The Mixtec – Mysterious Very Advanced Culture Of The Foremost Goldsmiths Of Mesoamerica
A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com - The Mixtec people called themselves the Ñuu Savi - "People of the Rain" and lived in three mountainous areas of present-day Oaxaca in Southwestern Mexico.
Their homeland was the Mixteca.
The Mixtec never built large cities similar to Tula or Teotihuacan, but instead lived and worked in smaller settlements in neighboring valleys.
From left: Mixtec Codex, (Latin American Studied.org); Turquoise mosaic mask. Mixtec-Aztec, 1400-1521 AD/British Museum; Plate 37 of the Codex Vindobonensis. The central scene supposedly depicts the origin of the Mixtecs as a people whose ancestors sprang from a tree; Mixtec Rain God (Wikipedia)
Much about the pre-history of these people is unknown but archaeological evidence shows that the culture flourished between 940 and 1500AD. Around 1350 AD, the Mixtecs took over control of the sacred, ceremonial site of Monte Alban, near the present-day city of Oaxaca, from the Zapotecs, who ruled Monte Alban for some about 12 centuries.
Later, archaeological evidence revealed that Monte Alban’s interior, especially Tomb No.7, contained lavish burial treasures of gold, silver, pearls and turquoise.
They were a complex society, which unlike other cultures had a continuous history that goes from the Preclassic (from at least 1500 BC), until the end of the Postclassic (900 AD and the Spanish arrival in 1519).
Interior of the Mixtec tomb, archaeological site at Zaachila, Oaxaca, Mexico. Image credit: El Agora/Wikipedia
In the 10th century, several Mixtec kingdoms were established, in which lived classes of nobles, artisans and peasants. Later, during 500-750 AD, the Mixtec created urban centers and developed a calendar, monumental architecture, terrace agriculture, impressive irrigation systems, and glyphic writing. Their most important and one of the oldest settlements in Oaxaca, was Tilantongo and the Mixtec picture codices tell stories about its kings.
Much place is devoted to one of the greatest of the Mixtec dynasties, the Tilantongo dynasty, established upon the marriage of two nobles in the holy Mixtec city of Tilantongo in 990 AD and Lord 8 Deer (also known as Eight Deer Jaguar Claw), a powerful Mixtec ruler 11th century Oaxaca referred to several Mixtec manuscripts, especially, the 15th-century deerskin manuscript "Codex Zouche-Nuttall"
However, only eight of the original Mixtec historic documents survived until today.
The chest plate (or chimalli) was made by Mixtec craftsmen using components such as gold and turquoise. The Mixtecs were masters in making gold and metal objects.
The Mixtecs’ legacy includes many more amazing achievements. For example, these people were considered the foremost goldsmiths of Mesoamerica," who mastered the ‘lost-wax casting’ of gold and its alloys, which resulted in remarkable gold work and the art of jewelry (necklaces, pectorals, rings, earmuffs and nose rings). The art of designing with feathers is also included in their rich legacy.
Another Mixtec achievement is a writing system of written signs and pictures that influenced other Mesoamerican cultures. The system was used to record (on deerskin) historical and cultural events such as the births, marriages and deaths of nobles, wars and victories, and other important events that affected the Mixtec society.
See also:
Mystery Of Monte Albán – Ancient City ‘At The Foot Of The Heavens’ Built By The Zapotecs
Aztecs: Facts And History About The Ancient And Powerful Mesoamerican Civilization From Aztlán
Dresden Codex – The Oldest And Best Preserved Book Of The Maya
Aztec Empire: ‘Tlatoani’ – The Ruler With The Ultimate Power In The Land
Aztecs: Facts And History About The Ancient And Powerful Mesoamerican Civilization From Aztlán
During their large expansion, the Aztecs conquered many lands in Mexico and Mesoamerica through wars.
The Mixtec were one of them; many died in sacrifices and some of the most skilled craftsmen moved to the Aztec capital, Tenochtitlan, to create new wonders in gold for their new rulers. The Mixtec nobles – as the other conquered lands - were obliged to pay tribute to the rulers in Tenochtitlan.
Today, they are considered the fourth largest group of native peoples of Mexico, after Nahua, Mayan and Zapotec - among the most numerous Indian towns of Mexico.
