Ukko: Karelian-Finnish God Of Thunderstorms, Harvest, Patron Of Crops And Cattle
A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com - In Karelian-Finnish mythology, Ukko ('grandfather 'or 'old man') was responsible for weather, lightning, and thunderstorms. He controlled the clouds and the harvest of the year.
Powerful thunderstorms were heard when the god Ukko drove his chariot through the skies, according to an ancient explanation of this natural phenomenon.
Frost, ice, snow, hail, wind and rain, sunshine, and shadow were believed to come from the hands of Ukko.
Ukko – the "The Pivot of the Heavens" - was often depicted as sitting upon a cloud in the sky's vault and bearing the firmament on his shoulders. As the god of heaven, he was pleased for the harvest to succeed. He was worshiped as the patron saint of crops and cattle.
Ukko created and maintained order in the world, and his act of creation of all things was described in the Finnish epic 'Kalevala':
"Ukko, that supreme Creator, he himself, Ukko, the god of heaven, separated water from heaven, he shared water with land (9: 33-36). "
Ukko Was Known By Many Epithets
In the Finnish epic 'The Kalevala,' Ukko was recognized as "The Leader of the Clouds," "The Shepherd of the Lamb-Clouds," "The God of the Breezes," "The Golden King," "The Silver Ruler of the Air," and "The Father of the Heavens."
The god of thunder has a long tradition in many ancient cultures. Some researchers suggested that Ilmarinen, divine blacksmith, inventor, and sky god, refers to the origin of Ukko because, in some legends, Ukko is the creator and blacksmith. Also, Ukko has counterparts in prominent deities described in Indo-European mythologies, including the Baltic god of thunder, Perkunas, the Norse god Thor, the Slavic god of heaven, and lightning, Perun, and Ukko's closest counterpart in Greek mythology, Zeus.
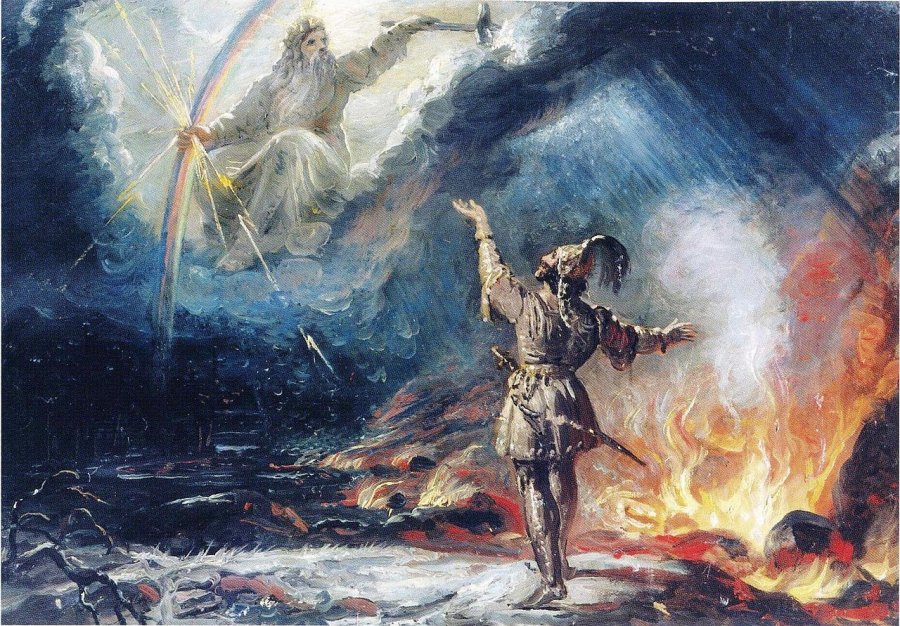 Painting by Robert Ekman in 1867 called Lemminkäinen asks help from Ukko ylijumala with crossing the lake in fire on his route to the wedding at Pohjola. Public Domain
Painting by Robert Ekman in 1867 called Lemminkäinen asks help from Ukko ylijumala with crossing the lake in fire on his route to the wedding at Pohjola. Public Domain
During the stove culture, a strong belief in the Karelian-Finnish god Ukko appeared among the Native Finns and the Sami people around 2,400 BC.
