Rio Tinto Bosses Quit Over Destruction Of One Of The Earliest Aboriginal Sites
Conny Waters - AncientPages.com - Following the destruction of sacred caves in Western Australia, three heavy bosses are leaving the mining giant Rio Tinto.
The company's board has agreed with CEO Jean-Sébastien Jacques and directors Chris Salisbury and Simone Niven that the three will leave their positions.
 Demonstration at Rio Tinto's offices in Perth on June 9th. Photo: Richard Wainwright / AP / TT
Demonstration at Rio Tinto's offices in Perth on June 9th. Photo: Richard Wainwright / AP / TT
It was in May that the company blew up the caves in the Juukan Gorge in an isolated area in northwestern Australia. The blasting decision was made despite archaeological excavations showing traces of human activity there for tens of thousands of years, and despite the fact that indigenous people in the area protested.
Rio Tinto announced the resignation of its CEO and two top lieutenants Friday over the mining giant's destruction of a 46,000-year-old Aboriginal site to expand an iron ore mine in Australia.
The Anglo-Australian firm faced a growing investor revolt over the destruction of the sacred site in the Juukan Gorge in Western Australia's remote Pilbara region – one of the earliest known locations inhabited by Australia's indigenous people.
Following a board investigation into the May 24 incident, Rio Tinto said CEO Jean-Sebastien Jacques was stepping down "by mutual agreement" along with the chief of the company's core iron ore division, Chris Salisbury, and corporate relations head Simone Niven.
"What happened at Juukan was wrong and we are determined to ensure that the destruction of a heritage site of such exceptional archaeological and cultural significance never occurs again at a Rio Tinto operation," chairman Simon Thompson said in a statement, as cited by Daily Sabah.
The cultural importance of Juukan Gorge was confirmed by an archaeological dig carried out at one of the caves – known as rock shelters – a year after Rio Tinto obtained approval to blast in the area.
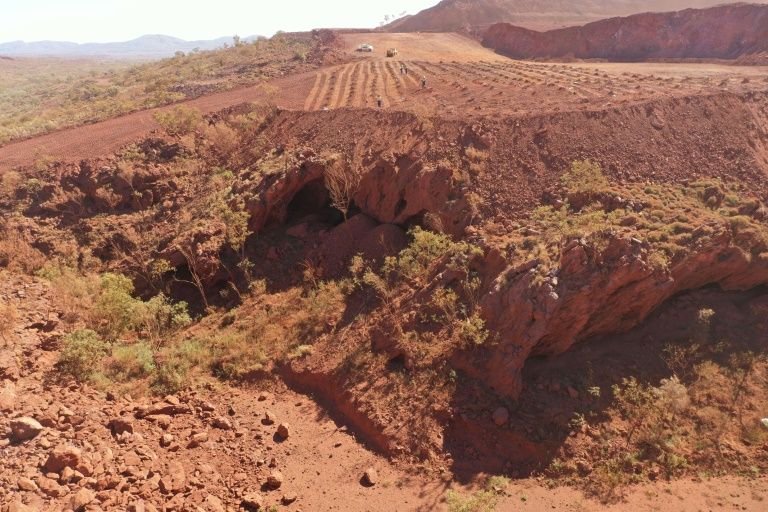 The Juukan Gorge in Western Australia -- one of the earliest known sites inhabited by Aboriginals in Australia, is shown in this photo by PKKP Aboriginal Corporation
The Juukan Gorge in Western Australia -- one of the earliest known sites inhabited by Aboriginals in Australia, is shown in this photo by PKKP Aboriginal Corporation
The dig uncovered the oldest known example of bone tools in Australia – a sharpened kangaroo bone dating back 28,000 years – and a plaited-hair belt that DNA testing linked to indigenous people still living in the area.
An internal company review in August determined that "a series of decisions, actions and omissions over an extended period of time" preceded the choice to go ahead with the Juukan Gorge blasting despite concerns over the fate of the sacred Aboriginal site.
In an initial response, the company stripped millions of dollars in bonuses from the three executives.
But the firm's shareholders and corporate responsibility bodies derided the move as insufficient and called for heads to roll.
'Crucial first step'
The National Native Title Council, which represents indigenous landowners, welcomed what it called the "dismissal" of the Rio Tinto executives, but said such staff changes were "only the crucial first step."
