Etruscan City Of Cerveteri With Magnificent House-Like Tombs Decorated With Scenes From Life And Death
A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com - Today, the town of Cerveteri is particularly famous for the numerous Etruscan cemeteries located on the surrounding hills.
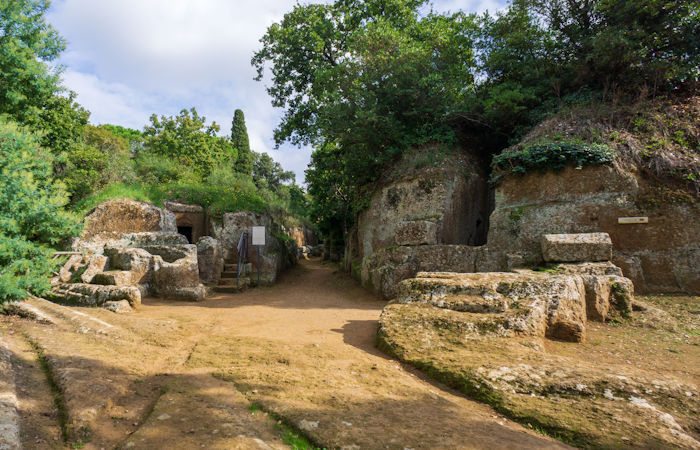
Etruscan necropolis Cerveteri Rome Province, Italy. Credit: Adobe Stock - Massimo
We know about the Etruscan civilization, after being conquered by Rome, thanks to its tombs that exist in massive necropolises outside of the Etruscan cities.
Necropoli were massive graveyards in which the Etruscans buried their family members to preserve their bodies and souls. Other surviving sources of their architecture are the remains of temples, city walls, houses, and even roads carved in stone.
The ancient city of the Etruscans, Caere (now Cerveteri) was founded according to tradition by Pelasgians in c. 1400 BC.
Cerveteri, a town on the West coast of Italy, is located in the province of Rome in the Italian region Lazio, just about 40 km North of Rome.
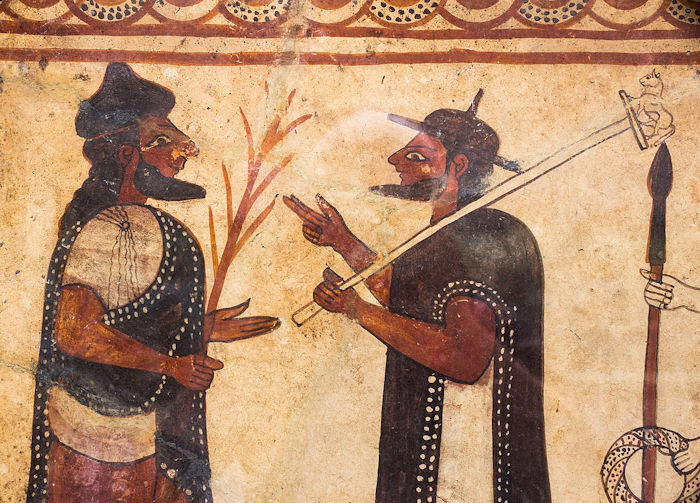
Painting on terracotta panels of the judgement of Paris from Cerveteri (Boccanera tomb). Credit: ArchaiOptix - CC BY-SA 4.0
Known by the Etruscans as Cisra, it was once one of the metropolitan areas of the ancient Mediterranean. The Romans called it Caere, and at that time, the Etruscan city was one of the most important Etruscan cities, with an area more than 15 times larger than the town of Cerveteri, as we call it today.
A rich and powerful city was an ally of Carthage and developed good relationships with its southern neighbors, the Romans. Formed from the Villanova culture settlement, Cerveteri belonged to the Federation of 12 Etruscan cities and was one of the richest and most important in Etruria.
