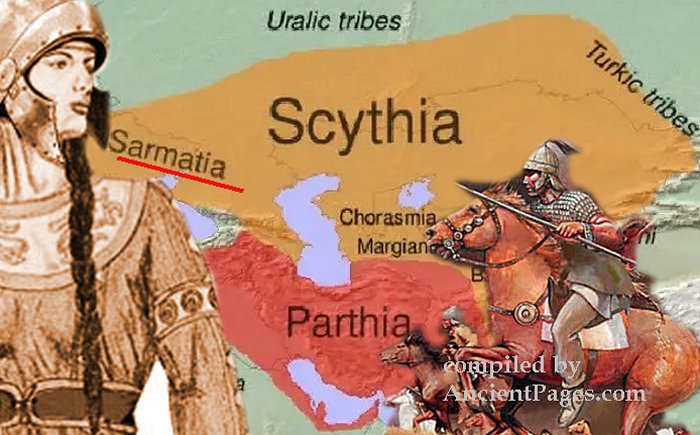 Among many women who lived in this part of the world, and roamed wild Scythian steppes, was Amage, a Sarmatian warrior queen who lived at the end of the 2nd century BC.
Among many women who lived in this part of the world, and roamed wild Scythian steppes, was Amage, a Sarmatian warrior queen who lived at the end of the 2nd century BC.
Many excavated Sarmatian military burials include the remains of armed Sarmatian women. The remains reveal clear signs of severe battle injuries, including stabs to their skulls and blows, similar to those observed on the remains of male warriors.
These findings, along with spears, axes, lances, and even double-edged short-swords (akinakes), found in the graves, strongly suggest that they all died in battle. The Sarmatian women, as were their husbands, brothers, and other relatives, were brave and skilled.
Among many women who lived in this part of the world, and roamed wild Scythian steppes, was Amage, a Sarmatian warrior queen who lived at the end of the 2nd century BC. She was the wife and co-ruler of the Sarmatian king Medosacus. Otherwise, very little is known about this Sarmatian queen and her rule. However, Sarmatian women became famous for having a prominent role in wars.
According to Hippocrates (c. 460 – c. 370 BC), Sarmatian women participated in warfare, and Herodotus (c. 484 – c. 425 BC), a Greek historian, described them as fighting in the same clothing as men. Some believe that the deeds of Amage's and other Sarmatian female warriors inspired those who created the Greek myths of the Amazons.
According to one source, her husband was a notorious drunkard who abused his power as a monarch for personal luxury. At the same time, another version points to the king's mental incompetence.
Amage Made An Important Decision In Difficult Times
From now on, the brave queen-warrior acted as regent; she took over the government into her own hands.
Polyaenus, a 2nd-century AD Macedonian author, writes in "Stratagems:
"She judged causes, stationed garrisons, repulsed the invasions of enemies, and directed everything with such a great ability that her fame extended through all Scythia."
She Was A Successful Ruler
Amage was impressed with the extraordinary military achievements - in the era of big but sluggish armies which depended more on size than strategy and tactics.
Instead, she organized a rally reminiscent of the actions of modern commandos. Her fame as a successful leader reached neighboring tribes and even far beyond the borders of her territories.
The inhabitants of the Chersonesus (once an ancient Greek colony founded about 2,500 years ago in the southwestern part of the Crimean Peninsula) also learned about her achievements. A king of the neighboring Scythians had systematically harassed these people. At last, they requested an alliance with her.
Polyaenus narrates that "in consequence of a treaty formed between the two nations, she wrote to the Scythian prince, requesting him not to repeat his ravages in the Chersonesus. When he treated her prohibition with disrespect, she marched against him with a hundred and twenty men of tried courage, and extraordinary strength, each of them provided with three horses."
In one night and day, she covered about two hundred kilometers (versions vary) and reached the enemy's palace.
In an unexpected attack, her troops captured the prince's palace, slew the guards, his friends, and his family, and ultimately killed the ruler.
Then "she put the inhabitants of Chersonesus back in free possession of their country, and gave his hereditary dominions to the son of the Scythian prince."
She allowed his son to live on the condition that he obeys her. She also warned him to be careful and take "a warning from his father's death, and not to invade the territories of the neighboring Greeks and barbarians."
Written by - A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com Senior Staff Writer
Updated on May 20, 2023
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
Expand for referencesReferences:
Mayor, Adrienne. The Amazons (p. 372). Princeton University Press.
Polyaenus: Stratagems
More From Ancient Pages
-
 Researchers Develop New Ways Of Visualizing Ancient Small Objects By Combining Technologies
Archaeology | Apr 20, 2022
Researchers Develop New Ways Of Visualizing Ancient Small Objects By Combining Technologies
Archaeology | Apr 20, 2022 -
 What Was Legio Martia And Why Were The Roman Soldiers Called The Martians?
Ancient History Facts | Jan 5, 2018
What Was Legio Martia And Why Were The Roman Soldiers Called The Martians?
