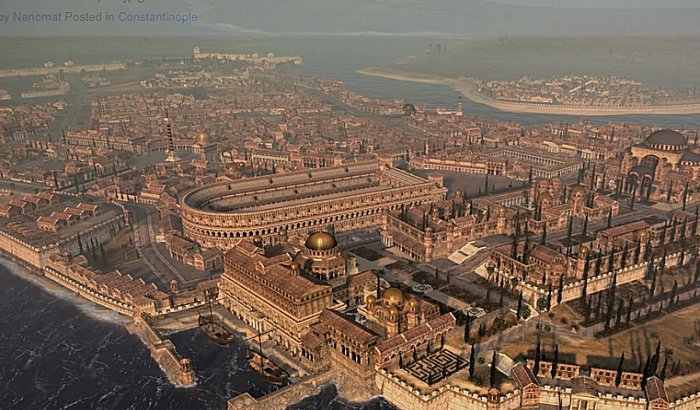
Why Was Constantinople Called New Rome?
A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com - Constantinople became a new Rome, and the Emperor Constantine the Great celebrated the inauguration of his new capital city, and the name of the town originates from his name.
In 330 AD, he split the Roman Empire into two parts: Eastern and Western, and the western half centered in Rome while the eastern half centered in Constantinople (City of Constantine).
![Map of Constantinople (1422) by Florentine cartographer Cristoforo Buondelmonti[39] is the oldest surviving map of the city, and the only one that predates the Turkish conquest in 1453.](https://www.ancientpages.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/constantinople14.jpg) Map of Constantinople (1422) by Florentine cartographer Cristoforo Buondelmonti is the oldest surviving map of the city and the only one that predates the Turkish conquest in 1453. Source
Map of Constantinople (1422) by Florentine cartographer Cristoforo Buondelmonti is the oldest surviving map of the city and the only one that predates the Turkish conquest in 1453. Source
After restoring the unity of the Empire, Constantine the Great introduced many governmental reforms and increased financial resources for the Christian church.
Then, he identified the site of Byzantium - a small Greek port - as the new center of the Empire and the seat of government, officially known as Nova Roma ('New Rome').
Rome, which had been the capital for over a thousand years, was too far from the frontiers of the Empire, and it might have seemed unimaginable to propose that ancient Rome be moved to another location.
Constantine's dedication of the new city was most probably the most significant moment of his reign. The new capital had a perfect strategic location; it was standing on a piece of land projecting into the Bosphorus, the narrow strait of water dividing two continents: Europe from Asia.
Constantinople could control the major trade routes between these two continents, as well as the passage from the Black Sea to the Mediterranean.
New Coins Struck And Greek And Roman Art Moved To 'Second Rome'
The 'New Rome' (Nova Roma) was built over six years and inaugurated on May 11, 330, and new coins were struck by Constantine I to commemorate the founding of Constantinople.
In many ways, the new city was an almost exact copy of the old and famous eternal city of Rome. Like Rome on the Tiber River, it was also located on seven hills and divided into fourteen administrative districts.
Coin struck by Emperor Constantine I to commemorate the founding of the ‘second Rome.’ Source
However, it was still much to do preparing the new capital's interior. Buildings began to appear in great haste, and Constantine ordered many marbles, columns, and tiles to be transported from Roman temples to the new capital. The best works of Greek and Roman art were used for decorations of streets and squares.
It was essential to give the new city the most impressive look possible. After all, his 'New Rome' was beginning its life as an imperial metropolis.
Many Similarities And One Significant Difference Between Two Rome Cities
The main difference between these two cities was that Constantinople was a Christian city with numerous basilicas and churches. From the beginning, it symbolized the break with Rome's pagan past.
The emperor stimulated private building by promising householders gifts of land from Asiana and Pontica – two of the four major administrative divisions of the Eastern Empire.
On May 18, 332, he announced that, as in Rome, free distributions of food would be made to the citizens, and thus, he encouraged settlement in the city.
Yet, at first, the Empire's new Rome did not have all the dignities of old Rome. It possessed its senate, a proconsul, but no praetors, tribunes, or quaestors authorized to investigate and handle murders.
There was also a lack of several other principal offices responsible for the city's temples, sewers, monuments, aqueducts, and other public works. Soon, however, the 'second Rome' grew prominent, wealthy, and densely populated.
For 1,000 years, under the Byzantine emperors, it was the intellectual, religious, and commercial center of the Greek-speaking world.
Today, Constantinople is Istanbul, the most populous city in Turkey and the country's economic, cultural and historic center, but its old name is still remembered.
