‘Joyeuse’ – Legendary Sword With Relics Of Saints Was A Private Treasure Of Emperor Charlemagne
A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com - Many legendary weapons have been described in ancient documents and books. Some were authentic weapons, and others gained a mythical status that inspired artisans who created weapons for famous knights and warriors over centuries.
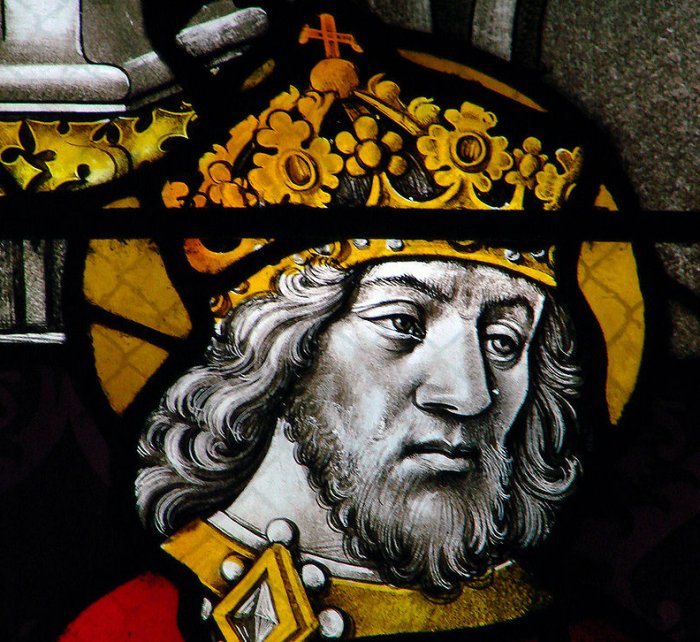
One such weapon is "Joyeuse" (which in French means "joyful") and is widely known as the legendary sword of Emperor Charlemagne. The fascinating fate of this sword can be found both in history and mythology, and these two sources of our knowledge lead us to one of the most dominating European rulers after the fall of the Roman Empire.
The crown jewels - Blaise Alexandre Desgoffe. Credit: Public Domain
Like Durendal and curtana, also an excellent weapon, the sword "Joyeuse" is mentioned in the famous French poem the Song of Roland," which makes it even more challenging to distinguish the truth about it from fiction.
This beautiful one-handed sword with a flat, double-edged, sharp wedge was forged about 802 AD by the famous blacksmith Galas, and it took three years to create this masterpiece. Designed for use with a shield held in the other hand, "Joyeuse" was initially decorated with dragons and later, with fleur-de-lis, a symbol associated with French royalty. However, this symbol was withdrawn for the coronation ceremony of Napoleon.
Charlemagne's mysterious sword was said to contain the relics of saints. Its magical power gave protection to the owner from death by poison. It could change color thirty times a day, and the sword blinded the enemy by shining brightly in the sun. It was almost the same with Excalibur, King Arthur's famous but legendary sword.
In the Christian emperor of the West, Charlemagne's hand, "Joyeuse," was not only a dangerous weapon but deadly. According to the 11th-century poem known as the "Song of Roland," the sword "Joyeuse" also took part in the Battle of Roncevaux Pass, between the rear guard of the Frankish troops of King Charlemagne, led by Count Roland, and the Basque Highlanders. At the Emperor Charlemagne's side hung "Joyeuse," "a sword such as none could match, and which changed its color thirty times a day…."
The sword was known for its various powers, one of which was the ability to spread a radiance stronger than the sun, capable of blinding entire armies standing before it.
In this battle on 15 August 778, most Franks died, including Count Roland himself.
In the Cathedral of Moulins, France, the end of the 15th century. Photo: Vassil/Wikipedia
Tradition has it that Charlemagne lost his sword once during a battle and promised enormous earthly possessions to whoever would return his personal and priceless treasure to him. One of the monarch's soldiers found the sword in the region called Ardèche (southeastern France). The emperor then kept his word. He drove the weapon to the ground and proclaimed his knight the ruler of this land, which he named "Joyeuse" after his sword.
The sword's fate after the death of Charlemagne in 814 remains unknown.
