Who Were The Ancient Maya Bat People?
Jan Bartek - AncientPages.com - Studies of ancient Maya codices, along with investigations of their glyphs and other important archaeological findings, reveal the Maya developed a special relationship with bats. The ancient Maya did not fear bats.
On the contrary, everything discovered so far indicated bats played a significant role in Maya religion and political organizations.
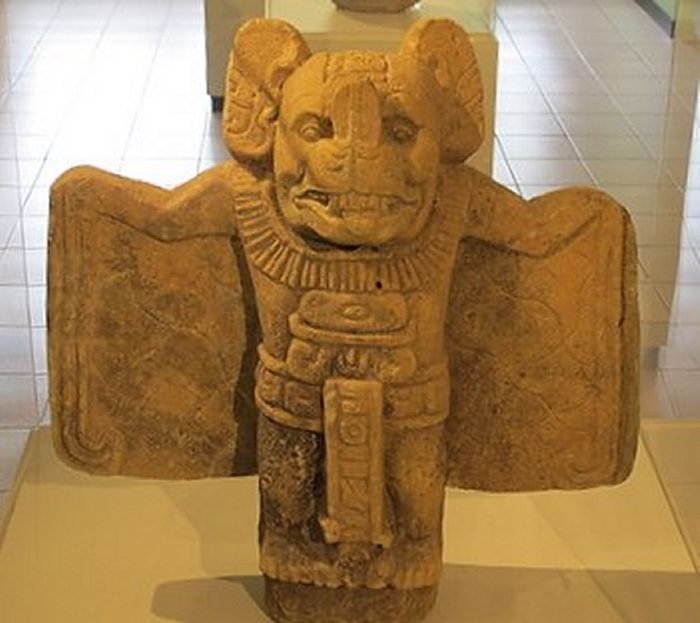
Pre-Columbian Maya bat god sculpture in Museo Popol Vuh in Guatemala City. Credit: Tracy Barnett - CC BY-SA 2.0
Among the people of this Mesoamerican civilization, three separate groups worshipped a bat deity. Two of these groups were so-called ancient Maya bat clans.
"Two species of bats native to the lowlands were of importance to the Maya: left-nosed bats of the family of Phyllostomatide and the vampire bat, Desmodus rufus." 1
Camazotz – The Ancient Maya Death Vampire
"In ancient Maya beliefs, Camazotz (Camoazotz) was a vampire bat god. Camazotz means "death bat" in the Quiché Maya language.
Associated with night, death, and sacrifice, Camazotz was often depicted holding his victim and a knife.
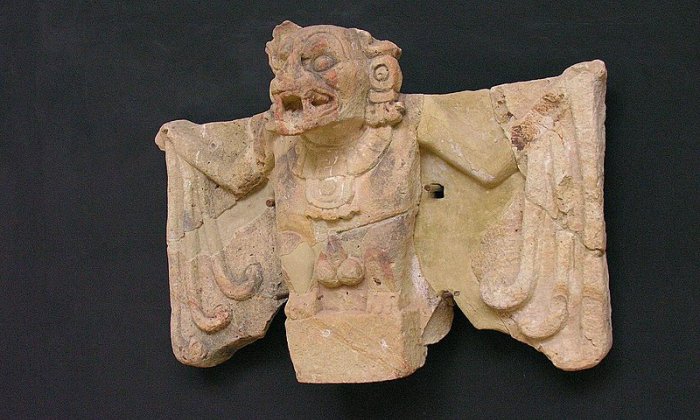
Camazotz is associated with the underworld, death, and sacrifice. The bat sculpture was found in the 1930’s, fallen from Structure 20 on the east edge of the Acropolis. Copan, Honduras. Credit: Dennis Jarvis - CC BY-SA 2.0
The Maya considered him a terrifying god who served death and ruled the domain of twilight. He lived in bloody grottoes and other dark places that people tried to avoid for fear of disturbing him.
In the beginning, bats in pre-Columbian cultures were not associated with evil. They were believed to be powerful creatures, spirits, and even gods. For example, in the Tajin pre-Columbian stone sculptures of Veracruz, vampire bats are depicted as gods and are also mentioned in epic myths and in the book of creation, "Popol Vuh".
