6,000-Year-Old Vast Settlement With Tools And Granite Structures Unearthed In Sotta, Corsica In France
Conny Waters - AncientPages.com - A team of archaeologists from INRAP (French National Institute for Preventive Archaeological Research) recently unearthed two Neolithic settlements of which one has well-preserved structures.
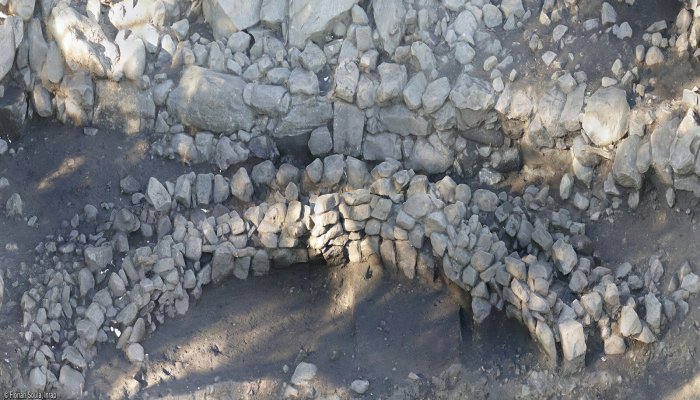
The excavataed arc was the best preserved of its kind at the site, experts said. Image credit: Florian Soula INRAP
INRAP researchers inform that the remains of this vast settlement are located on the slopes of the southern flank of Punta Campana, in Sotta, and include a large number of ancient artifacts.
In the first settlement that dates to the beginning of the fourth millennium B.C to about 6,000 years ago, researchers found a stone structure filled with remains of an obsidian cutting workshop. This part of the excavated place was found to be partially eroded.
The second settlement dates to the third millennium BC., about 4,000-5,000 years ago, it was better preserved, and there, the team uncovered a system of terraces, topped with an approximately 3-foot tall or fortified wall made of granite blocks, according to researchers. The structures were excavated between November 2022 and March 2023,.
General view of a bastion being excavated in Sotta (Southern Corsica) in 2023. © Florian Soula, Inrap
“The top of the excavation right-of-way presents a more complex organization, with a "bastion" supported by an imposing terrace wall, fully preserved and measuring about 0.9 to 1.2 m in height compared to the level of circulation preserved. This wall is built of large granite blocks with an upper base of blocks laid flat,” according to INRAP press release.
On the first terrace below it was a stone arc also made from granite blocks. The building techniques used in the arc indicate it was used as some kind of roof, but experts are investigating its exact purpose, they said. The excavataed arc was the best preserved of its kind at the site.
Within the terraced structure, researchers discovered a corridor and staircase that probably functioned as a passageway to the upper level of the system. .
Among the smaller remains were artifacts indicating artisan practices in daily life, researchers said. Florian Soula INRAP
Within the corridor, several vases were unearthed. A pear-shaped vase was among several vases discovered on the paving inside the wall of the terraced structure
Also, two other similar terraced systems were found at the site; but for now, their purpose is unclear. Possibly they were used for food storage, metallurgy, or other artisans' activities.
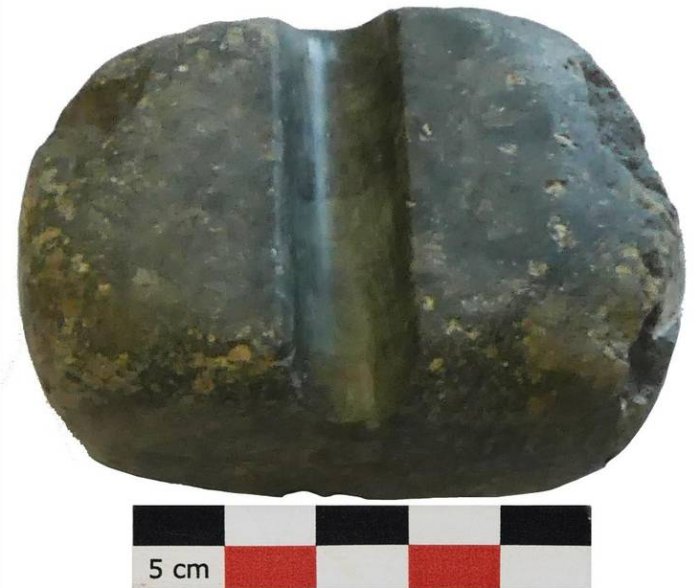
The excavating team discovered many unusual artefacts at the Neolithic site and particularly, in the terraced section. These include thousands of unusual copper and other metal artifacts, obsidian, quartz, pieces of flint, wheels, arrowheads; axes, and other metal objects.