Written by – A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com Senior Staff Writer
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
Expand for referencesReferences:
Norman F. Cantor, Civilization of the Middle Ages
Stephen Turnbull S. and Dennis Peter, The Walls of Constantinople AD 324–1453
More From Ancient Pages
-
 Ancient Mystery Of Acra Citadel – Solved
Archaeology | Nov 3, 2015
Ancient Mystery Of Acra Citadel – Solved
Archaeology | Nov 3, 2015 -
 Andvaranaut: Magical Ring That Made Gold And Was Stolen By Norse God Loki
Featured Stories | Apr 12, 2017
Andvaranaut: Magical Ring That Made Gold And Was Stolen By Norse God Loki
Featured Stories | Apr 12, 2017 -
 Encounter With Time Window At The Upper Current River And Curious Glimpses From The Past
Featured Stories | Jul 28, 2018
Encounter With Time Window At The Upper Current River And Curious Glimpses From The Past
Featured Stories | Jul 28, 2018 -
 10 Fascinating Facts About Pharaohs
Ancient History Facts | Jun 21, 2016
10 Fascinating Facts About Pharaohs
Ancient History Facts | Jun 21, 2016 -
 Stunning 2000-Year-Old Roman Silver Dagger Used By Legendary Germanic Warriors Discovered By Teenager
Archaeology | Feb 18, 2020
Stunning 2000-Year-Old Roman Silver Dagger Used By Legendary Germanic Warriors Discovered By Teenager
Archaeology | Feb 18, 2020 -
 Medicine in Antiquity: From Ancient Temples To Roman Logistics
Archaeology | Apr 13, 2018
Medicine in Antiquity: From Ancient Temples To Roman Logistics
Archaeology | Apr 13, 2018 -
 New Study Sheds Light On The Phenomenon Of Female Jewish Slavery And Uncovers Gang Rape In Livorno’s Slave Prison
Archaeology | May 18, 2022
New Study Sheds Light On The Phenomenon Of Female Jewish Slavery And Uncovers Gang Rape In Livorno’s Slave Prison
Archaeology | May 18, 2022 -
 How Ancient Cultures Explained Comets And Meteors
Archaeoastronomy | Jun 5, 2019
How Ancient Cultures Explained Comets And Meteors
Archaeoastronomy | Jun 5, 2019 -
 Real-Life Excalibur Found Underwater In Bosnia – Medieval Sword In Stone Pulled Out
Archaeology | Oct 31, 2019
Real-Life Excalibur Found Underwater In Bosnia – Medieval Sword In Stone Pulled Out
Archaeology | Oct 31, 2019 -
 Early Humans In The Hula Valley Invested In Systematic Procurement Of Raw Materials Hundreds Of Thousands Of Years Ago
Archaeology | Jul 19, 2023
Early Humans In The Hula Valley Invested In Systematic Procurement Of Raw Materials Hundreds Of Thousands Of Years Ago
Archaeology | Jul 19, 2023 -
 Hundreds Of Fascinating 24,000-Year-Old Cave Paintings Discovered In Eastern Iberia
Archaeology | Sep 11, 2023
Hundreds Of Fascinating 24,000-Year-Old Cave Paintings Discovered In Eastern Iberia
Archaeology | Sep 11, 2023 -
 Third-Century Sculpture Of Roman Emperor Aurelian Unearthed In Bulgaria
Archaeology | Sep 5, 2018
Third-Century Sculpture Of Roman Emperor Aurelian Unearthed In Bulgaria
Archaeology | Sep 5, 2018 -
 Rare Sphinx Seal Belonging To Roman Emperor Discovered In India Confirms Existence Of Legendary Muziris
Archaeology | Oct 1, 2020
Rare Sphinx Seal Belonging To Roman Emperor Discovered In India Confirms Existence Of Legendary Muziris
Archaeology | Oct 1, 2020 -
 Mysterious Judaculla Rock And The Slant-Eyed Giant Of The Cherokee
Featured Stories | May 8, 2021
Mysterious Judaculla Rock And The Slant-Eyed Giant Of The Cherokee
Featured Stories | May 8, 2021 -
 Traces Of Advanced Beings Who Walked Earth Millions Of Years Ago: Controversial Ancient History Examined
Ancient Mysteries | Jun 20, 2018
Traces Of Advanced Beings Who Walked Earth Millions Of Years Ago: Controversial Ancient History Examined
Ancient Mysteries | Jun 20, 2018 -
 Chogha Zanbil: Huge Ancient Still Existing Ziggurat Dedicated To God Inshushinak
Featured Stories | Mar 10, 2016
Chogha Zanbil: Huge Ancient Still Existing Ziggurat Dedicated To God Inshushinak
Featured Stories | Mar 10, 2016 -
 17th Century Medical Pop-Up Book Digitized
Archaeology | Jan 16, 2016
17th Century Medical Pop-Up Book Digitized
Archaeology | Jan 16, 2016 -
 Egyptian Royal Artifacts Found At ‘Ancient Buto’ Site, Egypt Probably Dated To King Psamtik I’s Reign
Archaeology | Jan 4, 2018
Egyptian Royal Artifacts Found At ‘Ancient Buto’ Site, Egypt Probably Dated To King Psamtik I’s Reign
Archaeology | Jan 4, 2018 -
 European-Made Sealed Bottles Of Cherries Dated To 18th Century Found At Washington’s Mount Vernon
Archaeology | Apr 23, 2024
European-Made Sealed Bottles Of Cherries Dated To 18th Century Found At Washington’s Mount Vernon
Archaeology | Apr 23, 2024 -
 Roman Mosaic Dated To Between 60 BC And 300 AD Unearthed In Baalbek
Archaeology | Dec 30, 2020
Roman Mosaic Dated To Between 60 BC And 300 AD Unearthed In Baalbek
Archaeology | Dec 30, 2020


