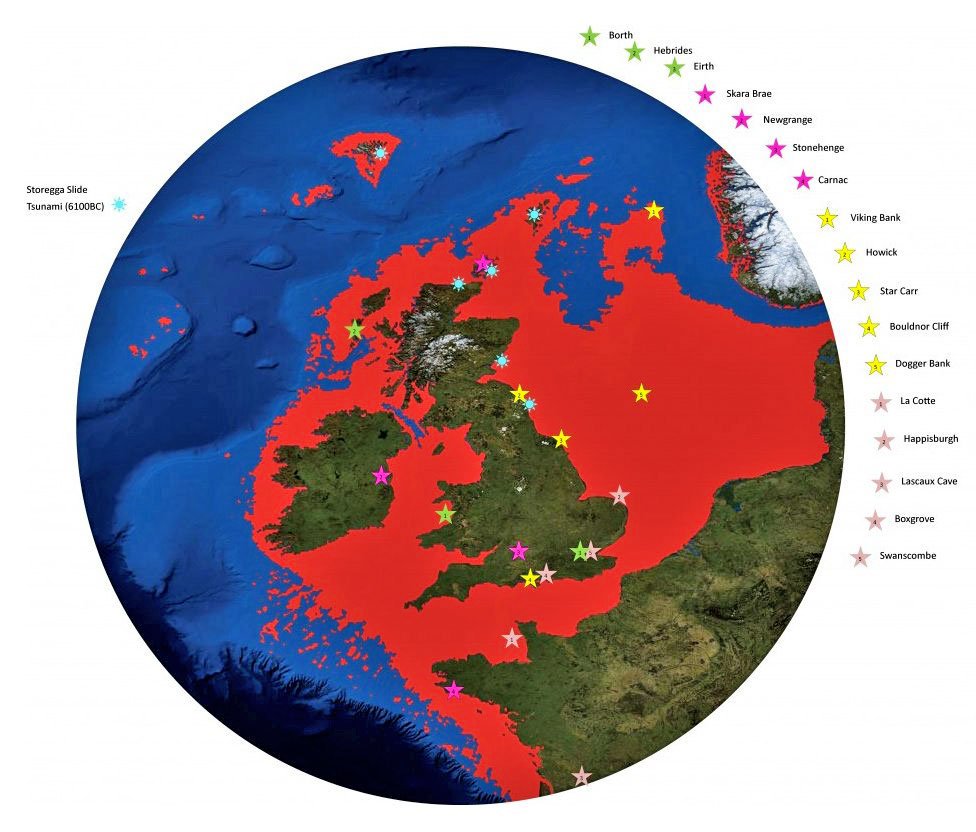
Could Doggerland Be Europe’s True ‘North Atlantis’ Of Stone Age?
Conny Waters - AncientPages.com - Under the North Sea lies a huge rural area, known as “Doggerland” and dating back to 7,000 years ago.
It is now submerged beneath the southern North Sea that connected the present-day United Kingdom to the east with the coasts of the Netherlands, Germany and Denmark.
Doggerland existed about 20,000 years ago. However, the land ceased to exist about 7,000 years ago, when ice melting in the Arctic led to the sea surface rising.
Doggerland was named in the 1990s, after the Dogger Bank which in turn got its name after the 17th century Dutch fishing boats called “doggers”.
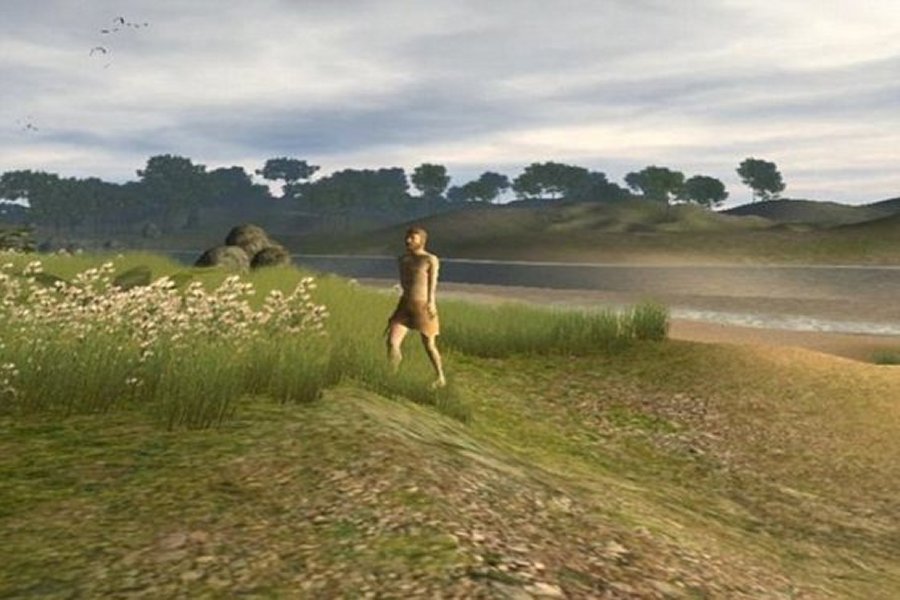
Before Doggerland was destroyed, this huge land mass was dry and inhabited by tens of thousands of people.