It flourished in the 7th century BC and the 6th century BC, thanks to maritime trade through the Etruscan ports in Altium (now known as Palo), Pyrgi (Santa Severa), and Punicum (Santa Marinella). At its height, around 600 BC, the city's population was most probably from 25,000 to 40,000 people.
Cerveteri Became Part Of A Coalition Fighting The Romans
In the 3rd century BC, Cerveteri was part of a coalition fighting the Romans; after the defeat of 273 BC, the flourishing Etruscan city lost half of its territory to pass under the authority of Rome in 90 BC.
It received only incomplete civil rights - "ius sine Suffragio" (without the right to vote). All those who lived in Caere and did not have the right to vote were called in Rome - caerites.
Due to close contact with Rome at the end of its long history, the Etruscan Caere became a sort of "satellite state" of the Roman capital and was eventually transformed into a prefecture in 273 BC.
During the decline of Etruscan cultures, also gradual decline of Cerveteri began in the 5th century BC. However, the sixth century BC marked the influence of Greek culture on Cerveteri, which became the main center of Ionian-Etruscan art.
Cerveteri And Etruscan Gigantic Tombs
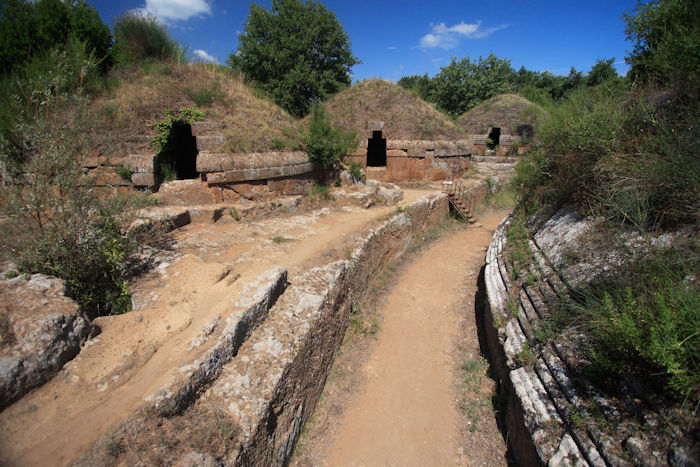
Necropolises, at first glance, resemble extinct cities and house-like graves, of which some resemble the Hobbit's household. Some of them have the shape of round bunkers; others form groups of mounds.
Cerveteri's rock-cut tombs imitate beautifully decorated houses, chambers with carved furniture, and decorations like frescoes, ceramics, and ancient paintings. Cerveteri's frescoes depict scenes from the life and death of the then-living Etruscans.
The ancient artists wanted to immortalize various scenes related to hunting, erotic acts, feasting, dancing, racing, and multiple faces of demons waiting for the dead.
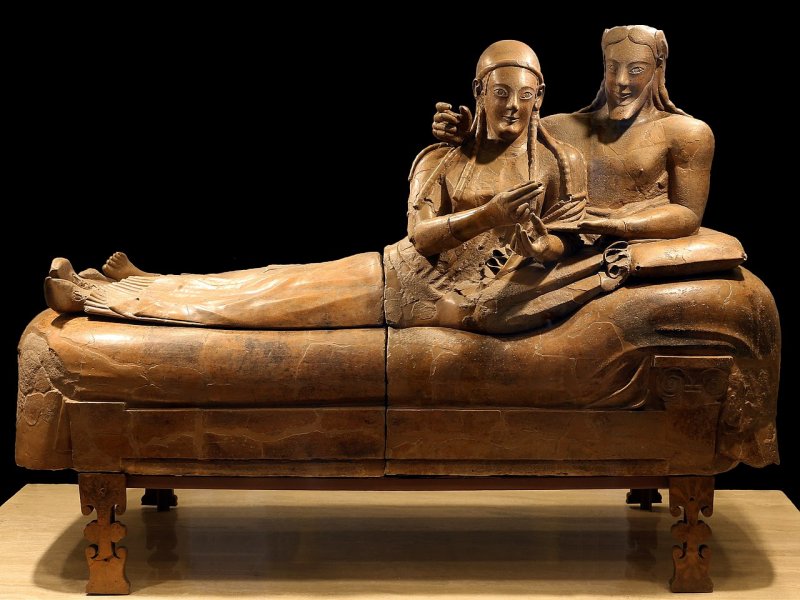 Sarcophagus of the Spouses from Caere, now in the National Etruscan Museum at Villa Giulia in Rome. Image credit: Sailko - CC BY-SA 4.