"We hope this will send a strong message to the whole mining sector: you need to join the 21st Century and start taking your environmental, social and corporate governance seriously," said NNTC chief executive Jamie Lowe.
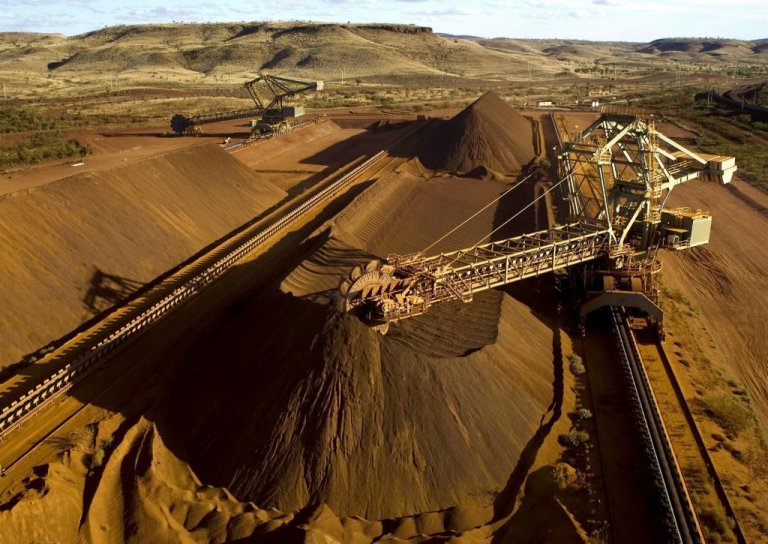 An internal review found that 'a series of decisions, actions and omissions' preceded the decision to go ahead with the Juukan Gorge blasting Photo: RIO TINTO
An internal review found that 'a series of decisions, actions and omissions' preceded the decision to go ahead with the Juukan Gorge blasting Photo: RIO TINTO
Jacques, who has been CEO since 2016, will remain in his role until a successor can be found or until March 31, whichever is sooner, and the other two executives will leave the company on Dec. 31.
In announcing their departure, Thomspon said all three executives would be paid undisclosed "separation terms" in line with their contracts, raising the specter of significant payouts which quickly rankled investors.
"We will ... be looking closely at the separation arrangements, with the expectation that any exit won't provide a windfall," said Louise Davidson, CEO of the Australian Council of Superannuation Investors.
The Australasian Centre for Corporate Responsibility (ACCR) for its part expressed concern at how long it took Rio Tinto to act.
"There are in fact two disasters: The first involves the tragic destruction of Juukan Gorge in May; the second is the dishonest malaise of Rio Tinto's board and senior management in the months since," said ACCR legal counsel James Fitzgerald.
'Vast distance'
Rio Tinto initially defended its blasting in the Juukan Gorge as authorized under a 2013 agreement with the state government.
But protests by Aboriginal leaders, who said they had not been informed of the planned blasting until it was too late to prevent it, led the company to issue an apology.
Australia's parliament has been conducting its own inquiry into the Juukan Gorge incident, and Western Australia's state government is reviewing the laws governing mining operations near indigenous heritage sites. Western Australia Treasurer Ben Wyatt, who is Aboriginal, said Rio Tinto, with dual headquarters in London and Melbourne, had allowed "a vast distance" to develop between its leadership and the Pilbara "where they make 75% of their earnings."
"There's no one on that board with any real understanding of the Aboriginal groups who own the country on which they operate," Wyatt, who is also the state's aboriginal affairs minister, told public broadcaster ABC.
"That, for me, screams risk, and it's something I am stunned hasn't been picked up over the years."
Written by Conny Waters - AncientPages.com Staff Writer
More From Ancient Pages
-
 12 Masonic Symbols Explained
Ancient Symbols | Jul 2, 2018
12 Masonic Symbols Explained
Ancient Symbols | Jul 2, 2018 -
 On This Day In History: Famous British Archaeologist And Egyptologist Sir Flinders Petrie Born – On June 3, 1853
News | Jun 3, 2016
On This Day In History: Famous British Archaeologist And Egyptologist Sir Flinders Petrie Born – On June 3, 1853
News | Jun 3, 2016 -
 Strange Medieval Figurine With A Crown On The Head And A Falcon On The Arm – Is It A King Or A Queen?
Archaeology | Dec 16, 2021
Strange Medieval Figurine With A Crown On The Head And A Falcon On The Arm – Is It A King Or A Queen?
