The Oseberg Tapestry And Other Artifacts Show Intense Colors Were A Viking Symbol Of Status And Wealth
Ellen Lloyd - AncientPages.com - If you were a Viking warrior, you didn't paint your shield with just any color. Picking the right color was not a matter of taste. It was a decision based on careful selection because the stain revealed a Viking's status and wealth.
Credit: Adobe Stock: Fotokvadrat
Rich Vikings liked showing off using particular colors to symbolize their high societal status. Based on old paint remnants, a Danish chemist and a conservator have managed to recreate a palette of 17 magnificent colors used by the Vikings to emphasize their high status.
Intense colors were popular because they were rare and symbolized status.
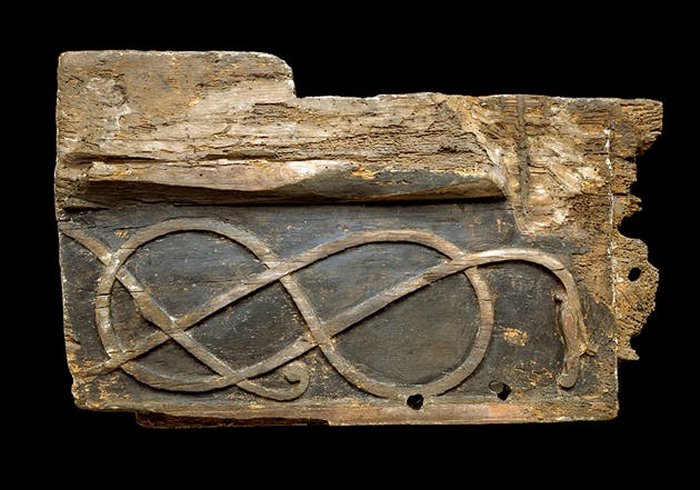
Chemist Mads Christian Christensen and conservator Line Bregnhøi from the National Museum in Copenhagen examined a piece of wood from a church built in Hørning in Denmark around 1060. After so many years, the colors were not visible to the naked eye, so chemical analyses were required to recreate them.
Red And Yellow Were A Viking Symbol Of Status And Wealth
The red and yellow shades are derived from minerals not found in Denmark but in Spain and Turkey, among others.
Hørningplankan, a piece of wood examine to discover the importance of Viking colors. Credit: National Museum of Copenhagen
The mineral arsenic sulfide is used to produce yellow colors and can be obtained in countries like Germany and Turkey. The red color is made from cinnabar, which comes from Spain. Researchers think such minerals must have been expensive because they had to be transported to Scandinavia. Colors like red and yellow were only used by rich people who could afford them. The importation of expensive minerals must have been a lucrative business.
Because of the cost, it's unlikely more than minor details were highlighted with these colors.
The seventeen colors from the Viking era. Credit: National Museum Of Copenhagen
Researchers have so far identified 17 colors used by Vikings, and they hope they can discover more shortly. It's an important discovery because it gives us a better understanding of the Viking society.
Scientists have also learned plenty about the importance of colors from artifacts discovered in Oseberg's burial in Norway.
"The magnificent Oseberg ship was used as a burial ship for two Viking women who died in 834. A burial chamber was dug right behind the ship's mast. The walls were decorated with fantastic woven tapestries, and the dead woman lay on a raised bed.
The women had several burial gifts with them. These included clothes, shoes and combs, ship equipment, kitchen equipment, farm equipment, three ornate sleds, five carved animal heads, five beds, and two tents. There were fifteen horses, six dogs, and two small cows. A remarkable collection of wooden and textile artifacts was left behind, and the colors were striking.
