Inca Llajta: Largest And Most Impressive Inca Complex In Bolivia
A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com - Inca Llajta (in Quechua means ‘Inca Town’) is considered the largest and most impressive Inca military complex in Bolivia, which served as the most eastern fortress of the large Inca-empire. The fort is strategically located in a mountain range (2,900 to 3,200 meters above sea level).
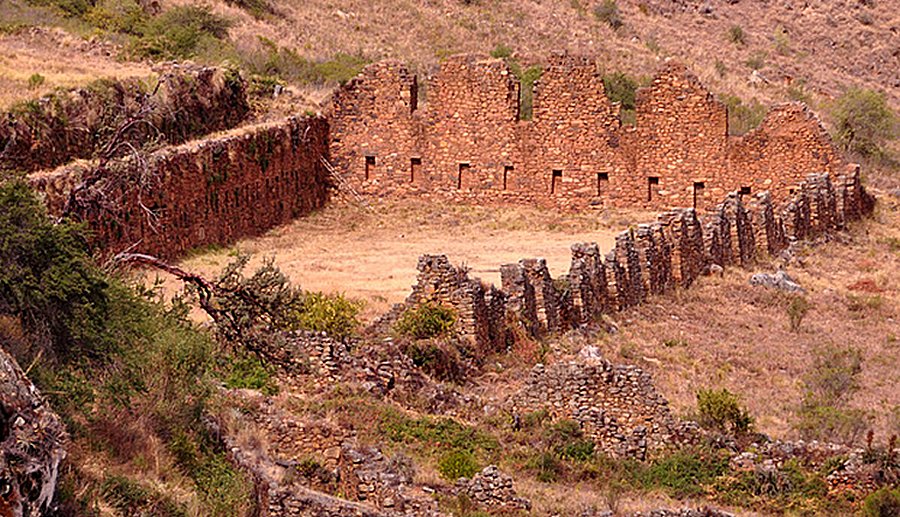
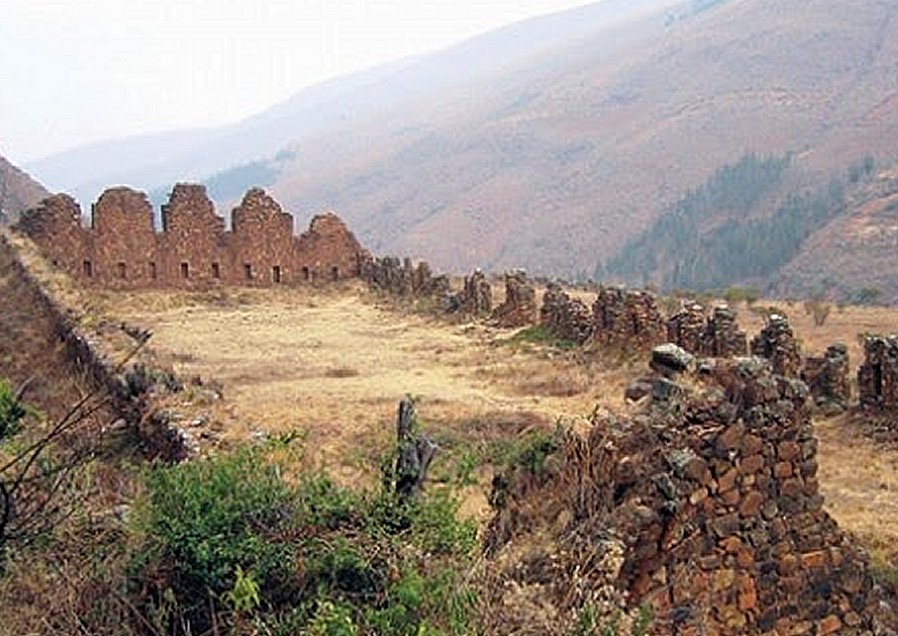
Whether Inca Llajta was built against attack by the Indian nation, Chiriguanos, who, as records say, were the toughest opposition the Spaniards ever faced in the center of South America, or against the increasing Spanish pressure in the area – is unclear. Photo via Explore Pangea
Around 1470, the Incas took residence in this stone fortress and were present there until 1525.
It is unclear, whether Inca Llajta (Inkaltajta ) was built against attacks organized by the Indian nation, Chiriguanos. According to ancient records, Chiriguanos people represented the toughest opposition the Spaniards ever faced in the center of South America.
Another possibility is that Inca Llajta was constructed for protection against the increasing Spanish pressure in the area.
According to the earliest accounts, the Indian tribe, Chiriguanos of the Eastern lowlands had their origin in migration of Guarani people from the lands located to the east of the Paraguay River.
