Battle Of Visby – Death Came With King Atterdag’s Ships
A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com - Once upon a time, there was an important commercial center on Gotland, the island located in the Baltic Sea, approximately 90 kilometers east of mainland Sweden.
Credit: Adobe Stock - Archivist
Gotland's center of an extensive trading network stretched from Karelia in northern Finland down to the Caspian Sea in the south. The island flourished during Antiquity and Middle Ages, and its wealth in medieval times led to impressive architecture and local art development.
The death came in the summer of 1361. When a Danish army sailed eastward summer of 1361, the Swedish king Magnus Eriksson knew Gotland was in danger.
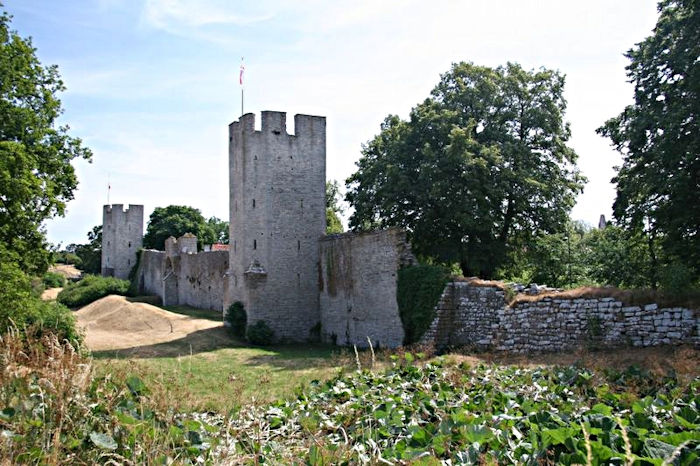
Picture of the Visby city wall, near the north gate. The main battle was fought within 300 meters of the city's fortifications. Credit: Benranton - Public Domain
He did what he could; he had issued a warning letter to the citizens of Gotland about a dangerous attack approaching the island of Gotland. The population of Gotland was preparing for the worst.
Early on the morning of Thursday, July 22, the enemy fleet was seen. The armada consisted of thirty ships, massive cogs, and smaller shells.
The rumor of the Danish attack spread rapidly across the island; soon, all church bells rang across the island – the danger was imminent.
Soon, the Danish king, Valdemar IV Atterdag, and his soldiers appeared on the horizon outside Visby's thick city walls.
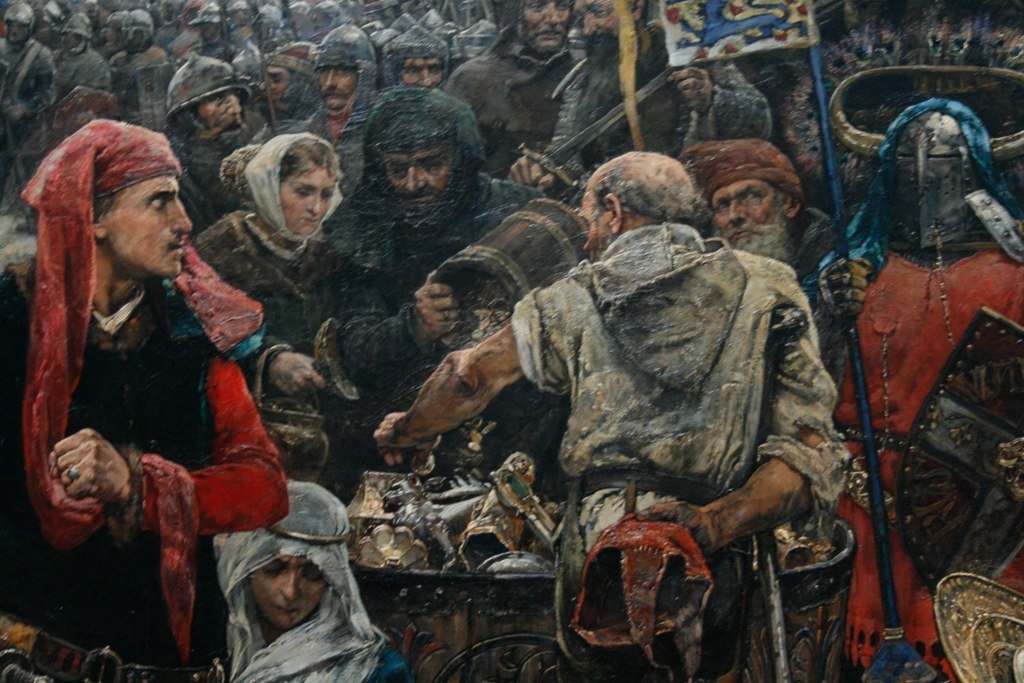
The cruel plundering of the island by King Valdemar definitely ended the island's prosperity. Credit: Carl Gustaf Hellqvist - Public Domain
They landed on the coast of Eksta Parish, Gotland, and the Danish troops moved towards Visby. The clashes began and culminated on July 27, just outside the city walls.