About 7,000 years ago, it was the real center of European continent and researchers confirmed that the name “Doggerland” refer to several periods when the North Sea was land. When the ice melted, more land was revealed but the sea level also rose, flooding the North Sea through the English Channel and cut off the British Isles from the European mainland. The UK coastline of today was formed.
See also:
Quest For Atlantis Of The Sands – Iram Of The Pillars – A Legendary Lost City
Lost Ancient Golden City Of Vineta – The Atlantis Of The North
Crimean Atlantis: Remarkable Ancient Underwater City Of Akra
The most recent and popular hypothesis suggests that much of the remaining coastal land was flooded by a megatsunami dated to about 6200 BC. The disaster was caused by a submarine landslide off the coast of Norway, known as – Storegga Slide. - considered to be amongst the largest known landslides.
Traces Of Submerged Doggerland
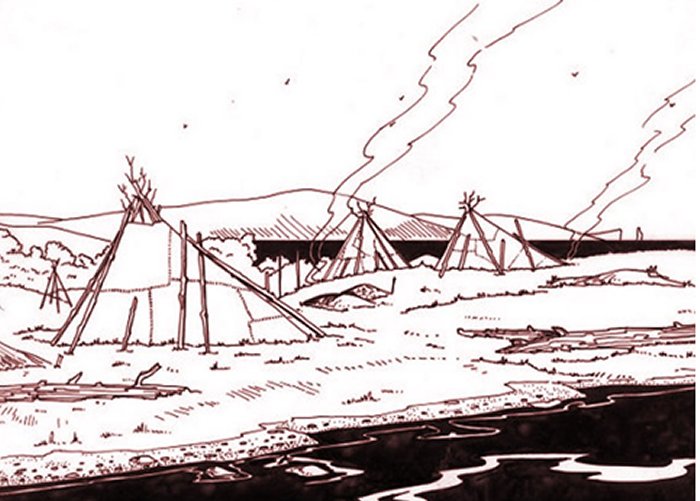
With help of measurements made by the North Sea oil company, British researchers have been able to map Doggerland. They have discovered large forests, hills, valleys and immense plains full of animals including aurochs, mammoth and red deer.
Doggerland offered an increasingly attractive environment for human settlement and hunters. In the meantime, global climate continued to warm and the habitat gradually began to change into a land of deep rivers and inlets, lagoons, wetlands, archipelagos and marshes with a great diversity of plants and animals.
"We're able to understand the types of people who were there," Dr. Richard Bates said. "It has been described as a Stone Age Atlantis - a starry-eyed image of a drowned lost kingdom. But it was certainly a land that would have been heavily populated and it has been lost."
The land became one of the richest hunting and fishing grounds in Europe.
Many researchers from the universities of Birmingham, St Andrews, Dundee, and Aberdeen studied Doggerland, and recently, it was possible to reproduce the remains of megafauna and the tools of hunter-gatherers who lived in Doggerland before the sea level rose dramatically and a devastating tsunami destroyed lives of people and animals.
Fishermen and geologists were occasionally able to find prehistoric artifacts such as mammoth teeth, antlers, some of which have been worked, and the tools that the humans used, including harpoons, arrows, fish prongs, axes and pieces of flint.
A mass grave was also discovered with mammoths, standing rocks, walls, fossilized tree trunks and a likely burial place for humans.