Ancient History Facts | Jan 5, 2018 -
 On This Day In History: Michael Servetus Burned At The Stake ‘Atop A Pyre Of His Own Books’ – On Oct 27, 1553
News | Oct 26, 2016
On This Day In History: Michael Servetus Burned At The Stake ‘Atop A Pyre Of His Own Books’ – On Oct 27, 1553
News | Oct 26, 2016 -
 Mysterious Medes: Was It An Ancient City Of Ecbatana?
Archaeology | Jul 3, 2020
Mysterious Medes: Was It An Ancient City Of Ecbatana?
Archaeology | Jul 3, 2020 -
 Fossil Teeth Reveal: Humans Were Present In Asia ‘20,000 Years Earlier’ Than Previously Thought
Archaeology | Oct 15, 2015
Fossil Teeth Reveal: Humans Were Present In Asia ‘20,000 Years Earlier’ Than Previously Thought
Archaeology | Oct 15, 2015 -
 Scientists Search For North America’s ‘Atlantis’ – Submerged Landscapes In The Gulf Of Mexico Studied
Archaeology | Jul 2, 2024
Scientists Search For North America’s ‘Atlantis’ – Submerged Landscapes In The Gulf Of Mexico Studied
Archaeology | Jul 2, 2024 -
 Cenomani People: Their Pre-Roman Celtic Cemetery Reveals Funerary Customs
Archaeology | Apr 18, 2019
Cenomani People: Their Pre-Roman Celtic Cemetery Reveals Funerary Customs
Archaeology | Apr 18, 2019 -
 2,000-Year-Old Rock Art Sites Discovered In Jalapão, Brazil
Archaeology | Mar 11, 2024
2,000-Year-Old Rock Art Sites Discovered In Jalapão, Brazil
Archaeology | Mar 11, 2024 -
 Nomenclator: Ancient Living-Human Calendar And Address Book
Ancient History Facts | Jul 4, 2018
Nomenclator: Ancient Living-Human Calendar And Address Book
Ancient History Facts | Jul 4, 2018 -
 Head Of The Great Sphinx Was Changed – It’s The Gateway To A Secret Underground City– Historians Suggest
Featured Stories | Jan 20, 2018
Head Of The Great Sphinx Was Changed – It’s The Gateway To A Secret Underground City– Historians Suggest
Featured Stories | Jan 20, 2018 -
 Caligula’s Stunning 2,000-Year-Old Sapphire Ring Tells Of A Dramatic Love Story
Artifacts | Jul 10, 2020
Caligula’s Stunning 2,000-Year-Old Sapphire Ring Tells Of A Dramatic Love Story
Artifacts | Jul 10, 2020 -
 Mystery Of The Watchers And Book Of Enoch – Fallen Angels And Their Secret Knowledge
Biblical Mysteries | Oct 27, 2017
Mystery Of The Watchers And Book Of Enoch – Fallen Angels And Their Secret Knowledge
Biblical Mysteries | Oct 27, 2017 -
 Our Ancestors Made Drawings In The Sand At The Beach 140,000 Years Ago – Scientists Say
Featured Stories | Jul 21, 2023
Our Ancestors Made Drawings In The Sand At The Beach 140,000 Years Ago – Scientists Say
Featured Stories | Jul 21, 2023 -
 8,600-Year-Old Bone Needles Found In Denizli Closely Associated With Old Textile Tradition
Artifacts | Sep 2, 2020
8,600-Year-Old Bone Needles Found In Denizli Closely Associated With Old Textile Tradition
Artifacts | Sep 2, 2020 -
 Nygrotta: Species Migration Occurred Due To Climatic Shifts Millennia Ago – Ancient DNA And Bones Show
Paleontology | Apr 5, 2024
Nygrotta: Species Migration Occurred Due To Climatic Shifts Millennia Ago – Ancient DNA And Bones Show
Paleontology | Apr 5, 2024 -
 Analysis Of Ancient Tools Challenges Long-Held Ideas About What Drove Major Changes In Ancient Greek Society
Archaeology | Aug 23, 2022
Analysis Of Ancient Tools Challenges Long-Held Ideas About What Drove Major Changes In Ancient Greek Society
Archaeology | Aug 23, 2022 -
 Why Was Celebration Of Christmas, Easter, Midsummer And Saint’s Day Forbidden In Scotland?
Ancient History Facts | Dec 27, 2019
Why Was Celebration Of Christmas, Easter, Midsummer And Saint’s Day Forbidden In Scotland?
Ancient History Facts | Dec 27, 2019 -
 King Mithradates VI Of Pontus Used Poison To Avoid Death By Poison
Ancient History Facts | Mar 5, 2016
King Mithradates VI Of Pontus Used Poison To Avoid Death By Poison
Ancient History Facts | Mar 5, 2016 -
 Why Was The Magical Sword Azoth Of Paracelsus So Special?
Featured Stories | Dec 24, 2020
Why Was The Magical Sword Azoth Of Paracelsus So Special?
Featured Stories | Dec 24, 2020 -
 Scientists Identify Birds On Magnificent Ancient Egyptian Artwork Found In Amarna
Archaeology | Dec 28, 2022
Scientists Identify Birds On Magnificent Ancient Egyptian Artwork Found In Amarna
Archaeology | Dec 28, 2022