The main battle was fought within 300 meters of the city of Visby's fortifications. Roughly 1,800 Gotlanders had been killed, up to half of the participants - an exceptionally high loss ratio.
Following the devastating battle, the citizens of Visby decided to surrender to avoid further losses.
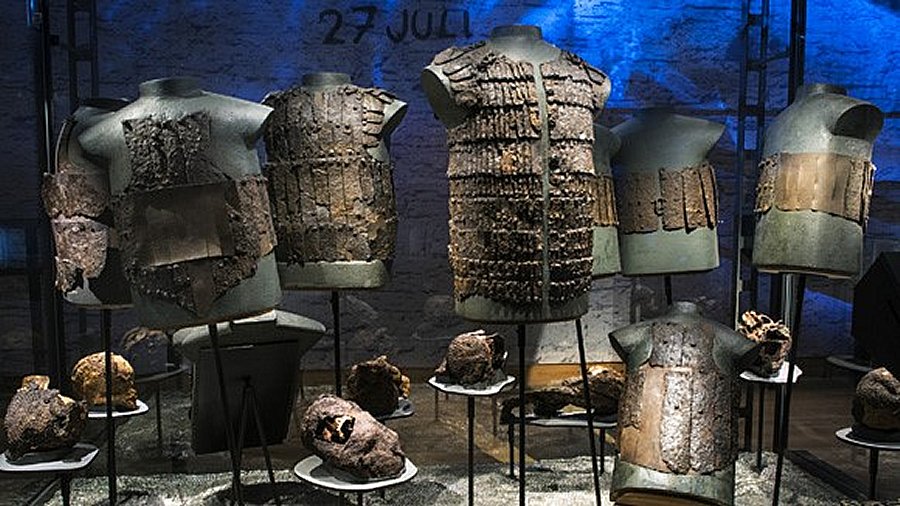
The exhibition "The massacre at the Great Wall, the Battle of Gotland in 1361" at the Historical Museum in Stockholm. "These findings are unique in the world, it is like a keyhole back to 1361. Photo: gotland.net/Historiska Museet Stockholm
Visby opened its gates to the victorious Danish army. Without outside help from fighting farmers, Visby would never be able to keep out Valdemar's forces.
Negotiations began. The inhabitants paid much of their wealth to King Valdemar to save the city from sacking. Despite the payment, the Danes still plundered several of the town's churches and monasteries on the island before they left. King Valdemar appointed sheriffs to govern Visby and then set sail again. It would take another year before Valdemar officially added "King of Gotland" to his many titles.
The cruel plundering of the island by King Valdemar definitely ended the island's prosperity.
However, one of Atterdag's ships carrying all the island's treasures sunk off the Carl islands west of Gotland.
Not long ago, a wood wreck was found outside the island Gotland, at a depth of 100 meters in a secret location between the two Baltic isles. Based on the sonar pictures, experts estimated that a small vessel was 28 meters long and 7 meters wide.
No cogs have ever been found in the area despite the extent of their use and the perfect conditions of the Baltic Sea for wreck preservation.
The seabed of the Baltic is flat, and the oxygen levels in the water are low enough to make it an ideal environment for wrecks to remain intact. Many shipwrecks were found in the Baltic Sea, according to researchers.
None of them, however, has been recognized as King Atterdag's lost ship with Gotland's treasures. The loot is resting somewhere in the underwater realm of the Baltic Sea near Gotland.
Only a few ancient written sources can tell about the Battle of Visby, Gotland. On the other hand, archaeological excavations have found out what happened on these tragic days of July 1361.
Outside Visby's city walls, archaeologists have unearthed five mass graves related to the tragic medieval battle.
The first grave was excavated in 1905, and each grave contained hundreds of victims; two more mass graves the research team investigated between 1909 and 1928.
One-third of the Gotland army were children, older men, and cripples. While the farmers were dying, the citizens of Visby just watched helplessly from the ramparts.
A few decades later, the memorial cross was erected on the mass graves.
Oral tradition is that the Danish king and his army raided southern Gotland for a month. On the return journey, some Danish ships with treasures are said to have been wrecked in a storm at the Karlsö islands - a group of islands off the west coast of Gotland that consists of Stora Karlsö and Lilla Karlsö.
People say that even today, when the weather is calm, you can see the treasures gleaming at the bottom of the sea. Is it symbolic revenge on the king, responsible for so much damage to the island and pain to the people of Gotland?
Written by – A. Sutherland AncientPages.com Staff Writer
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
Expand for referencesReferences:
Lingström, Maria (2007). Mästerby 1361- gutarnas strid mot Valdemar Atterdag.
More From Ancient Pages
-
 Biblical Cherubim – Sweet Angels Or Dangerous Creatures With A Hidden Agenda?
Ancient Mysteries | Jun 9, 2018
Biblical Cherubim – Sweet Angels Or Dangerous Creatures With A Hidden Agenda?