However, it became a national treasure used during the coronation of French kings. It appeared in 1270 in the cathedral of Reims during the coronation ceremony of Philip III The Bold. Later, "Joyeuse" played an essential role during the coronation of many monarchs in the following centuries, including the famous Louis XIV, also known as the enthronement as the Sun King, the longest-reigning monarch in European history.
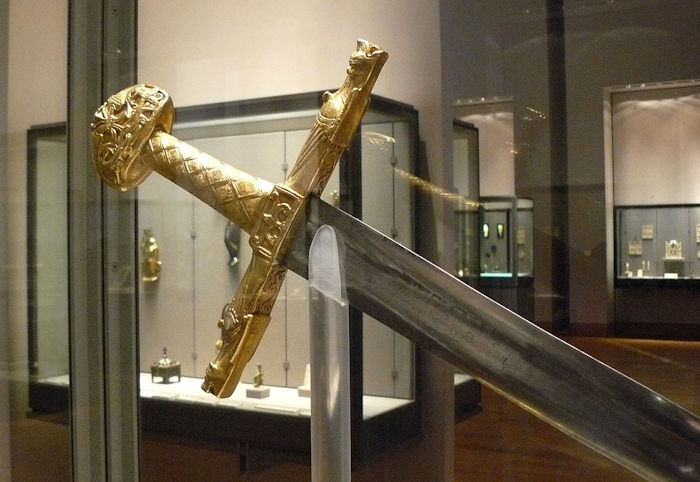
Joyeuse, the famous sword of Charlemagne, on display in the Louvre, France. Credit: Siren-Com - Public Domain
All this time, the sword was kept in Saint-Denis, in the monastery, under the watchful eye of the monks. The blade, which ceased to serve as a weapon, was subjected to many cosmetic procedures over the following years. The sword received a more prestigious look. Other artisans added numerous ornaments and gave the sword's head, handle, irons, and sheath a more prestigious look. All these changes have made Joyeuse an exciting mix of aesthetic styles from all over Europe.
Does The Louvre Have Only A Replica Of "Joyeuse"?
No one knows for sure. After the French Revolution (1793), the sword was transported to the Louvre museum in Paris, where it remains. The last coronation with the sword's participation was in 1824 and concerned Charles X.
Today, some believe that the weapon in the Louvre is only a replica, but no official document confirms this.
The Joyeuse remains one of the most famous swords of the French state, which was the only one used during royal coronations for many centuries, representing a symbol of power and glory, but also prestige and elegance, as it has retained its dazzling appearance to this day. It is one of the most frequently copied weapons from the past.
Updated on July 19, 2022
Written by – A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com Senior Staff Writer
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
Expand for referencesReferences:
Janet L. Nelson, King and Emperor: A New Life of Charlemagne
Thomas Bulfinch, Legends of Charlemagne, or Romance of the Middle Ages
Ewart Oakeshott, Records of the Medieval Sword
More From Ancient Pages
-
 Rare Discovery Of More Than 18,000 Inscribed Pot Sherds Document Life In Ancient Egypt
Archaeology | Jan 31, 2022
Rare Discovery Of More Than 18,000 Inscribed Pot Sherds Document Life In Ancient Egypt
Archaeology | Jan 31, 2022 -
 Luxor – Ever-Lasting Legacy Of The Ancient Egyptian Civilization And The Pharaohs
Featured Stories | Mar 29, 2021
Luxor – Ever-Lasting Legacy Of The Ancient Egyptian Civilization And The Pharaohs
Featured Stories | Mar 29, 2021 -
 Anartes: Forgotten Celtic Tribe And The Hercynian Forest With Strange Animals
Featured Stories | Jun 18, 2024
Anartes: Forgotten Celtic Tribe And The Hercynian Forest With Strange Animals
Featured Stories | Jun 18, 2024 -
 World’s Oldest Tattoos Discovered On Egyptian Mummies Re-Write History Of Tattoos
Archaeology | Mar 2, 2018
World’s Oldest Tattoos Discovered On Egyptian Mummies Re-Write History Of Tattoos
Archaeology | Mar 2, 2018 -
 Unsolved Mystery Of The Giant Footprints Outside The Ain Dara Temple
Featured Stories | Jun 7, 2014
Unsolved Mystery Of The Giant Footprints Outside The Ain Dara Temple
Featured Stories | Jun 7, 2014 -
 Secret Underground Chambers Of Caynton Caves And The Knights Templar Connection