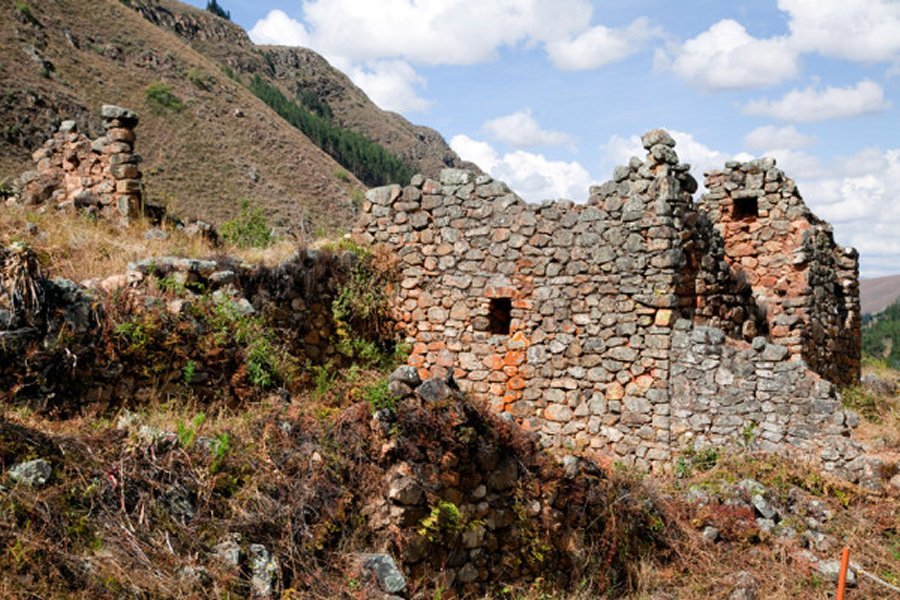
Destroyed by time and the Spanish Conquistadors, Inca Llajta remains in ruins.
Inca Llajta was ordered to be built by the Inka Tupac Yupanqui (in Quechua) "noble Inca accountant." Yupanqui was the eleventh Sapa Inca (1471–93) of the Inca Empire, and tenth of the Inca civilization.
His father was Pachacuti, the ninth Sapa Inca (1418–1471/1472) of the Kingdom of Cusco, and his son was Huayna Capac also the famous and powerful Inca ruler.
This fascinating historical Bolivian place was discovered in 1913 by Erland Nordenskiold, a Swedish archaeologist and anthropologist who focused his research on the prehistory of South America. Nordenskiold found the fortress in ruins as the town and its fortress were destroyed by the Spanish Conquistadors. He measured and mapped the ruins of Inca Llajta.
Inca Llajta was a military outpost to protect the region from raids by the unconquered Indian tribe, Chiriguanos of the Eastern lowlands, some believe.
Even if the complex is in ruins, it still remains an impressive example of architectural engineering of Inca, especially Inca Llajta’s defensive wall.
Interestingly, the original name of the complex of Inca Llajta has been lost a long time ago.
There are huge, zigzag defensive walls still standing, a network of dormitories, a prison, some remains of a strange tower that could have been an "intiwatana" (birth of the Sun), in which the seasonal changes were registered and were made other astronomical observations.
There are also remains of the largest Incan building to have ever been found that are still clearly visible. It is the kallanka’ (Kallanca), Inca Llajta’s most noteworthy structure, measuring 80 meters by 25 meters, with the roofed enclosure supported by massive columns and probably utilized for military purposes.
It is located on an ejection cone, in the strong almost completely inaccessible ravine. The Inca builders used trapezoidal shapes and the geometric figure characteristic of these particular ruins is the trapeze. ("La Cancha") or patio, is a polyfunctional mythical space, which most probably had multiple functions.
Outside the structure, there is a large boulder, probably a speakers’ platform.