Ancient Mysteries | Jun 9, 2018 -
 Archaeologists Have A Lot Of Dates Wrong For North American Indigenous History
Archaeology | May 4, 2020
Archaeologists Have A Lot Of Dates Wrong For North American Indigenous History
Archaeology | May 4, 2020 -
 Top 5 Terrors Of The World’s Seas, Rivers And Lakes
Featured Stories | Mar 27, 2021
Top 5 Terrors Of The World’s Seas, Rivers And Lakes
Featured Stories | Mar 27, 2021 -
 10 Ancient Celtic Symbols Explained
Ancient Symbols | Sep 9, 2023
10 Ancient Celtic Symbols Explained
Ancient Symbols | Sep 9, 2023 -
 Two Scribes Penned 8th Century ‘Samaria Ostraca’ Inscriptions Unearthed In Samaria
Archaeology | Jan 23, 2020
Two Scribes Penned 8th Century ‘Samaria Ostraca’ Inscriptions Unearthed In Samaria
Archaeology | Jan 23, 2020 -
 Frightening Ancient Underground World Discovered In Tibet – Evidence Of A Lost Advanced Civilization?
Featured Stories | Feb 17, 2024
Frightening Ancient Underground World Discovered In Tibet – Evidence Of A Lost Advanced Civilization?
Featured Stories | Feb 17, 2024 -
 Third-Century Sculpture Of Roman Emperor Aurelian Unearthed In Bulgaria
Archaeology | Sep 5, 2018
Third-Century Sculpture Of Roman Emperor Aurelian Unearthed In Bulgaria
Archaeology | Sep 5, 2018 -
 Pre-Pharaonic Petroglyphs Used To Study Egyptian Cult Of The Gods
Archaeology | Mar 15, 2023
Pre-Pharaonic Petroglyphs Used To Study Egyptian Cult Of The Gods
Archaeology | Mar 15, 2023 -
 Who Were The Blue People Of Kentucky?
Featured Stories | Apr 5, 2022
Who Were The Blue People Of Kentucky?
Featured Stories | Apr 5, 2022 -
 Legendary Pirate Black Sam And His Ship Discovered Off The Coast Of Cape Cod
Archaeology | Feb 12, 2018
Legendary Pirate Black Sam And His Ship Discovered Off The Coast Of Cape Cod
Archaeology | Feb 12, 2018 -
 Honey-Collecting In Prehistoric West Africa From 3500 Years Ago – Pottery Examined
Archaeology | Apr 14, 2021
Honey-Collecting In Prehistoric West Africa From 3500 Years Ago – Pottery Examined
Archaeology | Apr 14, 2021 -
 10 Ancient Chinese Musical Instruments You Didn’t Know About
Featured Stories | Jan 20, 2016
10 Ancient Chinese Musical Instruments You Didn’t Know About
Featured Stories | Jan 20, 2016 -
 Advanced Ancient Knowledge Of Chemistry – From Chrome Plating To Nanotubes
Ancient Technology | Jun 12, 2019
Advanced Ancient Knowledge Of Chemistry – From Chrome Plating To Nanotubes
Ancient Technology | Jun 12, 2019 -
 Palnatoke – Founder Of The Jomsvikings Brotherhood, Legendary Danish Hero And Enemy Of King Harald Bluetooth
Historical Figures | Nov 2, 2016
Palnatoke – Founder Of The Jomsvikings Brotherhood, Legendary Danish Hero And Enemy Of King Harald Bluetooth
Historical Figures | Nov 2, 2016 -
 First Peoples’ Early Migration To Australia – Influenced By Evolving Landscapes
Archaeology | May 6, 2024
First Peoples’ Early Migration To Australia – Influenced By Evolving Landscapes
Archaeology | May 6, 2024 -
 Rare 1,600-Year-Old Wooden Pagan Idol Discovered In Ireland
Archaeology | Aug 16, 2021
Rare 1,600-Year-Old Wooden Pagan Idol Discovered In Ireland
Archaeology | Aug 16, 2021 -
 Indus Valley Civilization Far Ahead Of Its Time Has Baffled Scientists For Centuries
Ancient Technology | May 18, 2017
Indus Valley Civilization Far Ahead Of Its Time Has Baffled Scientists For Centuries
Ancient Technology | May 18, 2017 -
 In Ancient Times We Had Weeks Of Different Lengths
Ancient History Facts | Sep 6, 2016
In Ancient Times We Had Weeks Of Different Lengths
Ancient History Facts | Sep 6, 2016 -
 On This Day In History: Treaty Of Seville Signed – On Nov 9, 1729
News | Nov 9, 2016
On This Day In History: Treaty Of Seville Signed – On Nov 9, 1729
News | Nov 9, 2016 -
 Baffling Unexplained Encounters With Tiny Mysterious Creatures Feeding On Energy
Featured Stories | Feb 20, 2025
Baffling Unexplained Encounters With Tiny Mysterious Creatures Feeding On Energy
Featured Stories | Feb 20, 2025