Written by – Conny Waters – AncientPages.com
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
Expand for referencesMore From Ancient Pages
-
 In Ancient California Matriarchal Society, Daughters Breastfed Longer And Women Accumulated Greater Wealth
Archaeology | Jul 13, 2023
In Ancient California Matriarchal Society, Daughters Breastfed Longer And Women Accumulated Greater Wealth
Archaeology | Jul 13, 2023 -
 LIDAR Discovers Giant Ancient Mesoamerican Calendar – Structures Were Aligned To The Stars
Archaeoastronomy | Jan 10, 2023
LIDAR Discovers Giant Ancient Mesoamerican Calendar – Structures Were Aligned To The Stars
Archaeoastronomy | Jan 10, 2023 -
 Invasion Of Mysterious Sea People – Enigmatic 3,200-Year-Old Luwian Hieroglyphic Inscription Sheds New Light On Ancient Puzzle
Archaeology | Oct 11, 2017
Invasion Of Mysterious Sea People – Enigmatic 3,200-Year-Old Luwian Hieroglyphic Inscription Sheds New Light On Ancient Puzzle
Archaeology | Oct 11, 2017 -
 Medieval Mystery Of The Booted Man Found In The Thames Mud
Archaeology | Dec 10, 2018
Medieval Mystery Of The Booted Man Found In The Thames Mud
Archaeology | Dec 10, 2018 -
 Mystery Of The Horrible ‘Thing’ Found In A Dominican Monastery
Featured Stories | Sep 4, 2023
Mystery Of The Horrible ‘Thing’ Found In A Dominican Monastery
Featured Stories | Sep 4, 2023 -
 Madame de Pompadour – Powerful And Hated Mistress – Sex, Manipulation And Intrigue In Versailles
Featured Stories | Jul 12, 2018
Madame de Pompadour – Powerful And Hated Mistress – Sex, Manipulation And Intrigue In Versailles
Featured Stories | Jul 12, 2018 -
 Clues To The Mysterious Dog-Headed St. Christopher And His Connection To The Egyptian Jackal God Anubis Found?
Featured Stories | Jan 14, 2025
Clues To The Mysterious Dog-Headed St. Christopher And His Connection To The Egyptian Jackal God Anubis Found?
Featured Stories | Jan 14, 2025 -
 ‘Homo Erectus’ From Gongwangling Could Have Been One Of The First Human Beings 1,6 Million Years Ago
Archaeology | Jun 14, 2022
‘Homo Erectus’ From Gongwangling Could Have Been One Of The First Human Beings 1,6 Million Years Ago
Archaeology | Jun 14, 2022 -
 Administrative Centre Dated To 2181–2055 BC Unearthed In Kom Ombo, Upper Egypt
Archaeology | Mar 4, 2022
Administrative Centre Dated To 2181–2055 BC Unearthed In Kom Ombo, Upper Egypt
Archaeology | Mar 4, 2022 -
 Long-Lost Wreck Of Crusader Ship And Gold Coins Discovered
Archaeology | Mar 14, 2017
Long-Lost Wreck Of Crusader Ship And Gold Coins Discovered
Archaeology | Mar 14, 2017 -
 Glass Technology Was Known In Sahara Centuries Before The Arrival Of Europeans
Ancient Technology | Jan 20, 2018
Glass Technology Was Known In Sahara Centuries Before The Arrival Of Europeans
Ancient Technology | Jan 20, 2018 -
 Why Was The Iron Age Village Near Elgin In Scotland Suddenly Abandoned And Burned Down?
Archaeology | Jul 29, 2022
Why Was The Iron Age Village Near Elgin In Scotland Suddenly Abandoned And Burned Down?
Archaeology | Jul 29, 2022 -
 Mesoamerican Rubber Ball Game Tradition Existed Earlier Than Thought
Ancient Traditions And Customs | Mar 17, 2020
Mesoamerican Rubber Ball Game Tradition Existed Earlier Than Thought
Ancient Traditions And Customs | Mar 17, 2020 -
 Similarities And Differences Between Living Spaces Of Neanderthals And Homo Sapiens
Archaeology | Apr 9, 2024
Similarities And Differences Between Living Spaces Of Neanderthals And Homo Sapiens
Archaeology | Apr 9, 2024 -
 What Did A Day In Pharaoh’ s Life Look Like?
Ancient History Facts | Dec 9, 2019
What Did A Day In Pharaoh’ s Life Look Like?
Ancient History Facts | Dec 9, 2019 -
 6,000 Years Ago, Europe’s Oldest Cities Relied On Fertilizer And Plant Protein, Isotope – Analysis Shows
Archaeology | Dec 19, 2023
6,000 Years Ago, Europe’s Oldest Cities Relied On Fertilizer And Plant Protein, Isotope – Analysis Shows
Archaeology | Dec 19, 2023 -
 Top 10 Discoveries About Our Ancient Ancestors In 2023
Archaeology | Dec 29, 2023
Top 10 Discoveries About Our Ancient Ancestors In 2023
Archaeology | Dec 29, 2023 -
 Sobek – Enigmatic Crocodile God Of Ancient Egypt
Civilizations | Sep 5, 2015
Sobek – Enigmatic Crocodile God Of Ancient Egypt
Civilizations | Sep 5, 2015 -
 Modern Humans Traveled Across The Eurasian Steppe 45,000 Years Ago
Archaeology | Aug 20, 2019
Modern Humans Traveled Across The Eurasian Steppe 45,000 Years Ago
Archaeology | Aug 20, 2019 -
 Last Homo Erectus Lived 117,000 Years Ago At Ngandong
Archaeology | Dec 19, 2019
Last Homo Erectus Lived 117,000 Years Ago At Ngandong
Archaeology | Dec 19, 2019