Written by – A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com Senior Staff Writer
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
More From Ancient Pages
-
 Naglfar Nail-Ship Carries Demonic Forces To Ragnarok In Norse Beliefs
Featured Stories | Aug 10, 2020
Naglfar Nail-Ship Carries Demonic Forces To Ragnarok In Norse Beliefs
Featured Stories | Aug 10, 2020 -
 Ancient Children Played Marbles Thousands Of Years Ago
Ancient History Facts | May 22, 2019
Ancient Children Played Marbles Thousands Of Years Ago
Ancient History Facts | May 22, 2019 -
 Mystery Of The Ancient Unknown Mining Civilization In North America – Puzzling Archaeological Discoveries – Part 1
Ancient Mysteries | Apr 18, 2022
Mystery Of The Ancient Unknown Mining Civilization In North America – Puzzling Archaeological Discoveries – Part 1
Ancient Mysteries | Apr 18, 2022 -
 170-Million-Year-Old Sea Monster Identified As The Oldest Mega-Predatory Pliosaur
Evolution | Oct 23, 2023
170-Million-Year-Old Sea Monster Identified As The Oldest Mega-Predatory Pliosaur
Evolution | Oct 23, 2023 -
![Horses in the Eurasian steppes: Already 5000 years ago, they served pastoralists as a source of milk and a means of… [more] © A. Senokosov](https://www.ancientpages.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/pastoraliststeppe15-307x150.jpg) Milk Enabled Massive Steppe Migration – A New Study
Archaeology | Sep 24, 2021
Milk Enabled Massive Steppe Migration – A New Study
Archaeology | Sep 24, 2021 -
 Evidence From Ancient Egypt Shows Smallpox Stretches Back At Least 3,000 Years
Archaeology | Jan 11, 2023
Evidence From Ancient Egypt Shows Smallpox Stretches Back At Least 3,000 Years
Archaeology | Jan 11, 2023 -
 2,000-Year-Old Roman Road Discovered In Cluj-Napoca, Romania
Archaeology | Jan 23, 2023
2,000-Year-Old Roman Road Discovered In Cluj-Napoca, Romania
Archaeology | Jan 23, 2023 -
 How Can AI Affect Human Evolution? Predicting Changes In Brain Size And Social Behaviors
Evolution | Nov 22, 2024
How Can AI Affect Human Evolution? Predicting Changes In Brain Size And Social Behaviors
Evolution | Nov 22, 2024 -
 Katanga Cross: Symbol Of Secrets, Power And Valuable Currency Of The Congolese People
Ancient Symbols | Sep 10, 2018
Katanga Cross: Symbol Of Secrets, Power And Valuable Currency Of The Congolese People
Ancient Symbols | Sep 10, 2018 -
 2,000-Year-Old Medusa Mosaic Is Considered The Pearl Of Ancient City Of Kibyra
Archaeology | Aug 25, 2020
2,000-Year-Old Medusa Mosaic Is Considered The Pearl Of Ancient City Of Kibyra
Archaeology | Aug 25, 2020 -
 Remote North Atlantic Islands Were Settled By An Unknown Group Of Humans Centuries Earlier Than Thought
Archaeology | Dec 27, 2021
Remote North Atlantic Islands Were Settled By An Unknown Group Of Humans Centuries Earlier Than Thought
Archaeology | Dec 27, 2021 -
 Early Christian Landmark – Re-Evaluation Of Its Architecture And Practices
Archaeology | Aug 19, 2024
Early Christian Landmark – Re-Evaluation Of Its Architecture And Practices
Archaeology | Aug 19, 2024 -
 Controversial Ancient Tomb Could Prove The Existence Of Biblical Jonah
Archaeology | Mar 9, 2014
Controversial Ancient Tomb Could Prove The Existence Of Biblical Jonah
Archaeology | Mar 9, 2014 -
 The Four Bases Of Anti-Science Beliefs – What Can Be Done About Them?
News | Jul 14, 2022
The Four Bases Of Anti-Science Beliefs – What Can Be Done About Them?
News | Jul 14, 2022 -
 Race Against Time: Crucial Expedition To Delve Into Bouldnor Cliff, Europe’s Mesolithic Underwater Stone Age Site
Underwater Discoveries | Apr 28, 2024
Race Against Time: Crucial Expedition To Delve Into Bouldnor Cliff, Europe’s Mesolithic Underwater Stone Age Site
Underwater Discoveries | Apr 28, 2024 -
 How The Horseshoe Became A Symbol Of Good Luck
Ancient Idioms & Superstitions | Jan 28, 2017
How The Horseshoe Became A Symbol Of Good Luck
Ancient Idioms & Superstitions | Jan 28, 2017 -
 Early Humans Were Probably Driven To Extinction By Climate Change- Study Suggests
Civilizations | Oct 15, 2020
Early Humans Were Probably Driven To Extinction By Climate Change- Study Suggests
Civilizations | Oct 15, 2020 -
 ‘Homo Erectus’ From Gongwangling Could Have Been One Of The First Human Beings 1,6 Million Years Ago
Archaeology | Jun 14, 2022
‘Homo Erectus’ From Gongwangling Could Have Been One Of The First Human Beings 1,6 Million Years Ago
Archaeology | Jun 14, 2022 -
 On This Day In History: Parachute Jump From 1,000 m Above Paris Is Recorded – On Oct 22, 1797
News | Oct 22, 2016
On This Day In History: Parachute Jump From 1,000 m Above Paris Is Recorded – On Oct 22, 1797
News | Oct 22, 2016 -
 On This Day In History: British Fleet Attacked The Spanish ‘Invincible Armada’ – On July 21, 1588
News | Jul 21, 2016
On This Day In History: British Fleet Attacked The Spanish ‘Invincible Armada’ – On July 21, 1588
News | Jul 21, 2016