Ukko's Powerful Divine Weapons
According to legends, Ukko presented himself as a broad-axed, older man with a gray beard and white hair, dressed in a blue dress, riding a chariot along the heavenly stone road.
His main attributes were lightning, an ax, a magical hammer ('Ukonvasara' or 'hammer of Ukko'), and a flaming sword, which produced powerful lightning when hitting the ground.
He also had a fiery bow and fire arrows, and by using his tremendous powers, the great Ukko could strike evil spirits in the mountains that could only hide from his attacks in the water.
Numerous abandoned stone weapons were found in Karelia, Finland, at the beginning of the Copper Age. Then, local shamans collected and protected them for many years. These stone artifacts possessed certain heavenly powers to perform cures and heal diseases. The Finnish people called flint 'Ukonkivi' ("Ukkos sten"), or the firestone of the god Ukko" (Ukon pii), and as tradition has it, Ukko carved lightning from it.
Limited Knowledge About Ukko Comes From Poems And Songs
Information about the gods in Finnish mythology has been passed orally through poems and songs. The god Ukko was considered a demon among Christians in the Finnish regions since ceremonies and cults were related to Satan.
In ancient beliefs, the gods were not only good or bad, but forces of good and evil often accompanied them.
In his account of the Bible Book of Psalms from 1551, Mikael Agricola (1510–1555), the 16th century Lutheran bishop and reformer, described the pantheon of gods worshiped by the Finnish people in ancient times. He mentioned the sacred marriage of Ukko and his wife, Rauni. It was believed that when Rauni swears, god begins to get angry, and thunder rumbles just before people saw the flashes of lightning. Finally, the blessed rainfalls provide a harvest.
However, Agricola was a churchman, and the purpose of this description was to criticize and root out pagan customs firmly and not to continue the tradition of old deities.
Juhannus - Midsummer Holiday
Initially, it was a pagan celebration known as Ukon juhla, the celebration of Ukko, the most important god in Finnish mythology. Tradition has it that people place birch bunches of a birch on either side of the front door of their cabins or even on their boats to welcome visitors. In Finland, people still observe the Ukon juhla festival. When Finland became a Christian country, the Pagan festival was officially renamed "Juhannus," held in honor of John the Baptist. During the festival, it's a tradition to large lit bonfires by lakes and the sea.
On June 21, many people worldwide (especially the northern Europeans) celebrate the summer solstice, the so-called Midsummer. The celebrations take place on the day between June 19 and June 25 and the preceding evening. The exact dates vary among different cultures.
Written by – A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com Senior Staff Writer
updated on June 30, 2021
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
Expand for referencesMore From Ancient Pages
-
 Shamash: Mesopotamian God Of Sun, Truth, Justice And Healing
Featured Stories | Jan 11, 2016
Shamash: Mesopotamian God Of Sun, Truth, Justice And Healing
Featured Stories | Jan 11, 2016 -
 Tragic Reign Of Caterina Cornaro – The Last Queen Of Cyprus And Patron Of The Arts
Featured Stories | Jul 4, 2019
Tragic Reign Of Caterina Cornaro – The Last Queen Of Cyprus And Patron Of The Arts
Featured Stories | Jul 4, 2019 -
 Unique Tomb Of Roman Noblewoman Caecilia Metella Reveals Secrets Of Ancient Concrete Resilience
Archaeology | Oct 14, 2021
Unique Tomb Of Roman Noblewoman Caecilia Metella Reveals Secrets Of Ancient Concrete Resilience
Archaeology | Oct 14, 2021 -
 Extremely Unique Ancient Roman Arm Guard Found At Trimontium Fort – Restored And On Display For The First Time Ever
Archaeology | Jan 22, 2024