In one story, Camazotz, a "death bat" takes the head of one of the twin heroes, who entered his underworld domain, and this head is later used in the ritual ball game." 2
Ancient Maya Bat People
"One division (clan?) of the Cakchiquel Maya of the highlands of Guatemala was called Zotzil, belonging to the bat, and its deity was a bat. Again, the Zotzil Maya lived, and still live, on the plateau of Chiapas. Formerly, they called themselves Zotzil uinic, batmen, claiming their ancestors found a stone bat which they took as their God. Their chief town was called Zinacantlan, a place of bats, by Nahuatl merchants from the valley of Mexico, a name which the modern town retains.
Finally, the emblem glyph of the great site of Copan, Honduras, is a bat with the addition of certain secondary elements, and stone representations of bats decorated one important temple at that site. Moreover, a man in the guise of a bat is one of the twelve dignitaries, half of whom are in animal guises, carved on the side of Altar T, Copan, and clearly representing important gatherings.
Thus there were three widely separated Maya groups who worshipped a bat deity. In two cases the groups called themselves bat people, and archaeological evidence suggests that the third groups may also have done so. There is weak evidence for totemic clans among the Maya, but possibly these bat groups fit into such pattern." 1
Ancient Jade Mask Of The Zapotec Bat God
Thousands of years ago, the Zapotec people built their magnificent city Monte Albán on a vast artificially flattened hilltop overlooking Oaxaca.
"Monte Albán (in Spanish: White Mountain) was the first capital of the Zapotecs, the 'city of temples' - the second-largest ceremonial center in Mexico after Teotihuacan.
The site consists of a huge rectangular area, the Grand Plaza, enclosed by groups of pyramids and other buildings laid out in precise geometrical relationships. It gives the appearance of being a place of harmony. Its proportion emerges from a well-ordered and symmetrical plan." 3
Ancient jade mask of the bat god worshipped by the Zapotec. Left: Credit: Adrian Hernandez - CC BY-SA 4.0 - Right: Detail of Bat God Figure - Oaxaca Hall - Museum of Anthropology - Mexico City - Mexico. Credit: Adam Jones - CC BY-SA 2.0
While excavating at Monte Albán, archaeologists discovered a curious ancient jade mask that most likely depicts the bat God of the Zapotec people.
Like the Maya, the "Zapotec of Oaxaca seems to have paid attention to a bat deity, for the main figure on many f their funerary urns is a bat deity, and small vases with the claws of bats are common. In one case a bat is seated on the top of a pyramid modeled in clay, ample evidence that the creature was a deity." 1
People in Mesoamerica held bats were held in high regard, which explains why even clans followed a particular deity, like bat clans we discussed in this article.
Written by Jan Bartek - AncientPages.com Staff Writer
Updated on November 2, 2023
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
Expand for references- Eric S. Thompson. "Maya Hieroglyphs of the Bat as Metaphorgrams." Man, New Series, 1, no. 2 (1966): 176-84.
- Sutherland - Camazotz: 'Death Bat' Vampire God In Ancient Maya Beliefs, AncientPages.com
- Sutherland - Mystery Of Monte Albán – Ancient City 'At The Foot Of The Heavens' Built By The Zapotecs, AncientPages.com
More From Ancient Pages
-
 Controversial Discovery Of 5,7-Million-Year-Old Footprints On Crete Could Re-Write History Of Human Evolution
Archaeology | Sep 5, 2017
Controversial Discovery Of 5,7-Million-Year-Old Footprints On Crete Could Re-Write History Of Human Evolution
Archaeology | Sep 5, 2017 -
 Face Of Norwegian Boy Who Lived 8,000 Years Ago Reconstructed
Archaeology | Mar 16, 2023
Face Of Norwegian Boy Who Lived 8,000 Years Ago Reconstructed
Archaeology | Mar 16, 2023 -
 Cimmerians – Ancient People Searching For A Home