Written by – A. Sutherland AncientPages.com Staff Writer
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
Expand for referencesReferences:
Spores R. Sr., Balkansky A. K. The Mixtecs of Oaxaca
More From Ancient Pages
-
 Natural Dyes To Color Clothing Were Used Thousands Of Years Ago – New Study
Archaeology | Apr 22, 2019
Natural Dyes To Color Clothing Were Used Thousands Of Years Ago – New Study
Archaeology | Apr 22, 2019 -
 Ancient Copy Of Jesus’ Secret Teachings To His Brother James Discovered – First Apocalypse And Future Events Described
Artifacts | Dec 2, 2017
Ancient Copy Of Jesus’ Secret Teachings To His Brother James Discovered – First Apocalypse And Future Events Described
Artifacts | Dec 2, 2017 -
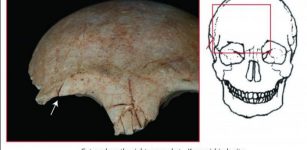 Population Pressure And Prehistoric Violence In The Yayoi Period Of Japan
Archaeology | Aug 30, 2021
Population Pressure And Prehistoric Violence In The Yayoi Period Of Japan
Archaeology | Aug 30, 2021 -
 Orthodox Church In Black Sea Region Looted By Treasure Hunters
Archaeology | Feb 24, 2021
Orthodox Church In Black Sea Region Looted By Treasure Hunters
Archaeology | Feb 24, 2021 -
 Unexpected Archaeological Discovery May Re-Write English Civil War History
Archaeology | Feb 3, 2023
Unexpected Archaeological Discovery May Re-Write English Civil War History
Archaeology | Feb 3, 2023 -
 La Garma Cave Offers Evidence Of Over 300,000 Years Of Human Activity
Featured Stories | Dec 5, 2023
La Garma Cave Offers Evidence Of Over 300,000 Years Of Human Activity
Featured Stories | Dec 5, 2023 -
 Thousand Unearted Artifacts Reveal ‘Major’ Ancient Migration To Timor Island
Archaeology | May 23, 2024
Thousand Unearted Artifacts Reveal ‘Major’ Ancient Migration To Timor Island
Archaeology | May 23, 2024 -
 The Sistine Chapel Cypher – Secret Messages In The Art Of Michelangelo
Featured Stories | Mar 3, 2018
The Sistine Chapel Cypher – Secret Messages In The Art Of Michelangelo
Featured Stories | Mar 3, 2018 -
 Rasputin – Controversial Mystic With Healing Powers – An Evil Or Misunderstood Man?
Featured Stories | Aug 4, 2018
Rasputin – Controversial Mystic With Healing Powers – An Evil Or Misunderstood Man?
Featured Stories | Aug 4, 2018 -
 7,000-Year-Old Kilns From Ceramics Workshop Unearthed In Northeast Bulgaria
Archaeology | Nov 20, 2020
7,000-Year-Old Kilns From Ceramics Workshop Unearthed In Northeast Bulgaria
Archaeology | Nov 20, 2020 -
 Egyptian Royal Artifacts Found At ‘Ancient Buto’ Site, Egypt Probably Dated To King Psamtik I’s Reign
Archaeology | Jan 4, 2018
Egyptian Royal Artifacts Found At ‘Ancient Buto’ Site, Egypt Probably Dated To King Psamtik I’s Reign
Archaeology | Jan 4, 2018 -
 Cremation In The Near East Dates Back To 7,000 B.C.
Archaeology | Aug 13, 2020
Cremation In The Near East Dates Back To 7,000 B.C.
Archaeology | Aug 13, 2020 -
 Thousands Of Petroglyphs And Inscriptions In Wadi Rum, Jordan – 12,000 Years Of Human Occupation
Civilizations | Oct 23, 2018
Thousands Of Petroglyphs And Inscriptions In Wadi Rum, Jordan – 12,000 Years Of Human Occupation
Civilizations | Oct 23, 2018 -
 Neanderthals Changed Ecosystems 125,000 Years Ago
Archaeology | Dec 16, 2021
Neanderthals Changed Ecosystems 125,000 Years Ago
Archaeology | Dec 16, 2021 -
 Most Of Medieval English Heroic Or Chivalric Stories Have Been Lost
Archaeology | Feb 18, 2022
Most Of Medieval English Heroic Or Chivalric Stories Have Been Lost
Archaeology | Feb 18, 2022 -
 The Main Gate Of Historical 9th-Century Old Harran Palace Unearthed
Archaeology | Oct 25, 2020
The Main Gate Of Historical 9th-Century Old Harran Palace Unearthed
Archaeology | Oct 25, 2020 -
 Rare Roman Mosaic Depicting The Adventures Of Greek Hero Achilles Discovered In Rutland, UK
Archaeology | Dec 4, 2021
Rare Roman Mosaic Depicting The Adventures Of Greek Hero Achilles Discovered In Rutland, UK
Archaeology | Dec 4, 2021 -
 Explore The Giant Gjellestad Viking Ship Burial In This Stunning Virtual Tour
Featured Stories | Apr 6, 2020
Explore The Giant Gjellestad Viking Ship Burial In This Stunning Virtual Tour
Featured Stories | Apr 6, 2020 -
 New England’s Abandoned Stone Walls Deserve A Science Of Their Own
Featured Stories | Jan 5, 2024
New England’s Abandoned Stone Walls Deserve A Science Of Their Own
Featured Stories | Jan 5, 2024 -
 Ancient Monuments The World Is Not Allowed To See – Forbidden Zone – Part 2
Featured Stories | Aug 27, 2020
Ancient Monuments The World Is Not Allowed To See – Forbidden Zone – Part 2
Featured Stories | Aug 27, 2020