Extremely Unique Ancient Roman Arm Guard Found At Trimontium Fort – Restored And On Display For The First Time Ever
Archaeology | Jan 22, 2024 -
 Incredible Find – 3,000-Year-Old Canoe Found In Wisconsin’s Lake Mendota
Archaeology | Sep 25, 2022
Incredible Find – 3,000-Year-Old Canoe Found In Wisconsin’s Lake Mendota
Archaeology | Sep 25, 2022 -
 Mayan Underwater Tunnels With Bones Of Humans, Elephant-Like Creatures, Tigers, Bears, Tigers And Extinct Horses, Rediscovered In Yucatan
Archaeology | Jan 19, 2018
Mayan Underwater Tunnels With Bones Of Humans, Elephant-Like Creatures, Tigers, Bears, Tigers And Extinct Horses, Rediscovered In Yucatan
Archaeology | Jan 19, 2018 -
 Strange Reports Of A Mysterious Stone-Throwing Phenomenon And Invisible Entity Encountered Worldwide
Featured Stories | Dec 4, 2023
Strange Reports Of A Mysterious Stone-Throwing Phenomenon And Invisible Entity Encountered Worldwide
Featured Stories | Dec 4, 2023 -
 On This Day In History: American Astronomer Edwin Hubble Announced Existence Of Other Galaxies – On Dec 30, 1924
News | Dec 30, 2016
On This Day In History: American Astronomer Edwin Hubble Announced Existence Of Other Galaxies – On Dec 30, 1924
News | Dec 30, 2016 -
 Mysterious 70-Million-Year-Old Underground Village And Magnificent Tower Of Eben-Ezer In Belgium
Featured Stories | Mar 20, 2017
Mysterious 70-Million-Year-Old Underground Village And Magnificent Tower Of Eben-Ezer In Belgium
Featured Stories | Mar 20, 2017 -
 Hidden Rare Map Reveals How American “Hero” William Clark Broke Peacy Treaty And Robbed Indigenous Americans Of Land
Archaeology | Feb 7, 2022
Hidden Rare Map Reveals How American “Hero” William Clark Broke Peacy Treaty And Robbed Indigenous Americans Of Land
Archaeology | Feb 7, 2022 -
 Controversial Study Of Ancient DNA Could Re-Write History Of South Florida And Prove Humans And Huge Prehistoric Animals Co-Existed
Archaeology | Sep 23, 2014
Controversial Study Of Ancient DNA Could Re-Write History Of South Florida And Prove Humans And Huge Prehistoric Animals Co-Existed
Archaeology | Sep 23, 2014 -
 History Of Middle Ages Altarpieces Has Been Re-Written
Archaeology | Mar 10, 2018
History Of Middle Ages Altarpieces Has Been Re-Written
Archaeology | Mar 10, 2018 -
 10 Spooky Ancient Places That Are Home To The Feared Living Dead
Featured Stories | Oct 31, 2020
10 Spooky Ancient Places That Are Home To The Feared Living Dead
Featured Stories | Oct 31, 2020 -
 Olympe De Gouges – First French Feminist Challenged Maximilien de Robespierre And The Jacobins
Featured Stories | Nov 12, 2018
Olympe De Gouges – First French Feminist Challenged Maximilien de Robespierre And The Jacobins
Featured Stories | Nov 12, 2018 -
 Unlocking The Secrets Of The Ancient Coastal Maya
Archaeology | Jul 8, 2022
Unlocking The Secrets Of The Ancient Coastal Maya
Archaeology | Jul 8, 2022 -
 Underground Civilizations – True Rulers Of Earth – Part 1
Featured Stories | May 7, 2019
Underground Civilizations – True Rulers Of Earth – Part 1
Featured Stories | May 7, 2019 -
 Unexpected Underwater Discovery Of 50,000 Ancient Coins Off Sardinia Hints At Hidden Shipwreck
Archaeology | Nov 10, 2023
Unexpected Underwater Discovery Of 50,000 Ancient Coins Off Sardinia Hints At Hidden Shipwreck
Archaeology | Nov 10, 2023 -
 Mighty Viking Harald Hardrada – The Last Great Viking And Most Feared Warrior Of His Time
Featured Stories | Jun 9, 2020
Mighty Viking Harald Hardrada – The Last Great Viking And Most Feared Warrior Of His Time
Featured Stories | Jun 9, 2020 -
 Ancient Greeks Reached Iceland Before The Vikings – New Theory Suggests
Featured Stories | Dec 10, 2022
Ancient Greeks Reached Iceland Before The Vikings – New Theory Suggests
Featured Stories | Dec 10, 2022 -
 Surtshellir Cave Reveals How Vikings Attempted To Prevent Ragnarök – Doom Of The Gods
Vikings | Jul 17, 2023
Surtshellir Cave Reveals How Vikings Attempted To Prevent Ragnarök – Doom Of The Gods
Vikings | Jul 17, 2023