Featured Stories | Aug 13, 2019
Secret Underground Chambers Of Caynton Caves And The Knights Templar Connection
Featured Stories | Aug 13, 2019 -
 Rare 1,400-Year-Old Temple Possibly Used By East Anglian Kings Discovered In Suffolk, UK
Archaeology | Nov 22, 2023
Rare 1,400-Year-Old Temple Possibly Used By East Anglian Kings Discovered In Suffolk, UK
Archaeology | Nov 22, 2023 -
 On This Day In History: Samuel Morey Patents The Internal Combustion Engine – On April 1, 1826
News | Apr 1, 2017
On This Day In History: Samuel Morey Patents The Internal Combustion Engine – On April 1, 1826
News | Apr 1, 2017 -
 Unique And Unusually Large 8000-Year-Old Building Discovered At Çatalhöyük Site, Turkey
Archaeology | Sep 26, 2022
Unique And Unusually Large 8000-Year-Old Building Discovered At Çatalhöyük Site, Turkey
Archaeology | Sep 26, 2022 -
 Hacksilber Hoard Dated To 11th Century BC: Eastern Mediterranean Silver Trade Reconstructed
Archaeology | Jul 5, 2021
Hacksilber Hoard Dated To 11th Century BC: Eastern Mediterranean Silver Trade Reconstructed
Archaeology | Jul 5, 2021 -
 Early Neolithic High Mountain Settlers Were Busy With Complex Livestock And Farming Activities – New Study
Archaeology | Dec 22, 2023
Early Neolithic High Mountain Settlers Were Busy With Complex Livestock And Farming Activities – New Study
Archaeology | Dec 22, 2023 -
 Early Farmers On The Baltic Coast Incorporated Fish Into Their Diets 6,000 Years Ago
Archaeology | Oct 17, 2023
Early Farmers On The Baltic Coast Incorporated Fish Into Their Diets 6,000 Years Ago
Archaeology | Oct 17, 2023 -
 Ancient DNA Reveals Unknown Genetic Exchanges Between North And South America
Archaeology | Nov 12, 2018
Ancient DNA Reveals Unknown Genetic Exchanges Between North And South America
Archaeology | Nov 12, 2018 -
 Was Princess Tadukhipa Of The Mitanni Kingdom Queen Nefertiti?
Civilizations | Mar 15, 2016
Was Princess Tadukhipa Of The Mitanni Kingdom Queen Nefertiti?
Civilizations | Mar 15, 2016 -
 Unique Flagship ‘Gribshunden’: Spectacular Discoveries
Archaeology | Oct 2, 2019
Unique Flagship ‘Gribshunden’: Spectacular Discoveries
Archaeology | Oct 2, 2019 -
 Seven Fires Prophecy Of The Anishinaabe People And The Future Of The Turtle Island – Are Humans Standing At The Crossroads?
Myths & Legends | Feb 14, 2019
Seven Fires Prophecy Of The Anishinaabe People And The Future Of The Turtle Island – Are Humans Standing At The Crossroads?
Myths & Legends | Feb 14, 2019 -
 Why Is The Black Prince Still A Controversial Historical Figure?
Ancient History Facts | Aug 15, 2019
Why Is The Black Prince Still A Controversial Historical Figure?
Ancient History Facts | Aug 15, 2019 -
 Unknown Energy Source Created The Image On The Shroud Of Turin Scientists Suggest
Archaeology | May 12, 2012
Unknown Energy Source Created The Image On The Shroud Of Turin Scientists Suggest
Archaeology | May 12, 2012 -
 Anasazi: Sophisticated Civilization That Disappeared Or Evolved Into American Indians Of Southwest
Civilizations | Dec 3, 2016
Anasazi: Sophisticated Civilization That Disappeared Or Evolved Into American Indians Of Southwest
Civilizations | Dec 3, 2016 -
 Mystery Of Mexico’s Bizarre Mummy May Never Be Solved
Featured Stories | Sep 17, 2024
Mystery Of Mexico’s Bizarre Mummy May Never Be Solved
Featured Stories | Sep 17, 2024



