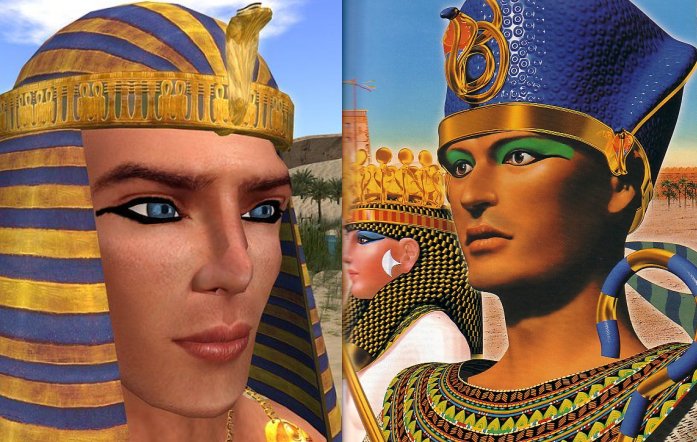
Ancient Egyptian Cosmetics – Why Was It So Important To Both Men And Women?
Conny Waters - AncientPages.com - Ancient Egyptians had several achievements in chemistry and cosmetology. They produced creams, perfumes, and facial colors. They created beautification techniques, and special soap to wash corpses as part of mummification.
The use of cosmetics was very important in ancient Egypt and makeup was used by both men and women.
4,000 years ago, the Egyptians used some kind of toothpaste or bleach (a person with bleached teeth looks healthier), which was made from ground pumice added to soap, scrubs, and other natural cosmetic recipes to provide exfoliation to the skin.
Makeup was once an important part of everyday life in Egypt and it was not only used to look better. There was a much more important purpose behind the use of cosmetics in ancient Egypt. Cosmetics was sacred to ancient Egyptians and used not only for aesthetic purposes but rather for magical and religious purposes.
Frescoes discovered in ancient Egyptian temples illustrating daily life reveal men often wore makeup. In fact, it’s almost impossible to find a portrait of an ancient Egyptian whose eyes are not decorated.
Men wore makeup in ancient Egypt.
During all periods and dynasties, eye makeup was a daily prerequisite for both men and women.
The use of cosmetics differed slightly between social classes. Higher class and wealthier individuals could afford more make-up.
Ancient Egyptians used a variety of cosmetics such as eye makeup, rouge, and perfumed oils that softened the skin and prevented burning in the sun and damage from the sandy winds. Galena powder possesses disinfectant and fly-deterrent properties. It is believed to offer the eyes protection from the intense sun.
In Ancient Egypt, the image of an individual often acted as a substitute for the body in the afterlife. Therefore, in funerary paintings, both males and females are shown in their best clothes, wigs, and makeup.
Ancient Egyptians often shaved their head because of lice infestations. People wore wigs made of real human hair that was adorned with flowers and braid.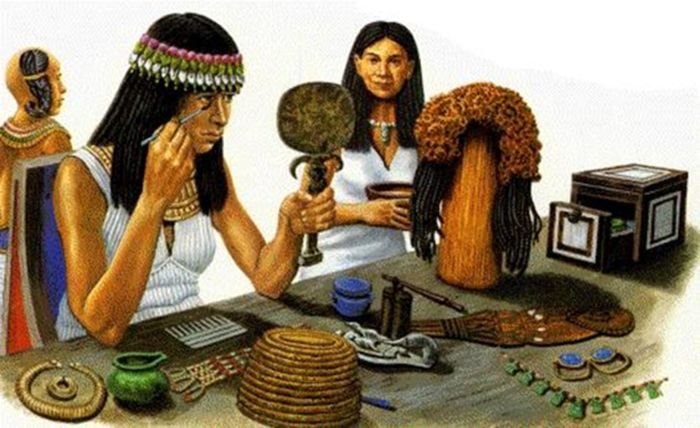
Makeup tools and accessories were very important too. Precious oils were stored in cosmetics jars made from glass, faience ceramics, and stone. The mirror was made of bronze and often carved in the form of an Egyptian goddess.
Ancient Egyptians used a variety of pigments to adorn the face. Most important of all was kohl, which was used to line the eyes. Kohl came from two sources: a green eye paint made of mineral malachite and a black liner derived from galena, a form of lead ore. Women used red ochre to form a light blush for cheeks and lips, while henna was used to paint the nails and dye the hair.
Cosmetics had also a religious resonance. The ancient Egyptians regarded beauty as a sign of holiness. In the holy sanctuary of the temple, the god was anointed with makeup as a symbol of celestial regeneration. This took place every day.
Written by Conny Waters – AncientPages.com Staff Writer
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
More From Ancient Pages
-
 New Method Reveals Falsified And Original Manuscripts Of Famous Robert Burns
Archaeology | Jul 28, 2018
New Method Reveals Falsified And Original Manuscripts Of Famous Robert Burns
Archaeology | Jul 28, 2018 -
 Focus On Unique And Spectacular Gallery Grave In Ancient City Of Dara, Mardin
News | Aug 24, 2020
Focus On Unique And Spectacular Gallery Grave In Ancient City Of Dara, Mardin
News | Aug 24, 2020 -
 New Evidence Vikings Failed To Wipe Out Communities And Anglo-Saxon Monasteries
Archaeology | Jan 30, 2023
New Evidence Vikings Failed To Wipe Out Communities And Anglo-Saxon Monasteries
Archaeology | Jan 30, 2023 -
 Enigmatic Ale’s Stones – Sweden’s Megalithic Ship-Like Formation
Featured Stories | Jan 17, 2023
Enigmatic Ale’s Stones – Sweden’s Megalithic Ship-Like Formation
Featured Stories | Jan 17, 2023 -
 What Is The Codex Sinaiticus And What Does It Mean?