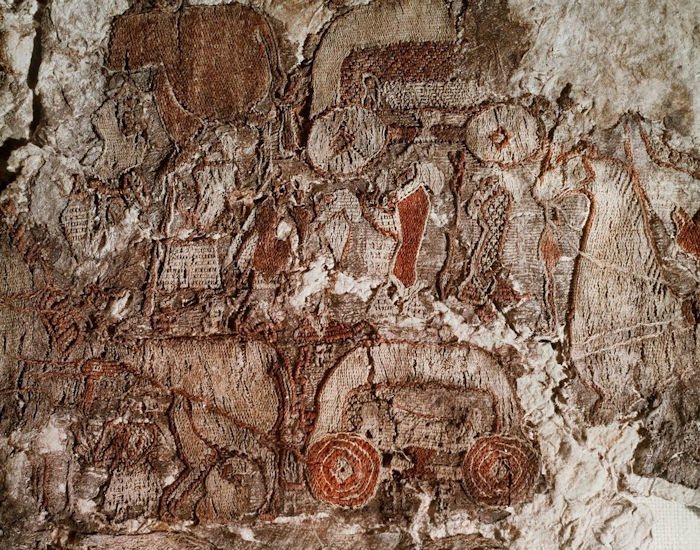
The Oseberg tapestry is poorly preserved, but it is clear that it was a long, narrow (20–23 centimeters wide) strip that probably was meant to hang on a wall. It is made from wool dyed in different colors, mainly red, yellow, and black.
A fragment of a tapestry from the Oseberg grave in Vestfold, Norway. Credit: Erik I. Johnsen/Kulturhistorisk museum - CC BY-SA 2.0
The Oseberg tapestry portrays a procession of two rows of horses with knotted tails. Three of the horses pull carts, one containing two people, apparently women. Scholars have speculated whether they represent the two women buried in the Oseberg burial (with a cart among their grave goods) and whether the tapestry was specially made to portray the burial procession. The procession in the tapestry also features a large number of men and women walking.
The women wear long dresses with trains and cloaks, and some carry spears like many men. Their hair appears to be stuffed into bulging headdresses.
In their attire, the women on the Oseberg tapestry are reminiscent of the valkyries welcoming slain warriors to Valhalla, as portrayed on the Gotland picture stones. On these stones, many women do not have their hair hidden by headdresses but have let it down, as Ermengard is reported to have done when Earl Ragnvald visited her in Narbonne.
The valkyries of the picture stones serve food and drink to the dead warriors, and they let their hair down, which may suggest sexual availability. Some women portrayed on picture stones hold drinking horns in their hands, as does a small silver figure of a woman found in Birka; they have been interpreted as valkyries serving drink to dead warriors arriving at Valhalla. The warriors typically arrive by horse. Sometimes, they ride a horse with eight legs, suggesting they are so important that the ruler of Valhalla, Odin, has sent his eight-legged horse, Sleipner, to pick them up. Such picture stones often depict ships." 1
These discoveries and studies are valuable as they give us a better idea of how Vikings decorated their objects and perceived different colors.
Written by - Ellen Lloyd – AncientPages.com
Updated on December 4, 2023
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
Expand for referencesMore From Ancient Pages
-
 Elysian Fields: Mysterious Resting Place For Heroic And Virtuous Souls In Greek Ancient Beliefs
Featured Stories | Feb 20, 2020
Elysian Fields: Mysterious Resting Place For Heroic And Virtuous Souls In Greek Ancient Beliefs
Featured Stories | Feb 20, 2020 -
 Katana ‘Soul Of The Samurai’ – Most Famous Japanese Sword With Long Tradition
Ancient History Facts | Apr 12, 2018
Katana ‘Soul Of The Samurai’ – Most Famous Japanese Sword With Long Tradition
Ancient History Facts | Apr 12, 2018 -
 Why Did God Zeus Give King Sisyphus An Eternal Punishment?
Featured Stories | Sep 2, 2019
Why Did God Zeus Give King Sisyphus An Eternal Punishment?
Featured Stories | Sep 2, 2019 -
 Major Underwater Archaeological Find On The Western Coast Of Sicily – Artifacts From The Battle Of The Egadi Islands?
Archaeology | Sep 11, 2023
Major Underwater Archaeological Find On The Western Coast Of Sicily – Artifacts From The Battle Of The Egadi Islands?