Civilizations | Feb 11, 2019
Cimmerians – Ancient People Searching For A Home
Civilizations | Feb 11, 2019 -
 Hoard Of Roman Bronze Coins Turns Out To Be Offering For Safe Crossing
Archaeology | Jul 2, 2021
Hoard Of Roman Bronze Coins Turns Out To Be Offering For Safe Crossing
Archaeology | Jul 2, 2021 -
 On This Day In History: Ramesses II Became Pharaoh Of Ancient Egypt – On May 31, 1279 BC
News | May 31, 2016
On This Day In History: Ramesses II Became Pharaoh Of Ancient Egypt – On May 31, 1279 BC
News | May 31, 2016 -
 The Aztec Sun Stone And Medusa Reveal An Intriguing Connection – Surprising Discovery – Part 1
Aztec Mythology | Jul 30, 2018
The Aztec Sun Stone And Medusa Reveal An Intriguing Connection – Surprising Discovery – Part 1
Aztec Mythology | Jul 30, 2018 -
 Jan Hus: Czech Reformer And Bohemian Religious Leader Was Burned At Stake For Heresy
Featured Stories | Dec 17, 2019
Jan Hus: Czech Reformer And Bohemian Religious Leader Was Burned At Stake For Heresy
Featured Stories | Dec 17, 2019 -
 Historic Event – Exeter Museum Returns Ceremonial Dress Of Famous Chief Crowfoot To Canada’s Siksika People
Artifacts | May 20, 2022
Historic Event – Exeter Museum Returns Ceremonial Dress Of Famous Chief Crowfoot To Canada’s Siksika People
Artifacts | May 20, 2022 -
 A 2,700-Year-Old Urartians’ Ayanis Castle And Haldi Temple – Soon An Open-Air Museum
Archaeology | Aug 10, 2020
A 2,700-Year-Old Urartians’ Ayanis Castle And Haldi Temple – Soon An Open-Air Museum
Archaeology | Aug 10, 2020 -
 Extremely Rare Medieval Folding Chair Reveals Its Secrets
Archaeology | Oct 13, 2023
Extremely Rare Medieval Folding Chair Reveals Its Secrets
Archaeology | Oct 13, 2023 -
 ‘King Arthur’s Hall’ Is 4,000 Years Older Than Previously Thought
Archaeology | Nov 12, 2024
‘King Arthur’s Hall’ Is 4,000 Years Older Than Previously Thought
Archaeology | Nov 12, 2024 -
 Ancient Thriving Market Of Khan al-Tujjar (The Merchants’ Caravanserai) Discovered In Lower Galilee
Archaeology | Feb 20, 2024
Ancient Thriving Market Of Khan al-Tujjar (The Merchants’ Caravanserai) Discovered In Lower Galilee
Archaeology | Feb 20, 2024 -
 1,700-Year-Old Roman Bust Excavated In Ancient City Of Soli Pompeiopolis In Turkey
Archaeology | Jul 19, 2018
1,700-Year-Old Roman Bust Excavated In Ancient City Of Soli Pompeiopolis In Turkey
Archaeology | Jul 19, 2018 -
 Tiger Cave: Rock-Cut Hindu Temple Complex Dated To East India’s Pallava Empire
Featured Stories | Jan 19, 2017
Tiger Cave: Rock-Cut Hindu Temple Complex Dated To East India’s Pallava Empire
Featured Stories | Jan 19, 2017 -
 Eye Of Horus – Powerful, Ancient Egyptian Symbol With Deep Meaning
Ancient Symbols | Jan 21, 2019
Eye Of Horus – Powerful, Ancient Egyptian Symbol With Deep Meaning
Ancient Symbols | Jan 21, 2019 -
 Michael Scott – Fascinating Wizard Who Tutored The Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II
Featured Stories | Mar 7, 2025
Michael Scott – Fascinating Wizard Who Tutored The Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II
Featured Stories | Mar 7, 2025 -
 On This Day In History: Sir Thomas Brisbane, Astronomer, Soldier And Governor Was Born – On July 23, 1773
On This Day In History | Jul 23, 2016
On This Day In History: Sir Thomas Brisbane, Astronomer, Soldier And Governor Was Born – On July 23, 1773
On This Day In History | Jul 23, 2016 -
 Mysterious Voynich Manuscript Was Written In Two Languages – Scientists Say
Archaeology | Apr 24, 2017
Mysterious Voynich Manuscript Was Written In Two Languages – Scientists Say
Archaeology | Apr 24, 2017 -
 How Did Norman Conquest Of 1066 Affect Everyday People’s Eating Habits?
Archaeology | Jul 7, 2020
How Did Norman Conquest Of 1066 Affect Everyday People’s Eating Habits?
Archaeology | Jul 7, 2020 -
 Cult Of Zeus Discovered In The Ancient City Of Metropolis
Archaeology | Dec 21, 2015
Cult Of Zeus Discovered In The Ancient City Of Metropolis
Archaeology | Dec 21, 2015