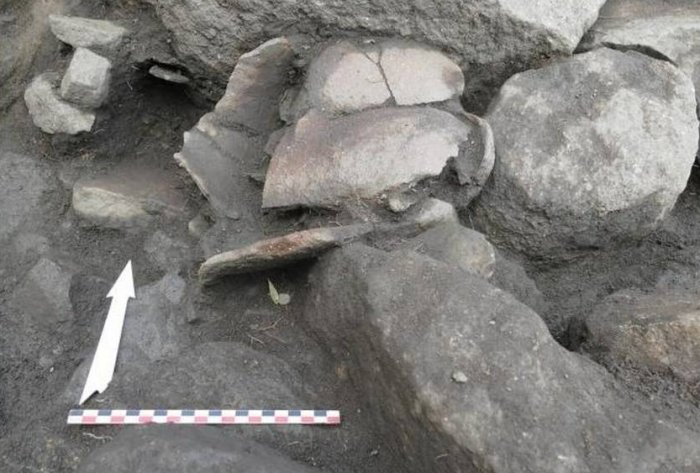 A storage vase was also found among the artifacts, experts said. Florian Soula INRAP
A storage vase was also found among the artifacts, experts said. Florian Soula INRAP
Some remains show traces of melting that took place at the site. There were also cattle teeth and rare cranial skeletal remains that seemed to have been burned, INRAP informed.
Other artifacts gave experts greater insight into life during the Neolithic era and at the settlement in particular. Among the smaller remains were artifacts indicating artisan practices in daily life, researchers said.
The artifacts indicate the presence of intense and/or long-term activities concerning all aspects of daily life and economy of Neolithic societies.
Further studies will no doubt will help to obtain give a greater view into ancient life of the ancient societies in Sotta on the island of Corsica.
Written by Conny Waters - AncientPages.com Staff Writer
More From Ancient Pages
-
 Central European Early Iron Age ‘Hascherkeller’ Reveals Its Secrets
Archaeology | Jul 20, 2022
Central European Early Iron Age ‘Hascherkeller’ Reveals Its Secrets
Archaeology | Jul 20, 2022 -
 Mysterious Sophisticated Gran Coclé Culture Reveals Its Ancient Secrets
Civilizations | Mar 9, 2020
Mysterious Sophisticated Gran Coclé Culture Reveals Its Ancient Secrets
Civilizations | Mar 9, 2020 -
 Why Was The Face Of Mysterious Ust-Taseyevsky Stone Idol Suddenly Changed?
Archaeology | Jan 18, 2021
Why Was The Face Of Mysterious Ust-Taseyevsky Stone Idol Suddenly Changed?
Archaeology | Jan 18, 2021 -
 Unique Purbeck Marble Found On England’s Oldest Historic Shipwreck
Archaeology | Jun 14, 2024
Unique Purbeck Marble Found On England’s Oldest Historic Shipwreck
Archaeology | Jun 14, 2024 -
 Drinking Horn: Important Yule Symbol And Its Connection To Biblical Magi And Christmas
Christmas Traditions | Dec 25, 2024
Drinking Horn: Important Yule Symbol And Its Connection To Biblical Magi And Christmas
Christmas Traditions | Dec 25, 2024 -
 3,000-Year-Old Nimrud Lens Could Re-Write The History Of Science – Was The World’s Oldest Telescope Developed By Ancient Assyrian Astronomers?
Ancient Technology | Oct 19, 2014
3,000-Year-Old Nimrud Lens Could Re-Write The History Of Science – Was The World’s Oldest Telescope Developed By Ancient Assyrian Astronomers?