Sarcophagus of the Spouses from Caere, now in the National Etruscan Museum at Villa Giulia in Rome. Image credit: Sailko - CC BY-SA 4.
All these treasures represent famous Etruscan artwork, of which one of the most famous is the Sarcophagus of the Spouses.
Religious Traditions Of Etruscan People And Network Of Corridors And Stairways
The city of Cerveteri has yet another fascinating area. It is a religious complex in the city's center, known as the "hypogeum of Clepsina," containing a network of corridors and stairways and an underground room with frescoes, sketches, and inscriptions. The hypogeum represented the cult place of the community's ancestors and the seat of rituals associated with its foundation, its destiny, and the people's religious and cosmological beliefs.
Cerveteri necropolis. Credit: Adobe Stock - francescodemarco
There is still much to discover in the region of Cerveteri, Veies, Tarquinia, or Vulci necropolises of Etruria, located in an area that covered part of what are now Tuscany, Lazio, and Umbria.
Their constructions are essential for understanding the Etruscans' mythology, religion, everyday life, and architecture.
For now, in Tarquinia, approximately 6,000 burial sites have been discovered, though not all are possible to visit and contemplate the atmosphere of ancient Etruscan people's atmosphere of life, death, and traditions.
Written by – A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com Senior Staff Writer
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
Expand for referencesReferences:
Haynes S. Kulturgeschichte der Etrusker
History, Captivating. The Etruscans
More From Ancient Pages
-
 Jomon Period: Triangle-Shaped Stone Artifact Depicting Human Face Found For The First Time In Japan
Archaeology | Dec 25, 2017
Jomon Period: Triangle-Shaped Stone Artifact Depicting Human Face Found For The First Time In Japan
Archaeology | Dec 25, 2017 -
 Was The Discovery Of Biblical Abel’s Giant Grave In Syria Covered-Up?
Ancient Mysteries | Oct 28, 2014
Was The Discovery Of Biblical Abel’s Giant Grave In Syria Covered-Up?
Ancient Mysteries | Oct 28, 2014 -
 Birch Bark Tar Production Techniques Offer Evidence Neanderthals Had Cognitive Skills Similar To Modern Thinking
Archaeology | Sep 26, 2023
Birch Bark Tar Production Techniques Offer Evidence Neanderthals Had Cognitive Skills Similar To Modern Thinking
Archaeology | Sep 26, 2023 -
 Knights Templar – Strict Rules For Clothing And Eating Habits
Featured Stories | Jan 2, 2018
Knights Templar – Strict Rules For Clothing And Eating Habits
Featured Stories | Jan 2, 2018 -
 Mysterious Ancient Egyptian Royal Tomb Sheds Light On Little-Known Abydos Dynasty
Archaeology | Mar 17, 2025
Mysterious Ancient Egyptian Royal Tomb Sheds Light On Little-Known Abydos Dynasty
Archaeology | Mar 17, 2025 -
 Young Boy Discovers Rare Ancient Roman Treasure In Sussex, UK
Archaeology | Apr 15, 2024
Young Boy Discovers Rare Ancient Roman Treasure In Sussex, UK
Archaeology | Apr 15, 2024 -
 Beautiful 2,300-Year-Old Gold Ring Found In The City Of David