Ancient History Facts | Feb 5, 2019
What Is The Codex Sinaiticus And What Does It Mean?
Ancient History Facts | Feb 5, 2019 -
 Paleolithic Standing Bird Figurine – East Asian 3-D Art – Recovered From Refuse Heap
Archaeology | Jun 23, 2020
Paleolithic Standing Bird Figurine – East Asian 3-D Art – Recovered From Refuse Heap
Archaeology | Jun 23, 2020 -
 Mysterious Ancient Tomb Reveals ‘Impossible’ Human Connection To Cosmos – Human Anomaly? – Part 2
Ancient Mysteries | Oct 15, 2020
Mysterious Ancient Tomb Reveals ‘Impossible’ Human Connection To Cosmos – Human Anomaly? – Part 2
Ancient Mysteries | Oct 15, 2020 -
 Excavations Reveal New Artifacts That Change History Of Ancient City Of Pergamon
Archaeology | Jul 4, 2020
Excavations Reveal New Artifacts That Change History Of Ancient City Of Pergamon
Archaeology | Jul 4, 2020 -
 Controversial Discovery Of Rama’s Bridge – A 1,700,000 Year Old Man-Made Structure
Featured Stories | Jun 19, 2014
Controversial Discovery Of Rama’s Bridge – A 1,700,000 Year Old Man-Made Structure
Featured Stories | Jun 19, 2014 -
 This Is The Mysterious Hilltop Where Civilization Began Scientists Say
Archaeology | Jun 24, 2022
This Is The Mysterious Hilltop Where Civilization Began Scientists Say
Archaeology | Jun 24, 2022 -
 Tooth Analysis Sheds Light On South Australia’s Early Colonial History
Archaeology | Jul 6, 2022
Tooth Analysis Sheds Light On South Australia’s Early Colonial History
Archaeology | Jul 6, 2022 -
 Powerful Thunderbird Sent By The Gods To Protect Humans From Evil In Native American Legends
Native American Mythology | Mar 26, 2017
Powerful Thunderbird Sent By The Gods To Protect Humans From Evil In Native American Legends
Native American Mythology | Mar 26, 2017 -
 Startling 3,000-Year-Old Gold Bowl Decorated With A Sun Motif Discovered Is A Truly Unique Artifact
Archaeology | Oct 17, 2021
Startling 3,000-Year-Old Gold Bowl Decorated With A Sun Motif Discovered Is A Truly Unique Artifact
Archaeology | Oct 17, 2021 -
 On This Day In History: Emperor Gordian II Loses The Battle Of Carthage – On Apr 12, 238 AD
News | Apr 12, 2016
On This Day In History: Emperor Gordian II Loses The Battle Of Carthage – On Apr 12, 238 AD
News | Apr 12, 2016 -
 First Carbon-Based Paleolithic Paintings Found In Font-De-Gaume Cave, France Could Be 19,000 Years Old
Archaeology | Dec 29, 2023
First Carbon-Based Paleolithic Paintings Found In Font-De-Gaume Cave, France Could Be 19,000 Years Old
Archaeology | Dec 29, 2023 -
 New Study Challenges Theories Of Earlier Human Arrival In Americas – Archaeological Evidence Has Been Misinterpreted – Scientists Say
Archaeology | Apr 21, 2022
New Study Challenges Theories Of Earlier Human Arrival In Americas – Archaeological Evidence Has Been Misinterpreted – Scientists Say
Archaeology | Apr 21, 2022 -
 Spells, Charms, Erotic Dolls: Love Magic In The Ancient Mediterranean
Featured Stories | Oct 24, 2022
Spells, Charms, Erotic Dolls: Love Magic In The Ancient Mediterranean
Featured Stories | Oct 24, 2022 -
 Nude Athletes And Fights To The Death: What Really Happened At The Ancient Olympics
Featured Stories | Aug 2, 2024
Nude Athletes And Fights To The Death: What Really Happened At The Ancient Olympics
Featured Stories | Aug 2, 2024 -
 Eleanor Of Aquitaine – Mother Of King Richard The Lionheart And One Of Most Powerful Women Of Middle Ages
Featured Stories | Feb 26, 2018
Eleanor Of Aquitaine – Mother Of King Richard The Lionheart And One Of Most Powerful Women Of Middle Ages
Featured Stories | Feb 26, 2018 -
 What A Bath, Taken 1,000 Years Ago, Can Tell Us About The Conflicted English Kingdom Of The 11th Century
Featured Stories | Jun 14, 2024
What A Bath, Taken 1,000 Years Ago, Can Tell Us About The Conflicted English Kingdom Of The 11th Century
Featured Stories | Jun 14, 2024