Archaeology | Sep 11, 2023 -
 On This Day In History: Bishop of Gloucester John Hooper is Burned At The Stake For Heresy- On Feb 9, 1654
News | Feb 9, 2017
On This Day In History: Bishop of Gloucester John Hooper is Burned At The Stake For Heresy- On Feb 9, 1654
News | Feb 9, 2017 -
 Never-Before-Seen Face Of A Tattooed Tashtyk Man Hidden Behind A Gypsum Death Mask Revealed
Archaeology | Jul 17, 2020
Never-Before-Seen Face Of A Tattooed Tashtyk Man Hidden Behind A Gypsum Death Mask Revealed
Archaeology | Jul 17, 2020 -
 Sobekneferu: First Female Pharaoh In Ancient Egypt
Featured Stories | Mar 9, 2019
Sobekneferu: First Female Pharaoh In Ancient Egypt
Featured Stories | Mar 9, 2019 -
 Unique Headstones Of Kela Mazin Cemetery In Kurdistan Are Probably 3,000 Years Old Or Much More
Archaeology | May 7, 2022
Unique Headstones Of Kela Mazin Cemetery In Kurdistan Are Probably 3,000 Years Old Or Much More
Archaeology | May 7, 2022 -
 On This Day In History: ‘Edict Of Nantes’ About Freedom Of Religion Issued By Henry IV – On Apr 13, 1598
News | Apr 13, 2017
On This Day In History: ‘Edict Of Nantes’ About Freedom Of Religion Issued By Henry IV – On Apr 13, 1598
News | Apr 13, 2017 -
 Egypt Recovers Ancient Wooden Coffin From Houston Museum In The US
Archaeology | Oct 4, 2022
Egypt Recovers Ancient Wooden Coffin From Houston Museum In The US
Archaeology | Oct 4, 2022 -
 Strange 1,200-Year-Old Anglo-Saxon Artifact Used For Unknown Purpose Found In Norfolk, UK
Archaeology | Jan 18, 2024
Strange 1,200-Year-Old Anglo-Saxon Artifact Used For Unknown Purpose Found In Norfolk, UK
Archaeology | Jan 18, 2024 -
 Strange Prophecy Of Oleg Of Novgorod’s Death – Where Is Russia’s Viking Ruler Buried?
Featured Stories | Jan 2, 2021
Strange Prophecy Of Oleg Of Novgorod’s Death – Where Is Russia’s Viking Ruler Buried?
Featured Stories | Jan 2, 2021 -
 Artifacts Discovered In Ancient Florida Sinkhole Can Re-Write History Of North America
Archaeology | May 14, 2016
Artifacts Discovered In Ancient Florida Sinkhole Can Re-Write History Of North America
Archaeology | May 14, 2016 -
 65 Byzantine-Era Tombs Unearthed In Stratonikeia – World’s Largest Marble City
Archaeology | Feb 24, 2017
65 Byzantine-Era Tombs Unearthed In Stratonikeia – World’s Largest Marble City
Archaeology | Feb 24, 2017 -
 Few Witches Were Executed In Wales In The Middle Ages – Why?
Featured Stories | Oct 29, 2024
Few Witches Were Executed In Wales In The Middle Ages – Why?
Featured Stories | Oct 29, 2024 -
 11 Ancient Submerged Canoes Found In Wisconsin’s Lake Mendota – Evidence Of A Lost Village?
Archaeology | May 27, 2024
11 Ancient Submerged Canoes Found In Wisconsin’s Lake Mendota – Evidence Of A Lost Village?
Archaeology | May 27, 2024 -
 Boxer At Rest – Rare Sculpture And Masterpiece Of Hellenistic Bronze Art
Artifacts | May 21, 2021
Boxer At Rest – Rare Sculpture And Masterpiece Of Hellenistic Bronze Art
Artifacts | May 21, 2021 -
 When And Why Was Yakuza, The Japanese Mafia Founded?
Ancient History Facts | Jun 12, 2021
When And Why Was Yakuza, The Japanese Mafia Founded?
Ancient History Facts | Jun 12, 2021 -
 Humans May Be The Result Of An Evolution ‘Accident’- Scientists Say
Evolution | Sep 8, 2023
Humans May Be The Result Of An Evolution ‘Accident’- Scientists Say
Evolution | Sep 8, 2023 -
 Aaru – Field Of Reeds: Kingdom Of Osiris Was The Ancient Egyptian Paradise
Myths & Legends | Feb 29, 2024
Aaru – Field Of Reeds: Kingdom Of Osiris Was The Ancient Egyptian Paradise
Myths & Legends | Feb 29, 2024