Archaeology | May 30, 2024
Beautiful 2,300-Year-Old Gold Ring Found In The City Of David
Archaeology | May 30, 2024 -
 Llangernyw Yew: Chilling Prophecy Of The Oldest Tree In Wales
Featured Stories | Oct 28, 2022
Llangernyw Yew: Chilling Prophecy Of The Oldest Tree In Wales
Featured Stories | Oct 28, 2022 -
 Ancient Mesoamerican Board Games ‘Patollis’ Discovered In Mexico
Archaeology | Sep 9, 2024
Ancient Mesoamerican Board Games ‘Patollis’ Discovered In Mexico
Archaeology | Sep 9, 2024 -
 On This Day In History: Johannes Kepler ‘Father Of Modern Astronomy’ Was Born – On Dec 27, 1571
News | Dec 27, 2016
On This Day In History: Johannes Kepler ‘Father Of Modern Astronomy’ Was Born – On Dec 27, 1571
News | Dec 27, 2016 -
 Re-Discovered Ancient Ksâr ‘Akil Fossils Shed New Light On Human Evolution
Archaeology | Mar 28, 2023
Re-Discovered Ancient Ksâr ‘Akil Fossils Shed New Light On Human Evolution
Archaeology | Mar 28, 2023 -
 Okanagan Indians’ Fascinating Myth Of A Lost Paradise Island Inhabited By White Giants – Are Their Descendants Living in British Columbia?
Featured Stories | Mar 27, 2025
Okanagan Indians’ Fascinating Myth Of A Lost Paradise Island Inhabited By White Giants – Are Their Descendants Living in British Columbia?
Featured Stories | Mar 27, 2025 -
 Mystery Of The Unique Tiarp Dolmen – One Of Oldest The Stone Burial Chambers In Scandinavia
Archaeology | Jan 30, 2024
Mystery Of The Unique Tiarp Dolmen – One Of Oldest The Stone Burial Chambers In Scandinavia
Archaeology | Jan 30, 2024 -
 Kali – Hindu Goddess Of Death, Fear And Horror Who Destroys Ignorance, Evil And Establishes World Order
Featured Stories | Sep 28, 2021
Kali – Hindu Goddess Of Death, Fear And Horror Who Destroys Ignorance, Evil And Establishes World Order
Featured Stories | Sep 28, 2021 -
 History Set In Stone – Maya Rulers Put Their Personal Stamp On Ancient Monuments
Archaeology | Sep 22, 2021
History Set In Stone – Maya Rulers Put Their Personal Stamp On Ancient Monuments
Archaeology | Sep 22, 2021 -
 Magical Adder Stone And Its Immense Power
Celtic Mythology | Jul 14, 2018
Magical Adder Stone And Its Immense Power
Celtic Mythology | Jul 14, 2018 -
 ‘Saimaluu-Tash’ Time Capsule: Largest Millennia-Old Collection Of Petroglyphs In Central Asia
Civilizations | Nov 20, 2018
‘Saimaluu-Tash’ Time Capsule: Largest Millennia-Old Collection Of Petroglyphs In Central Asia
Civilizations | Nov 20, 2018 -
 On This Day In History: Astronomer Johannes Kepler Observes Supernova – On Oct 17, 1604
News | Oct 17, 2016
On This Day In History: Astronomer Johannes Kepler Observes Supernova – On Oct 17, 1604
News | Oct 17, 2016 -
 Etowah Indian Mounds: A Legacy Of The Ancient Mississippian Culture
Featured Stories | Oct 9, 2018
Etowah Indian Mounds: A Legacy Of The Ancient Mississippian Culture
Featured Stories | Oct 9, 2018 -
 Ostrich Eggs Dated More Than 4,000 Years Discovered In Negev Desert Of Southern Israel
Archaeology | Jan 13, 2023
Ostrich Eggs Dated More Than 4,000 Years Discovered In Negev Desert Of Southern Israel
Archaeology | Jan 13, 2023