Archaeology | Dec 16, 2021 -
 What Caused The Year Without A Summer In 1816?
Ancient History Facts | Sep 17, 2018
What Caused The Year Without A Summer In 1816?
Ancient History Facts | Sep 17, 2018 -
 Necropolis of Porta Nola, Pompeii – new discoveries
Civilizations | Aug 30, 2015
Necropolis of Porta Nola, Pompeii – new discoveries
Civilizations | Aug 30, 2015 -
 Pompey The Great: One Of Roman Empire’s Most Successful Military Commanders
Featured Stories | Jun 14, 2019
Pompey The Great: One Of Roman Empire’s Most Successful Military Commanders
Featured Stories | Jun 14, 2019 -
 Neanderthals’ History Retrieved From Cave Sediments In Siberia And Spain – New Method
Archaeology | Apr 19, 2021
Neanderthals’ History Retrieved From Cave Sediments In Siberia And Spain – New Method
Archaeology | Apr 19, 2021 -
 Luxor – Ever-Lasting Legacy Of The Ancient Egyptian Civilization And The Pharaohs
Featured Stories | Mar 29, 2021
Luxor – Ever-Lasting Legacy Of The Ancient Egyptian Civilization And The Pharaohs
Featured Stories | Mar 29, 2021 -
 The Battle Of Anghiari – Lost Painting Of Leonardo Da Vinci – One Of Art History’s Greatest Mysteries
Artifacts | Jan 24, 2018
The Battle Of Anghiari – Lost Painting Of Leonardo Da Vinci – One Of Art History’s Greatest Mysteries
Artifacts | Jan 24, 2018 -
 Hammurabi: The Great King Of Babylon And His Laws
Civilizations | Oct 21, 2016
Hammurabi: The Great King Of Babylon And His Laws
Civilizations | Oct 21, 2016 -
 Ice Age Cycles Played A Key Role In Early Human Interbreeding
DNA | Oct 19, 2023
Ice Age Cycles Played A Key Role In Early Human Interbreeding
DNA | Oct 19, 2023 -
 Advanced Ancient Technology – Talos A Greek Robot Created By The God Of The Forge
Featured Stories | Jun 28, 2014
Advanced Ancient Technology – Talos A Greek Robot Created By The God Of The Forge
Featured Stories | Jun 28, 2014 -
 Delatores – Who Were The Professional Gossip Collectors In Ancient Rome?
Featured Stories | Mar 21, 2025
Delatores – Who Were The Professional Gossip Collectors In Ancient Rome?
Featured Stories | Mar 21, 2025 -
 11 Ancient Sacred Indian Symbols Explained
Ancient Symbols | Feb 19, 2017
11 Ancient Sacred Indian Symbols Explained
Ancient Symbols | Feb 19, 2017 -
 ‘Impossible’ Ancient Knowledge Of The Gods’ Star – First Observations – Part 1
Ancient Mysteries | Aug 29, 2021
‘Impossible’ Ancient Knowledge Of The Gods’ Star – First Observations – Part 1
Ancient Mysteries | Aug 29, 2021 -
 LIDAR Technology Reveals Secrets Of Ancient Maya Civilization
Archaeology | Feb 3, 2018
LIDAR Technology Reveals Secrets Of Ancient Maya Civilization
Archaeology | Feb 3, 2018 -
 Calakmul Was Powerful Ancient Maya Seat Of The Snake Kingdom
Featured Stories | Apr 15, 2019
Calakmul Was Powerful Ancient Maya Seat Of The Snake Kingdom
Featured Stories | Apr 15, 2019 -
 Archaeologists Highlight The Tartessos Culture’s Sustainable Construction Skills
Archaeology | Oct 4, 2024
Archaeologists Highlight The Tartessos Culture’s Sustainable Construction Skills
Archaeology | Oct 4, 2024 -
 Viking Children Were Buried With Extremely Sharp Knives – Afterlife Tools To Be Used In Valhalla?
Ancient History Facts | Nov 29, 2017
Viking Children Were Buried With Extremely Sharp Knives – Afterlife Tools To Be Used In Valhalla?
Ancient History Facts | Nov 29, 2017 -
 Mysterious Lost City Of The Tairona Hidden In The Jungles Of Colombia
Civilizations | Nov 9, 2018
Mysterious Lost City Of The Tairona Hidden In The Jungles Of Colombia
Civilizations | Nov 9, 2018