Ancient Technology | Oct 19, 2014 -
 Unique 1,000-Year-Old Medieval Golden Treasure Unearthed By Dutch Historian Using Metal Detector
Archaeology | Mar 24, 2023
Unique 1,000-Year-Old Medieval Golden Treasure Unearthed By Dutch Historian Using Metal Detector
Archaeology | Mar 24, 2023 -
 Circular-Shaped 4000-Year-Old Wooden Henge Discovered In Yorkshire, Historic County of Northern England
Archaeology | Jan 3, 2018
Circular-Shaped 4000-Year-Old Wooden Henge Discovered In Yorkshire, Historic County of Northern England
Archaeology | Jan 3, 2018 -
 New Discoveries Regarding Gladiatorial Games In Roman City Of Carnuntum
Archaeology | Apr 7, 2017
New Discoveries Regarding Gladiatorial Games In Roman City Of Carnuntum
Archaeology | Apr 7, 2017 -
 The Assyrian Siege Ramp And Breached Walls At Canaanite City Of Lachish – Studied
Archaeology | Nov 10, 2021
The Assyrian Siege Ramp And Breached Walls At Canaanite City Of Lachish – Studied
Archaeology | Nov 10, 2021 -
 Tezcatlipoca: Enigmatic Aztec God Who Looked Inside People’s Hearts And Observed Their Deeds On Earth
Aztec Mythology | Jul 22, 2021
Tezcatlipoca: Enigmatic Aztec God Who Looked Inside People’s Hearts And Observed Their Deeds On Earth
Aztec Mythology | Jul 22, 2021 -
 North America’s First Languages Originate From Siberia
Linguistic Discoveries | Apr 10, 2024
North America’s First Languages Originate From Siberia
Linguistic Discoveries | Apr 10, 2024 -
 Early Harappan Cultures Can Solve Mysteries Of Several Lost Cities Of Indus Valley Civilization
Artifacts | May 30, 2019
Early Harappan Cultures Can Solve Mysteries Of Several Lost Cities Of Indus Valley Civilization
Artifacts | May 30, 2019 -
 2,000-Year-Old Altar Depicting Snake Figure Unearthed In Lycian City Of Patara
Archaeology | Oct 20, 2020
2,000-Year-Old Altar Depicting Snake Figure Unearthed In Lycian City Of Patara
Archaeology | Oct 20, 2020 -
 3,000-Year-Old City Of Sillyon That Alexander The Great Failed To Conquer
Archaeology | Aug 31, 2020
3,000-Year-Old City Of Sillyon That Alexander The Great Failed To Conquer
Archaeology | Aug 31, 2020 -
 1,600-Year-Old Pendants Depicting Humans And Animals Excavated In Ancient Port-City Of Assos
Archaeology | Jan 21, 2020
1,600-Year-Old Pendants Depicting Humans And Animals Excavated In Ancient Port-City Of Assos
Archaeology | Jan 21, 2020 -
 Early Christian Necropolis Unearthed In Sant’Appianu Cathedral In Sagone, Corsica
Archaeology | Aug 3, 2020
Early Christian Necropolis Unearthed In Sant’Appianu Cathedral In Sagone, Corsica
Archaeology | Aug 3, 2020 -
 Surprising Time Capsule In Antarctica – Evidence Of Toxic Heavy Metal Pollution 800 Years Ago
Earth Changes | Jan 18, 2024
Surprising Time Capsule In Antarctica – Evidence Of Toxic Heavy Metal Pollution 800 Years Ago
Earth Changes | Jan 18, 2024 -
 Oldest Known Sami Manuscript Discovered – It’s Undeciphered And Written By An Unknown Author
Linguistic Discoveries | Nov 26, 2024
Oldest Known Sami Manuscript Discovered – It’s Undeciphered And Written By An Unknown Author
Linguistic Discoveries | Nov 26, 2024 -
 On This Day In History: Sir Thomas Brisbane, Astronomer, Soldier And Governor Was Born – On July 23, 1773
On This Day In History | Jul 23, 2016
On This Day In History: Sir Thomas Brisbane, Astronomer, Soldier And Governor Was Born – On July 23, 1773
On This Day In History | Jul 23, 2016



